The Azure Injector module provides the ability to push Tag data to an Azure IoT Hub, Azure IoT Edges, Azure Event Hubs and Azure IoT Central endpoints.
The configuration for this module are located under the Configure tab of the Ignition Gateway web UI in the left hand navigation pane under 'Azure Injector Settings'.
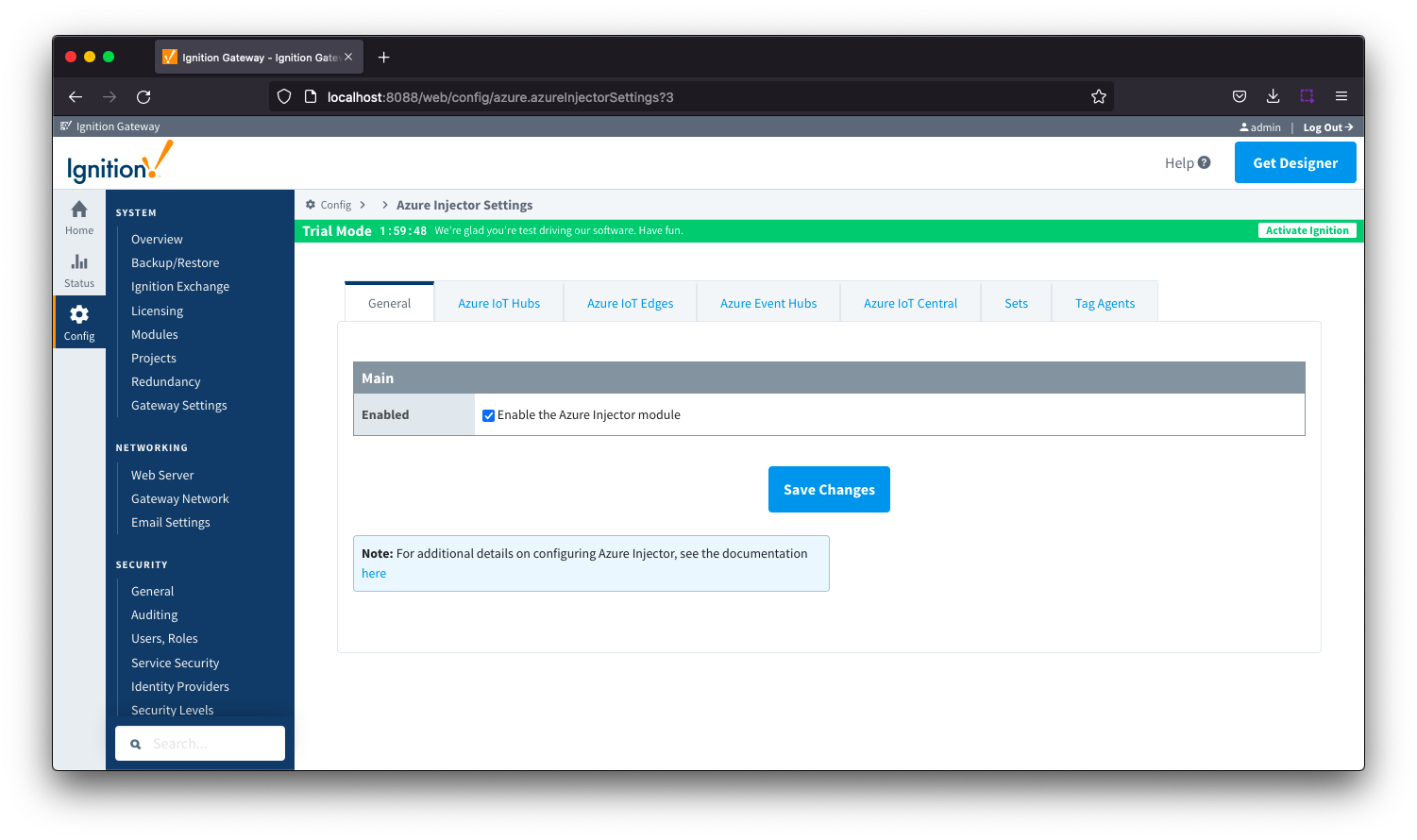
The configuration options for each of the seven tabs - General, Azure IoT Hubs, Azure IoT Edges, Azure Event Hubs, Azure IoT Central, Sets and Tag Agents - are detailed below.
General
The configuration section available is Main. 
- Enabled
- Sets whether the module is enabled or disabled. If disabled, the Tag Agents will not run and now data will be pushed to any configured endpoints.
Azure IoT Hubs
The Azure IoT Hubs tab has two parts - Settings and Certificates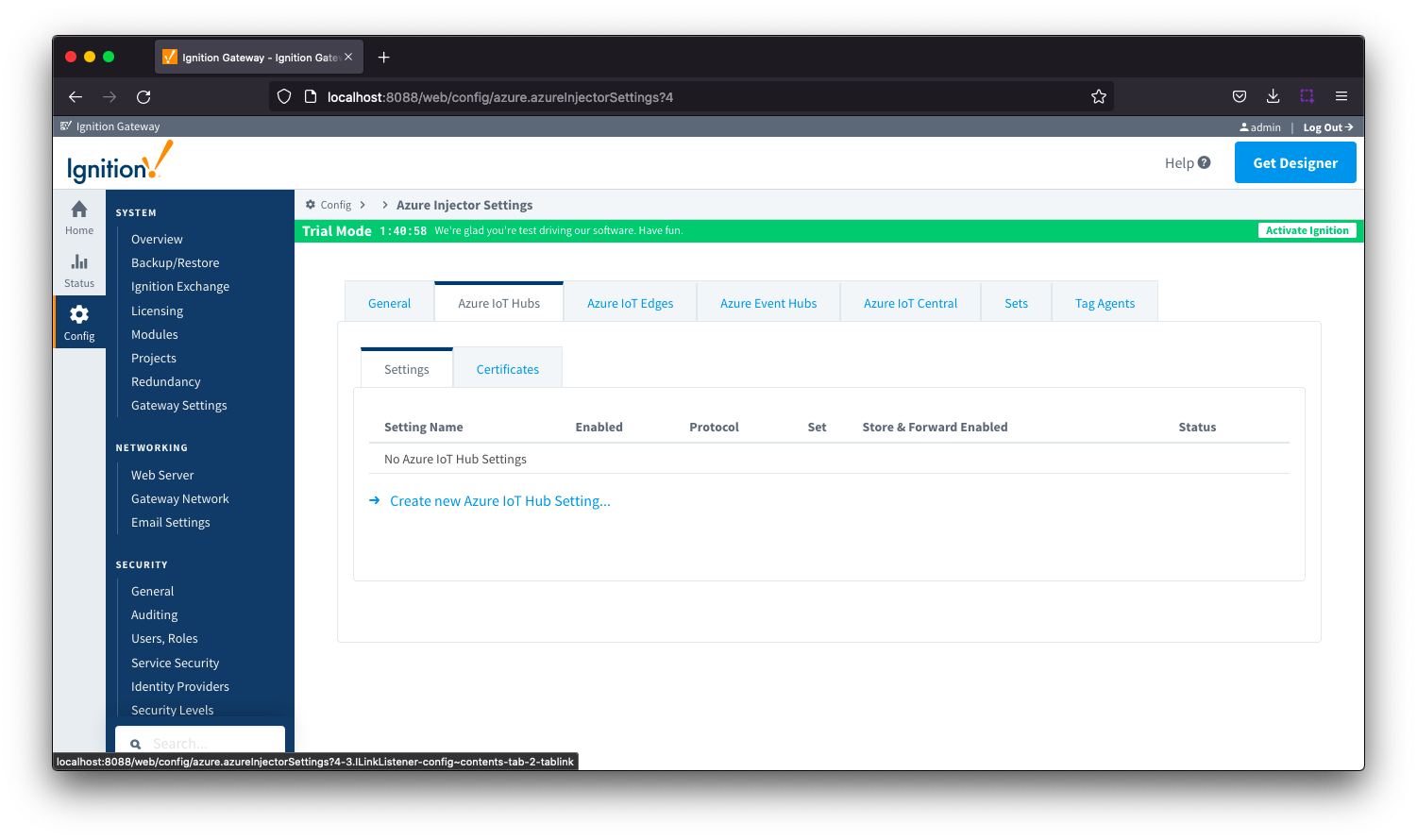
Azure IoT Hubs - Settings
This tab provides a list of the Azure IoT Hub endpoints that the module should connect to to push tag data. One or more Azure IoT Hub endpoints can be configured on this tab.
Clicking on the 'Create new Azure IoT Hub ..' link will bring up the following form to add a new Azure IoT Hub. The configuration sections available are Main, Authentication, Store & Forward and Advanced
Azure IoT Hub Settings - Main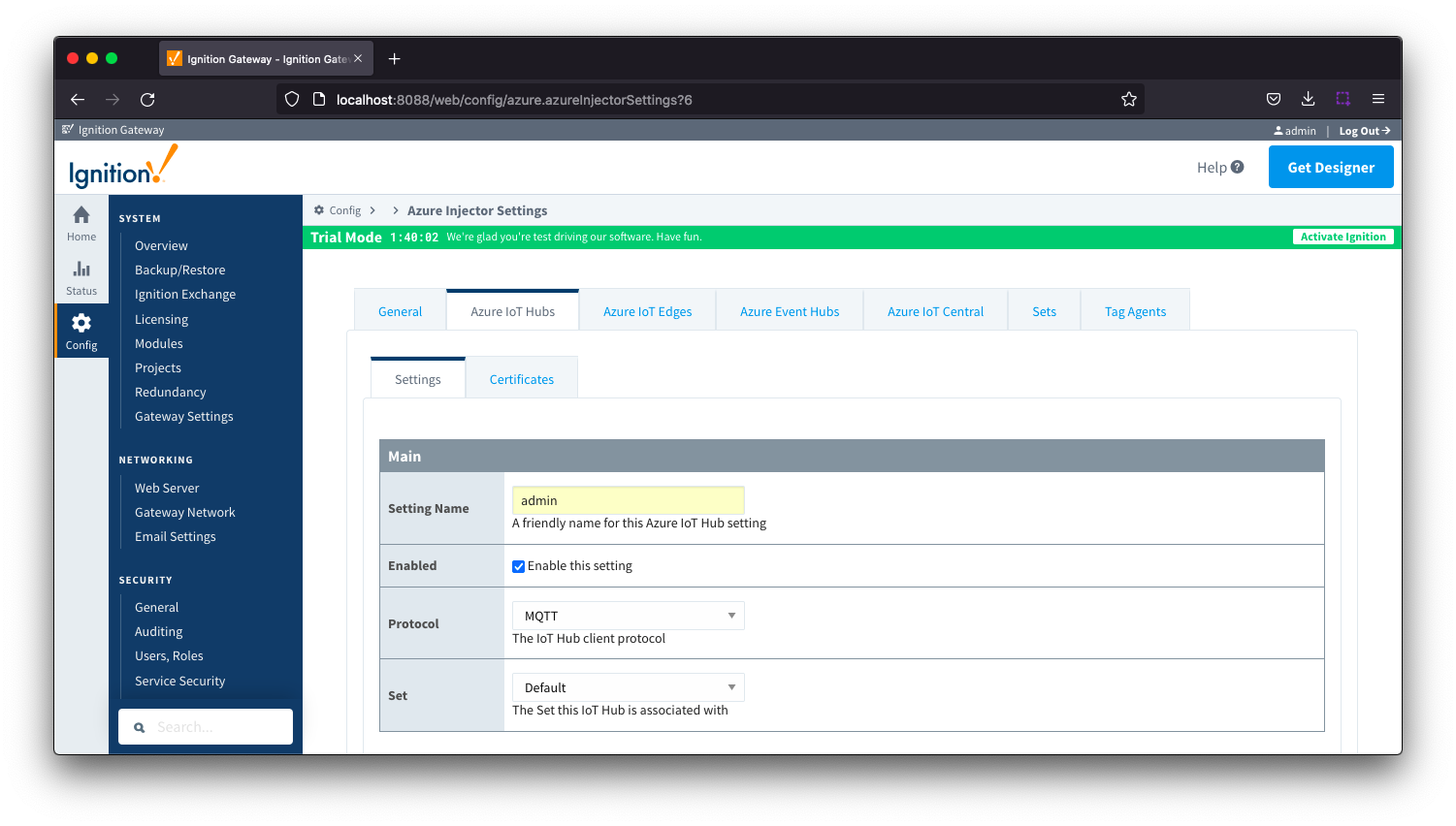
- Setting Name
- This is a friendly name of the Azure IoT Hub used to easily identify it. This must also be unique.
- Enabled
- Whether or not this connection is enabled.
- Protocol
- The protocol to use when connecting to the Azure IoT Hub. Currently MQTT only is available.
- Note: When using MQTT as the protocol, the connection string must be a 'device' connection string when not using certificate based authentication.
- Set
- The Set to associate this Azure IoT Hub connection with.
Azure IoT Hub Settings - Authentication
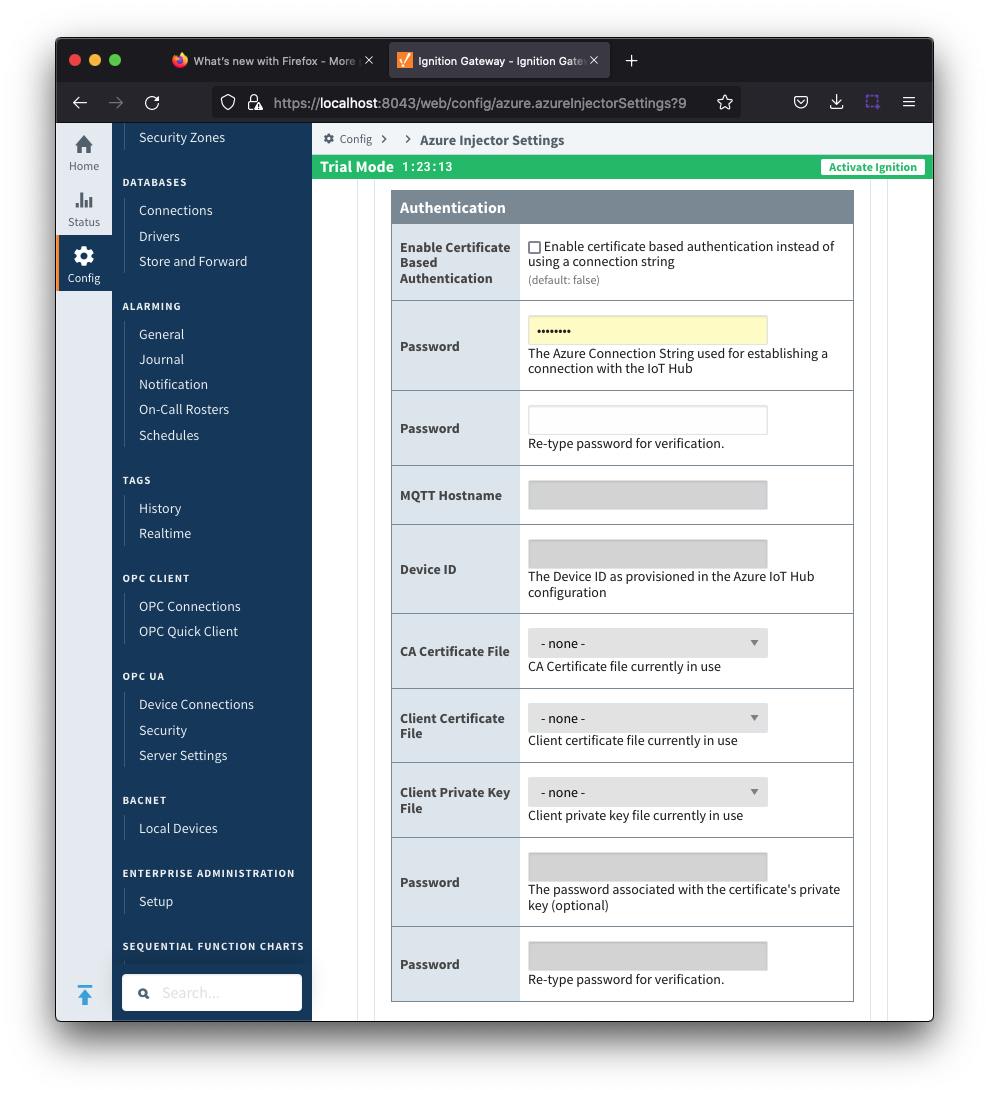
- Enable Certificate Based Authentication
- Whether or not to use certificate based authentication.
- If not using certificate based authentication, the 'Password' field must be used.
- If certificate based authentication is used, the other Authentications fields must be used.
- Password (required if not using certificate based authentication)
- This is the Azure IoT Hub connection string used to connect. This string can be one of the following:
- An IoT Hub connection string with the following format:
- HostName=<Host Name>;SharedAccessKeyName=<Key Name>;SharedAccessKey=<SAS Key>
- An IoT Hub's Event Hub-compatible connection string with the following format:
- Endpoint=<ENDPOINT>;SharedAccessKeyName=<Key Name>;SharedAccessKey=<KEYVALUE>
- An IoT Hub device connection string with the following format:
- HostName=<Host Name>;DeviceId=<Device Name>;SharedAccessKey=<Device Key>
- Note: If using MQTT as the protocol, this is the connection string format that must be used.
- MQTT Hostname (required if using certificate based authentication)
- This is the DNS endpoint name of your IoT Hub
- Device ID (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The Device ID as provisioned in the IoT Hub to connect as
- CA Certificate File
- The CA certificate file of your IoT Hub. See this document for more information.
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Hub/Certificates tab.
- Client Certificate File (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The client certificate file as provisioned for this device.
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Hub/Certificates tab.
- Client Private Key File (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The client private key file that was used in generating the certificate for this device
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Hub/Certificates tab.
- Password/Private key password
- The password used for the private key if one was specified for the key
Azure IoT Hub Settings - Store & Forward
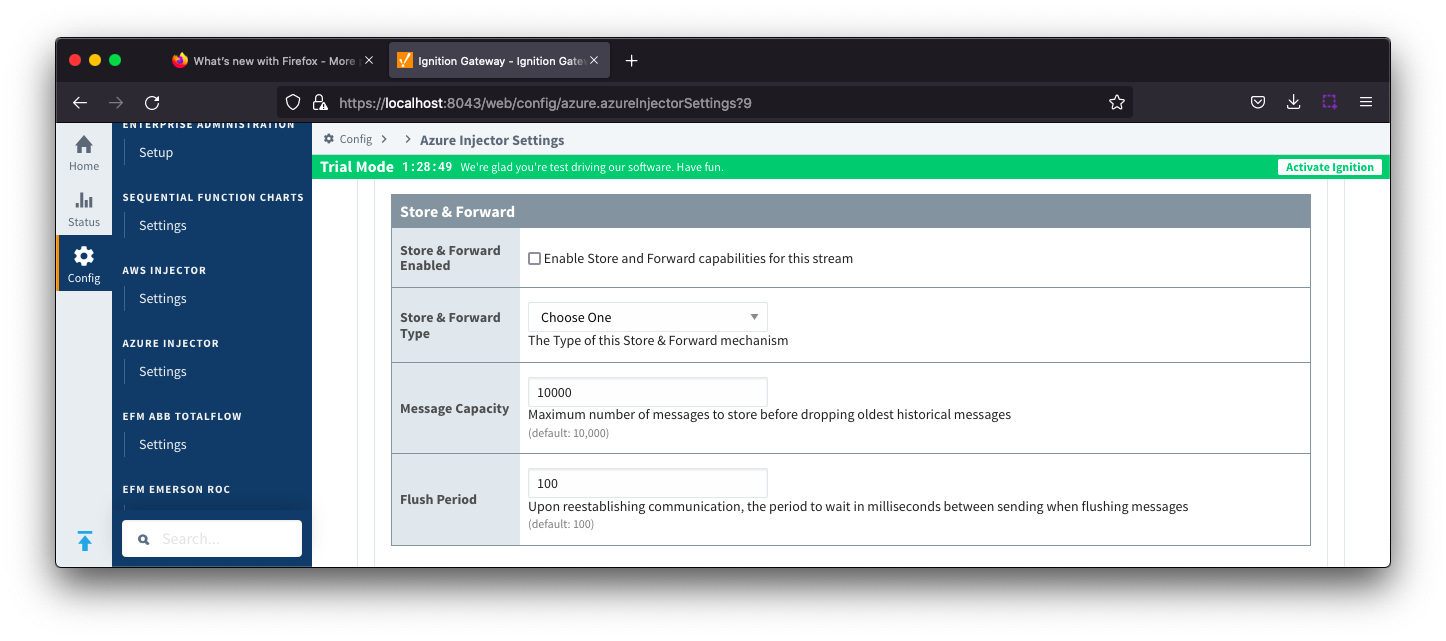
- Store & Forward Enabled
- Whether to enable Store & Forward capabilities for this endpoint
- Store & Forward Type
- The type of the Store & Forward mechanism
- Message Capacity
- The Maximum number of messages to store before dropping the oldest historical messages
- Flush Period
- The period of time to wait (in milliseconds) between sending when flushing messages
Azure IoT Hub Settings - Advanced
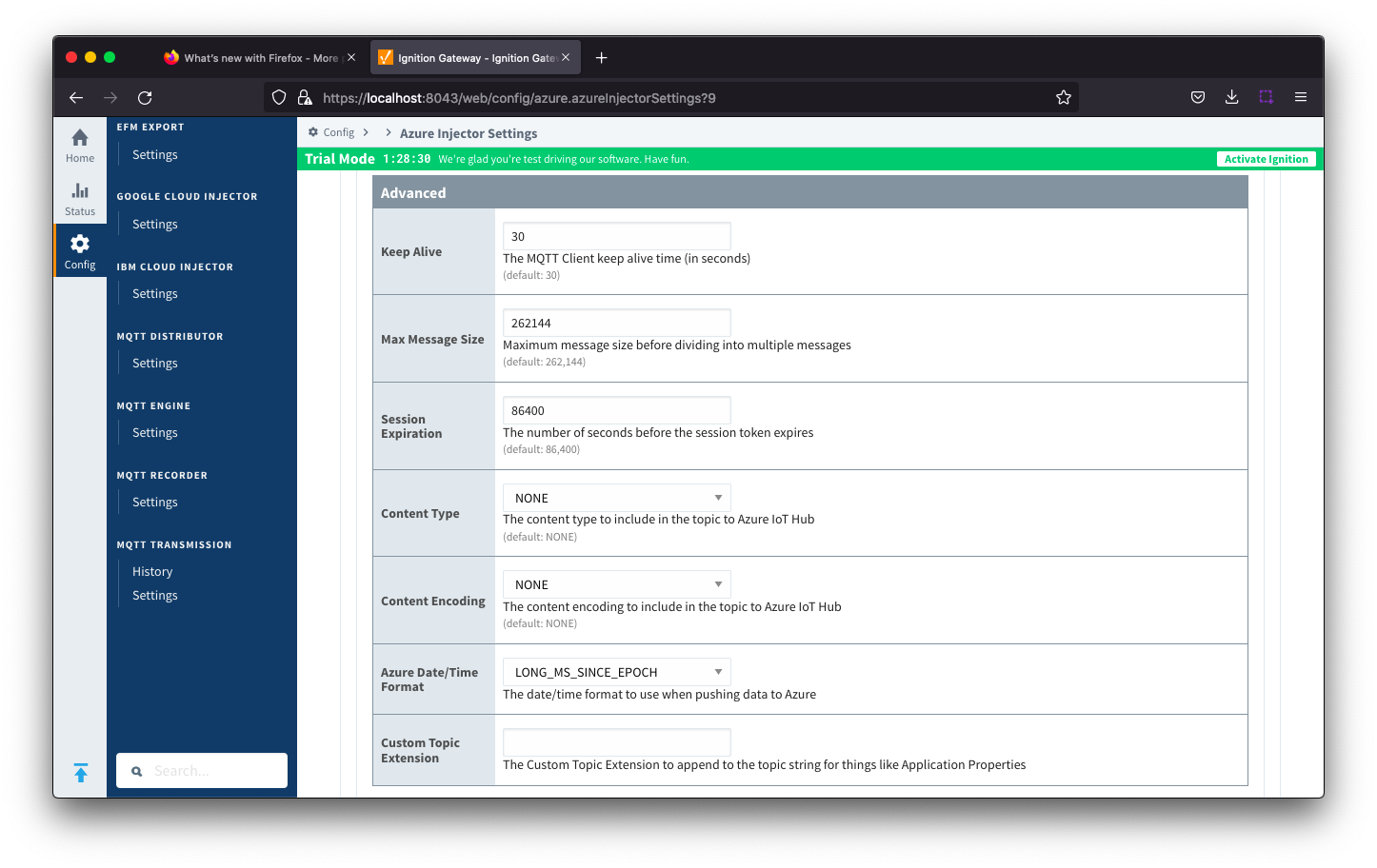
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT keep alive timeout in seconds
- Max Message Size
- The maximum message size in bytes that any message can be when pushing to IoT Hub.
- Session Expiration
- How long in seconds to specify for session token timeouts when not using certificate based authentication
- Content Type
- Content Encoding
- The content encoding to include in the topic to Azure IoT Hub
- NONE (default) - No content encoding header will be included with the message
- UTF_8 - The 'utf-8' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- UTF_16 - The 'utf-16' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- UTF_32 - The 'utf-32' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- See Using IoT Hub Message Based Routing tutorial for more details
- Azure Date/Time Format
- The date/time format to use when pushing messages to IoT Hub
- LONG_MS_SINCE_EPOCH (default) - The timestamp values will all be as numbers in milliseconds since epoch (Jan 1, 1970) in UTC
- STRING_AZURE_COMPAT - The timestamp will be pushed as described here. This is useful when wanting to use 'edge' timestamps in Azure Time Series insights.
- See Pushing Data to Azure Time Series Insights tutorial for more details
Azure IoT Hubs - Certificates
This tab provides a list of the certificate or private keys if loaded and available for certificate based authentication. This should generally include the root CA for your IoT Hub, the client certificate file, and the client private key file.

Clicking on the 'Create new Certificate ..' link will bring up the following form to add a new Certificate. The Certificates tab contains a single Main section.
Azure IoT Hub Certificates - Main
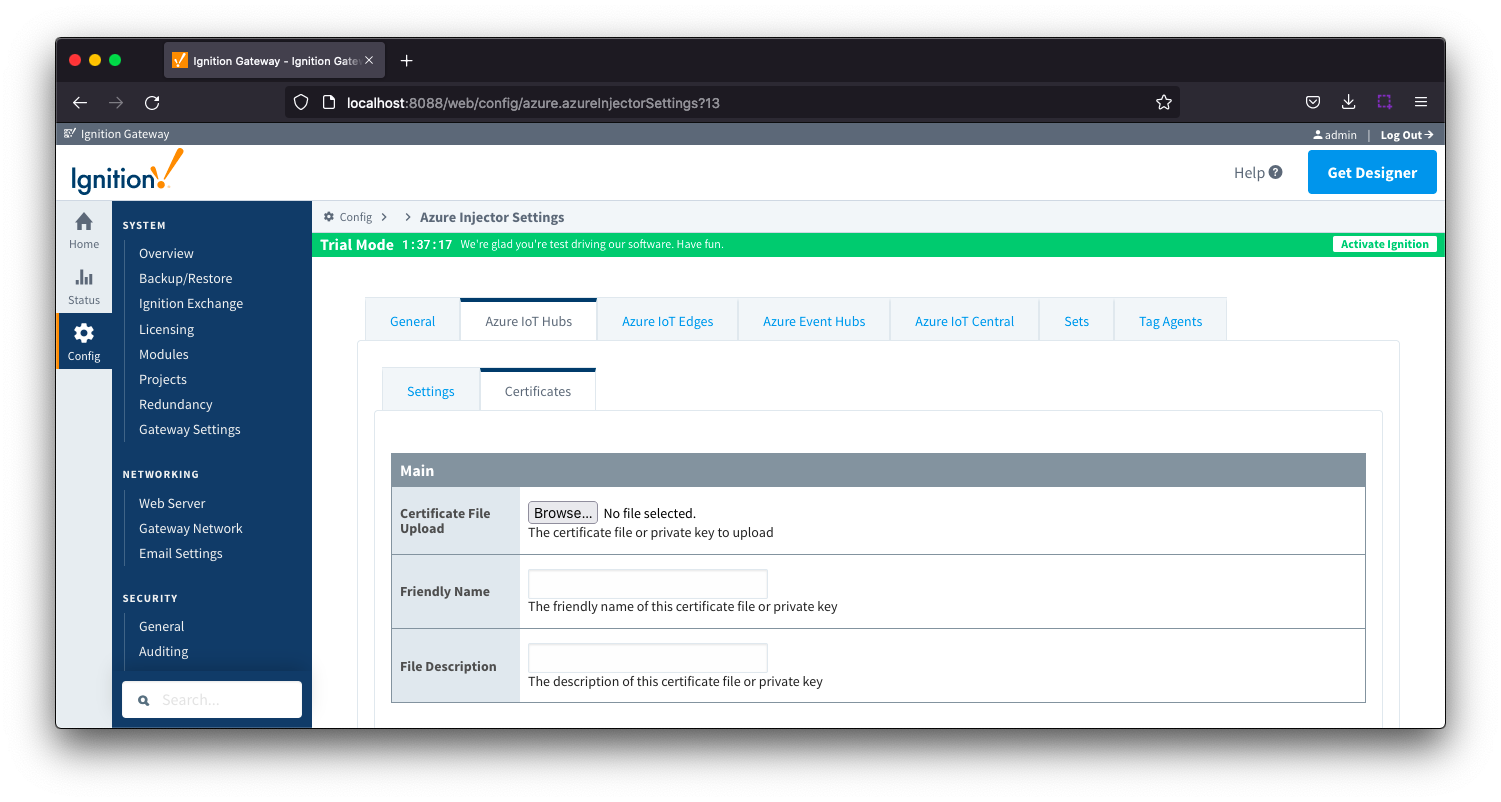
- Certificate File Upload
- Browse to the certificate file or private key to upload.
- Friendly Name
- The friendly name of the certificate file or private key.
- File Description
- The description of the certificate file or private key.
Azure IoT Edges
The Azure IoT Edges tab has two parts - Settings and Certificates
Azure IoT Edge - Settings
This tab provides a list of Azure IoT Edge endpoints that the module should connect to to push tag data. One or more Azure IoT Edge endpoints can be configured on this tab.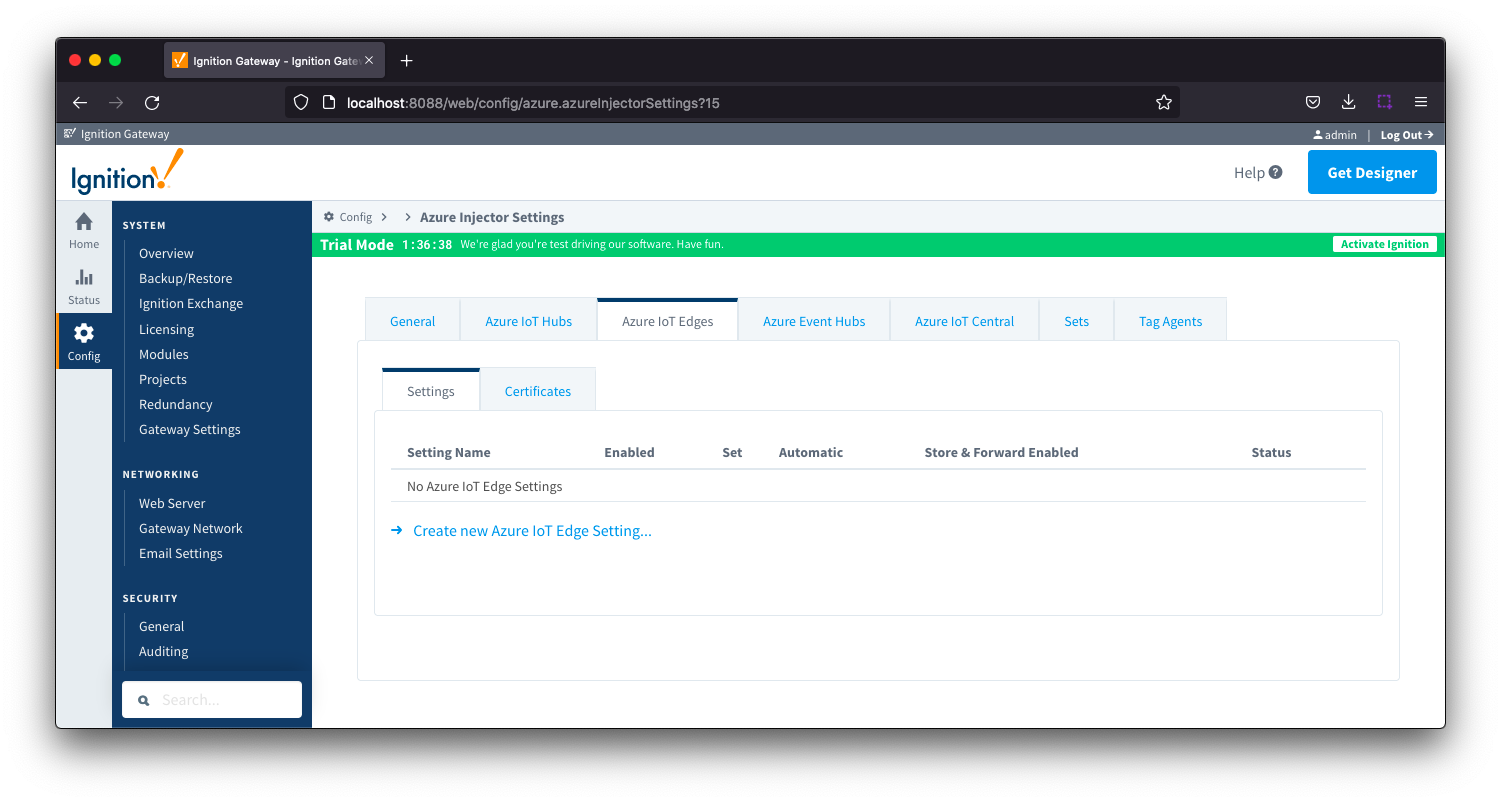
Clicking on the 'Create new Azure IoT Edge..." link will bring up the following form to add a new Azure IoT Edge. The configuration sections available are Main, Connectivity, Authentication, Store & Forward and Advanced.
Azure IoT Edges Settings - Main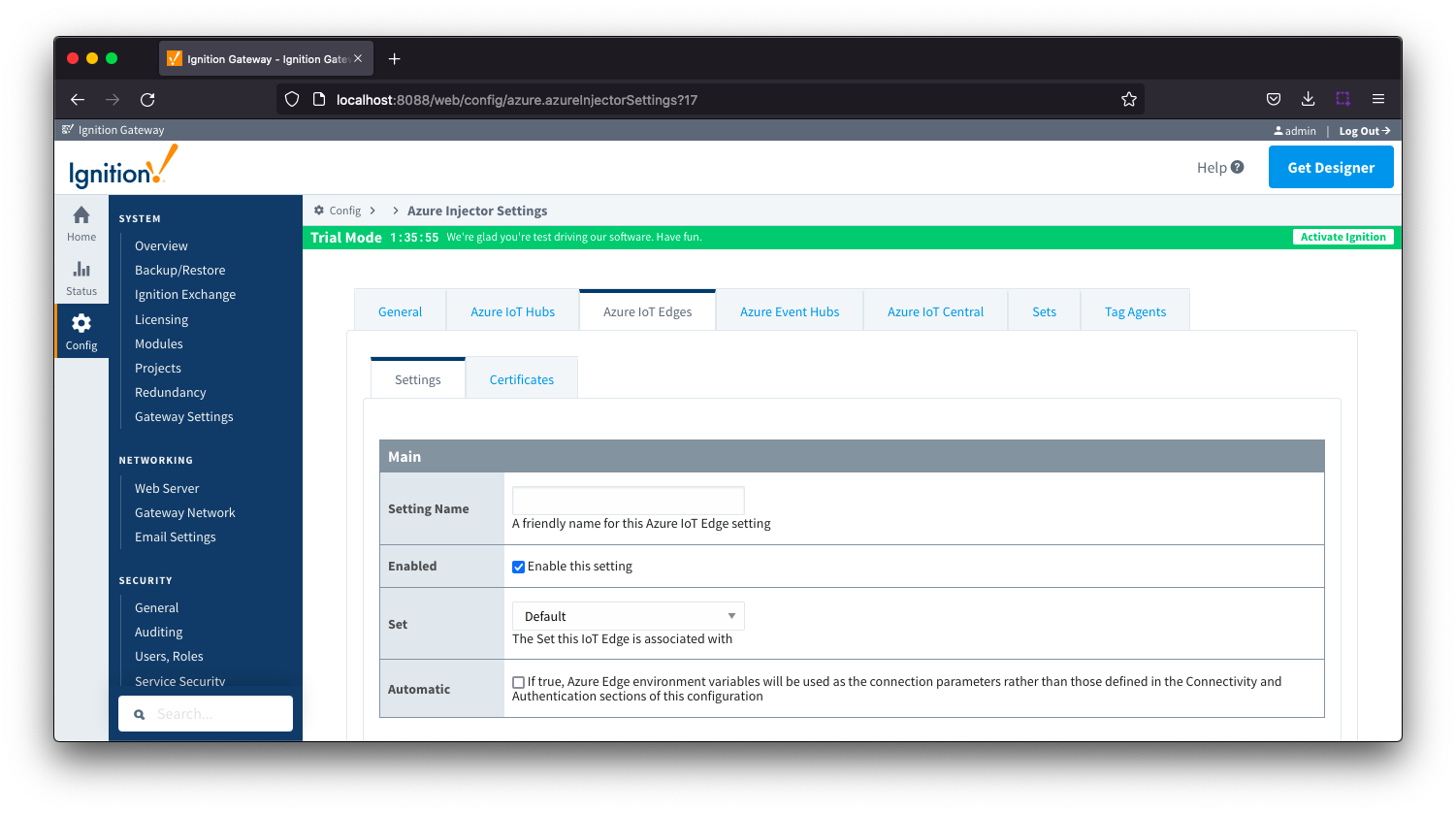
- Setting Name
- This is the friendly name of the Azure IoT Edge used to easily identify it. This must be unique.
- Enabled
- Whether or not this connection is enabled.
- Set
- The Set to associate this Azure IoT Edge connection with
- Automatic
- Whether the Azure Edge environment variables will be used as the connection parameters rather than those defined in the connectivity and Authentication sections of the configuration.
Azure IoT Edges Settings - Connectivity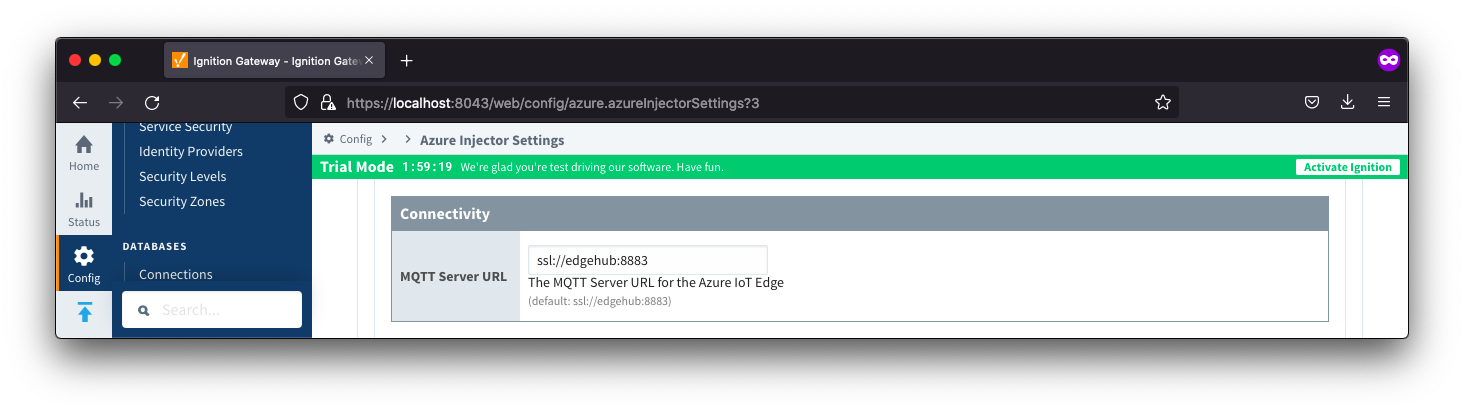
- MQTT Server URL
- The MQTT Server URL for the Azure IoT Edge. Default: ssl://edgehub:8883
Azure IoT Edges Settings - Authentication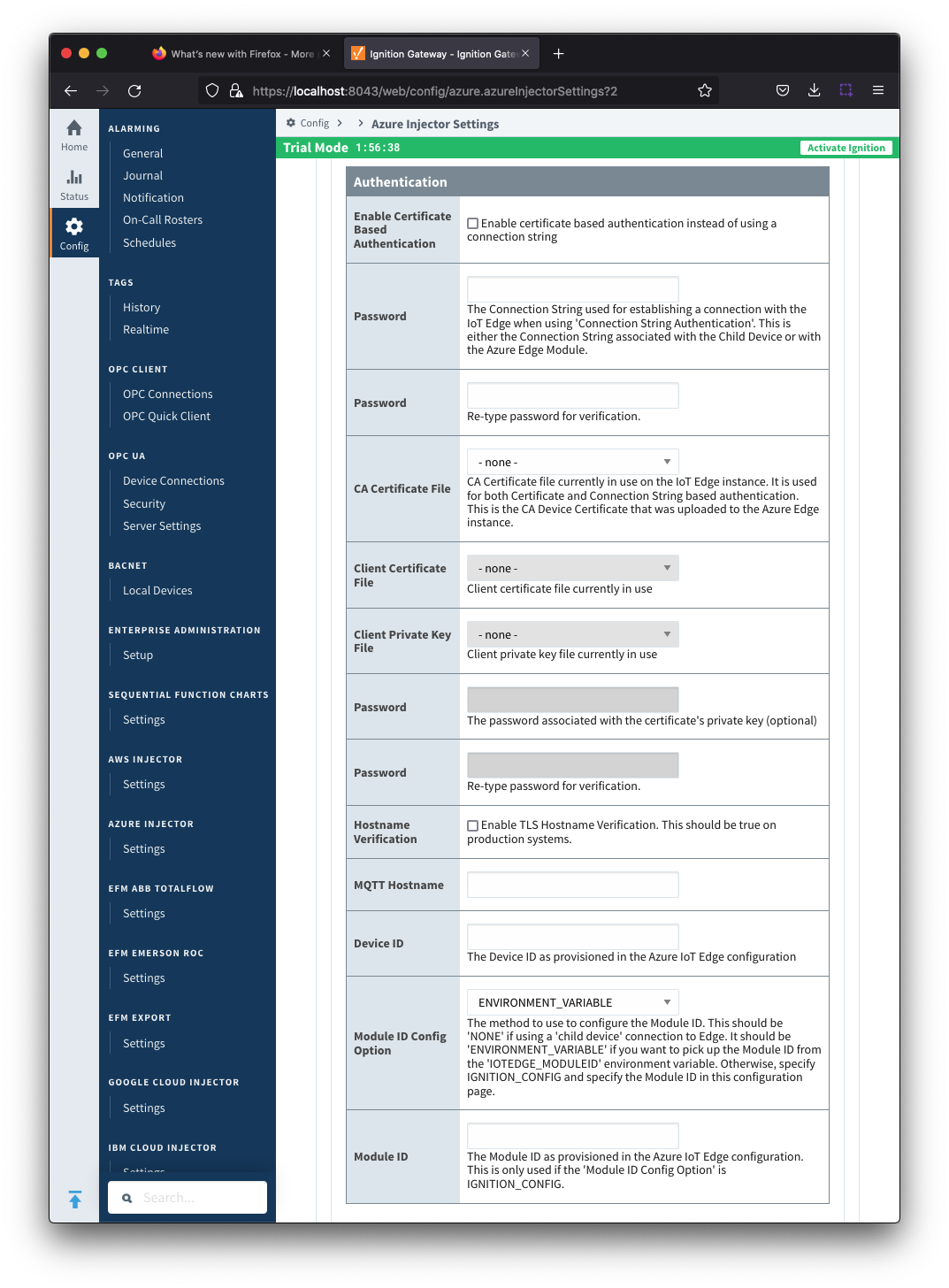
- Enable Certificate Based Authentication
- Whether or not to use certificate based authentication.
- If not using certificate based authentication, the 'Password' field must be used.
- If certificate based authentication is used, the other Authentications fields must be used.
- Password (required if not using certificate based authentication)
- This is the Azure IoT Edge connection string used to connect. T
- This is either the Connection string associated with the Child Device or with the Azure Edge Module
- CA Certificate File
- The CA certificate file currently in use on the IoT Edge instance.
- It is used for both Certificate and Connection String based authentication and is the CA Device Certificate that was uploaded to the Azure Edge instance.
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Edge/Certificates tab.
- Client Certificate File (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The client certificate file currently in use
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Edge/Certificates tab.
- Client Private Key File (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The client private key file currently in use
- The drop down is populated from a list of files that have been uploaded to the IoT Edge/Certificates tab.
- Password/Private key password
- The password used for the private key if one was specified for the key
- MQTT Hostname (required if using certificate based authentication)
- This is the DNS endpoint name of your IoT Hub
- Device ID (required if using certificate based authentication)
- The Device ID as provisioned in the Azure IoT Edge configuration
- Module ID Config Option
- The method to use to configure the Module ID. This should be 'NONE' if using a 'child device' connection to Edge. It should be 'ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE' if you want to pick up the Module ID from the 'IOTEDGE_MODULEID' environment variable. Otherwise, specify IGNITION_CONFIG and specify the Module ID in this configuration page.
- Module ID
- The Module ID as provisioned in the Azure IoT Edge configuration. This is only used if the 'Module ID Config Option' is IGNITION_CONFIG.
Azure IoT Edges Settings - Store & Forward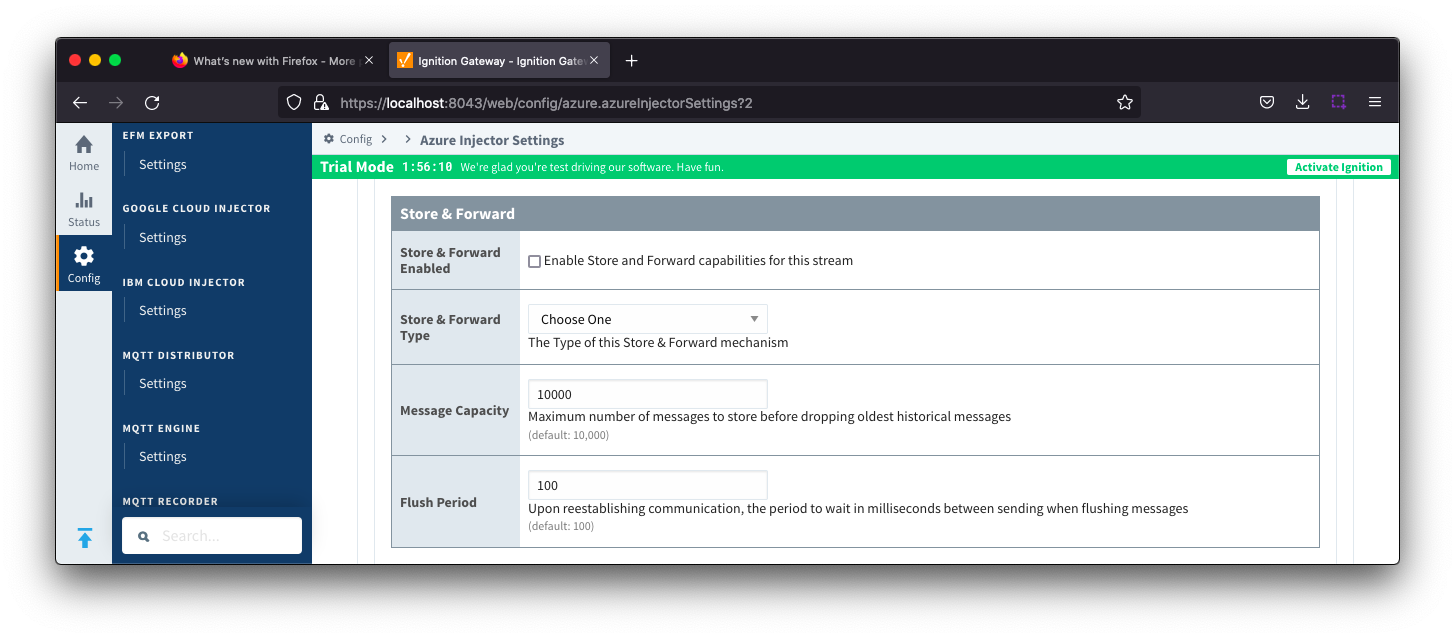
- Store & Forward Enabled
- Whether Store and Forward capabilities are enabled for this stream
- Store & Forward Type
- The type of Store & Forward mechanism. Default is In_Memory
- Message Capacity
- Maximum number of messages to store before dropping the oldest historical messages
- Flush Period
- The period of time to wait (in milliseconds) between sending when flushing messages
Azure IoT Edges Settings - Advanced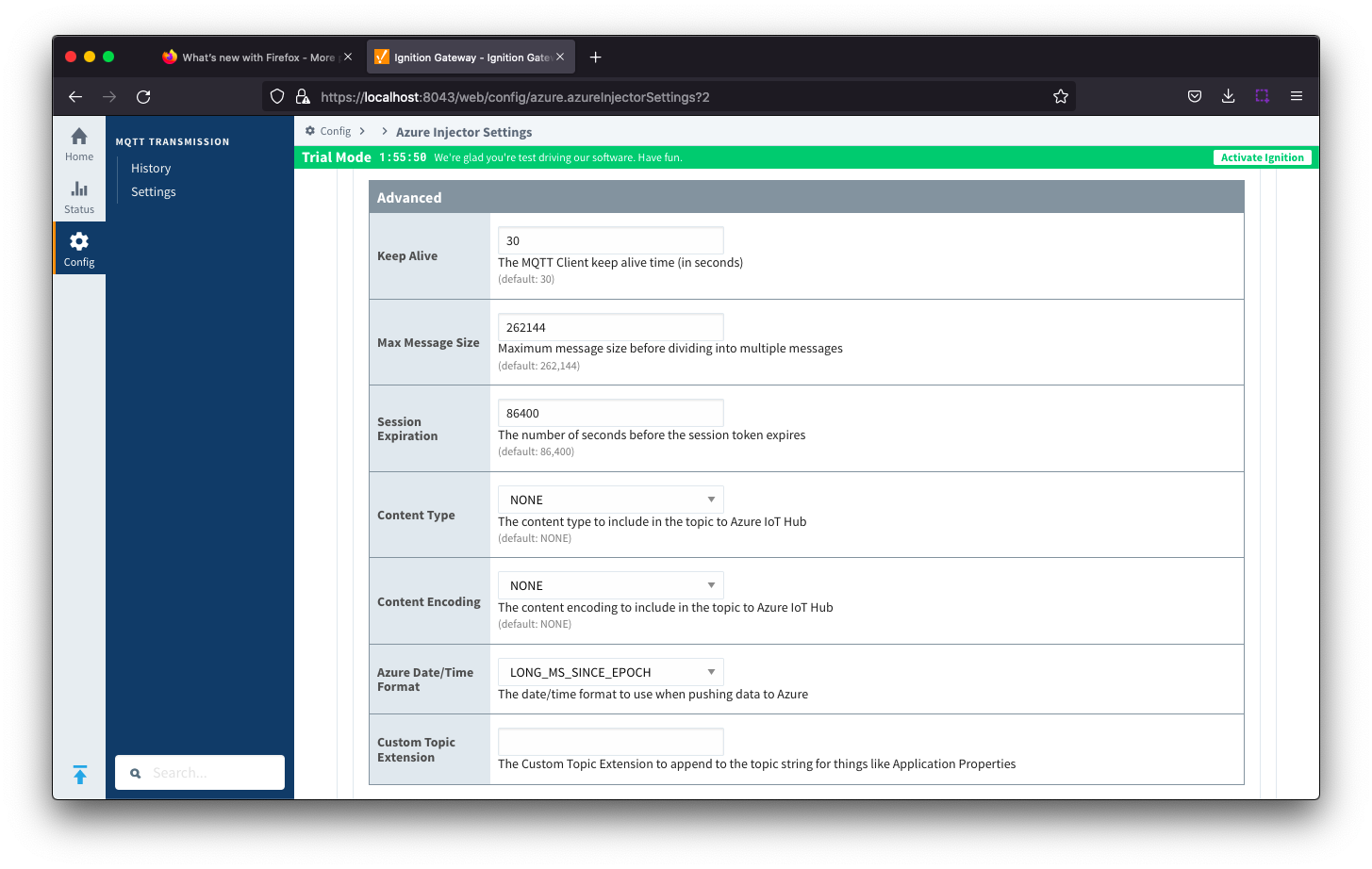
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT keep alive in seconds
- Max Message Size
- The maximum message size in bytes that any message can be when publishing to IoT Edge
- Session expiration
- How long in seconds to specify for token timeouts when not using certificate based authentication
- Content Type
- The content type to include in the topic to Azure IoT Edge
- NONE (default) - No content type header will be included with the message
- APPLICATION_JSON - The application/json header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if content encoding is also not 'NONE'
- Content encoding
- The content encoding yo include in the topic to Azure IoT Edge
- NONE (default) - No content encoding header will be included with the message
- UTF_8 - The 'utf-8' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- UTF_16 - The 'utf-16' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- UTF__32 - The 'utf-32' header will be included with the message and make the body of the message available for routing if the content type is also set to APPLICATION_JSON
- Azure Date/Time Format
- The date/time for mat to use when pushing messages to IoT Edge
- LONG_MS_SINCE_EPOCH (default) - The timestamp values will all be as numbers in milliseconds since epoch (Jan 1, 1970) in UTC
- STRING_AZURE_COMPAT - The timestamp will be pushed as described here. This is useful when wanting to use 'edge' timestamps in Azure Time Series Insights.
- Custom Topic Extension
- The Custom Topic Extension to append to the topic string for things like Application Properties
Azure IoT Edges - Certificates
This tab provides a list of the certificate or private keys loaded and available for certificate based authentication. This should generally include the root CA for your IoT Edge, the client certification file and the client private key file.
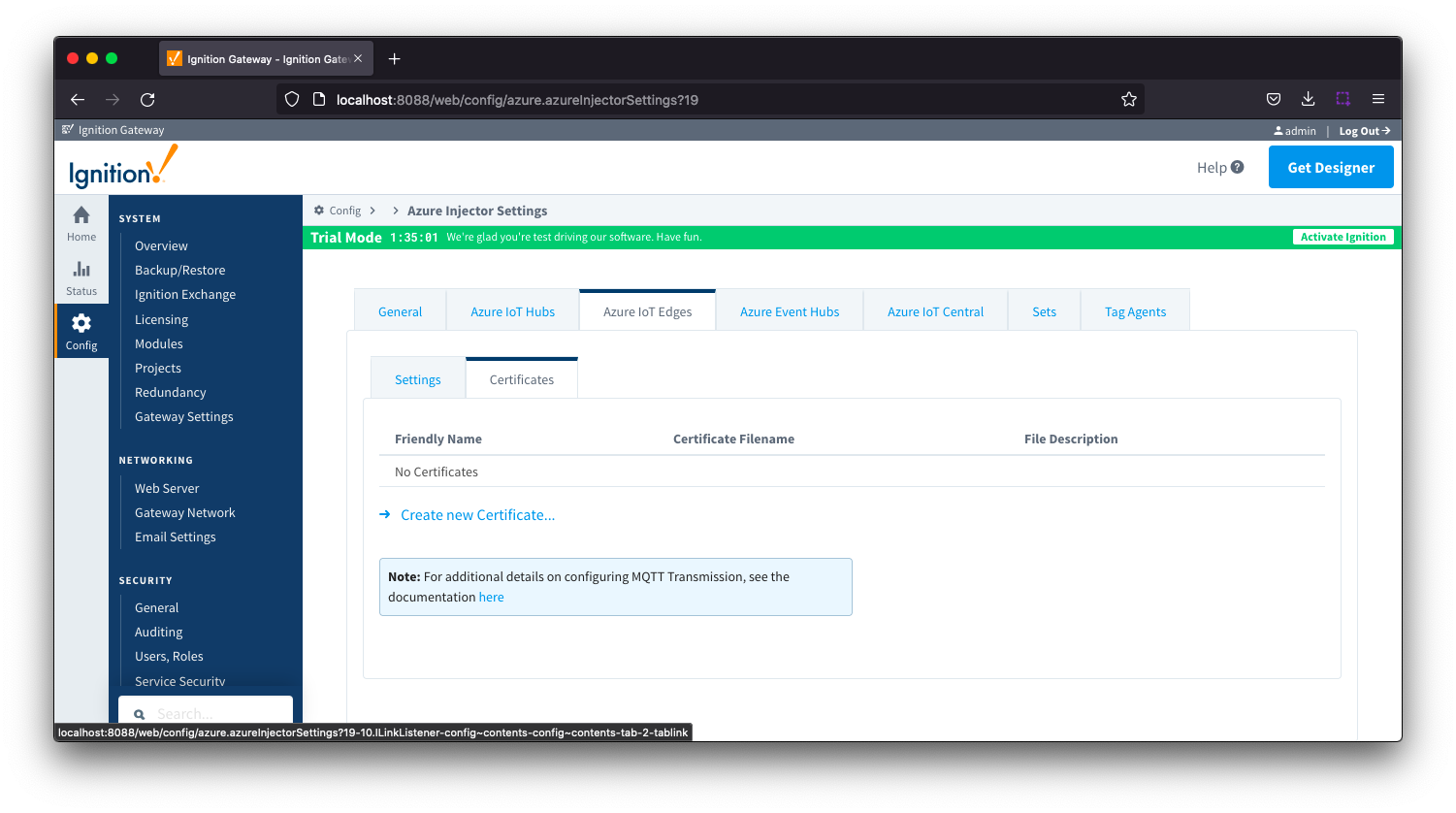
Clicking on the 'Create new Certificate...' will bring up the following form to add a new certificate. The Certificates tab contains only a single Main section.
Azure IoT Edges Certificates - Main
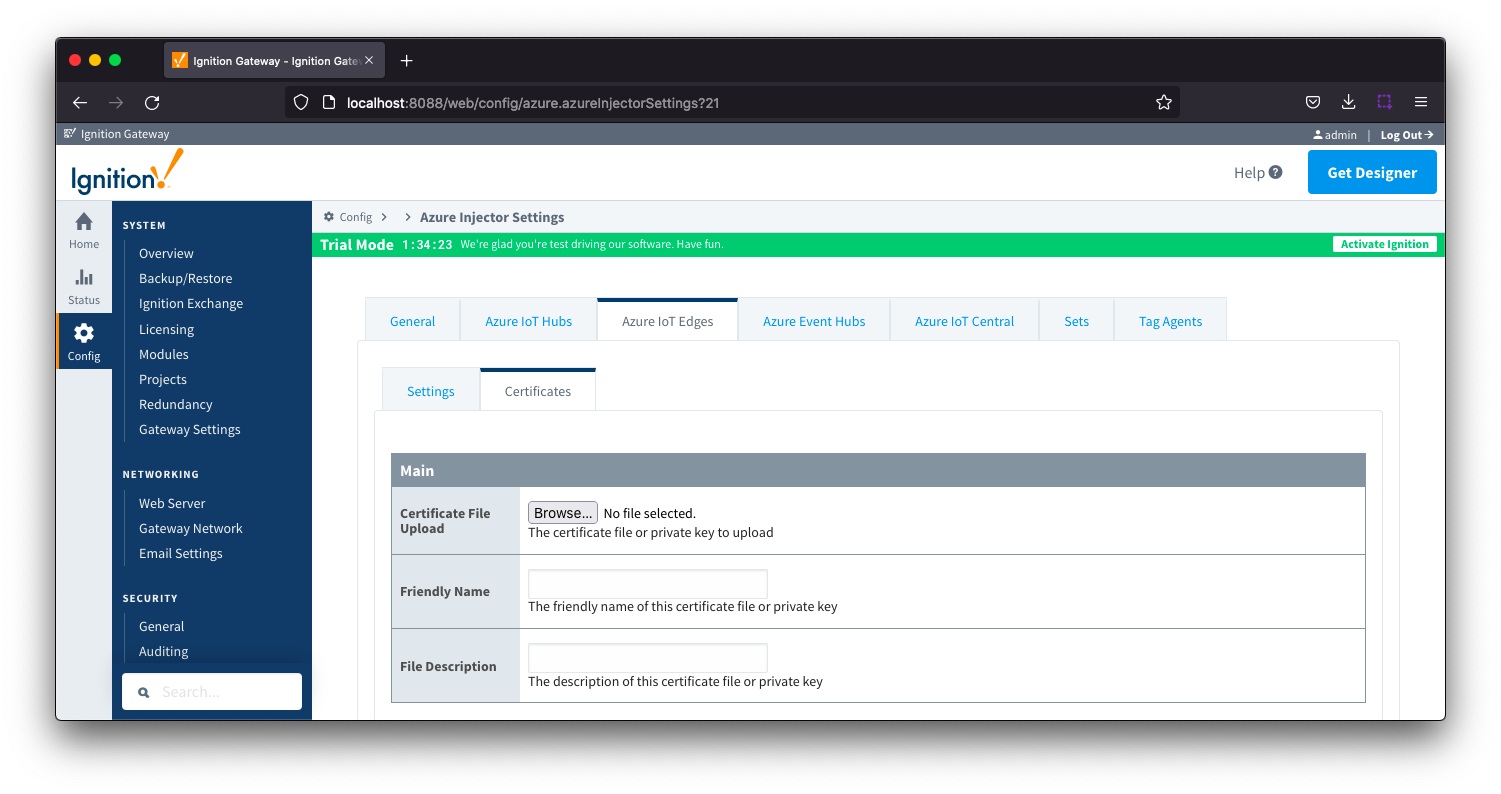
- Certificate File Upload
- Browse to the certificate or private key to upload
- Friendly Name
- The friendly name of the certificate file or private key
- File Description
- The description of the certificate file or private key
Azure Event Hubs
This tab provides a list of Azure Event Hub endpoints that the module should connect to to push tag data. One or more Azure Event Hub endpoints can be configured on this tab. 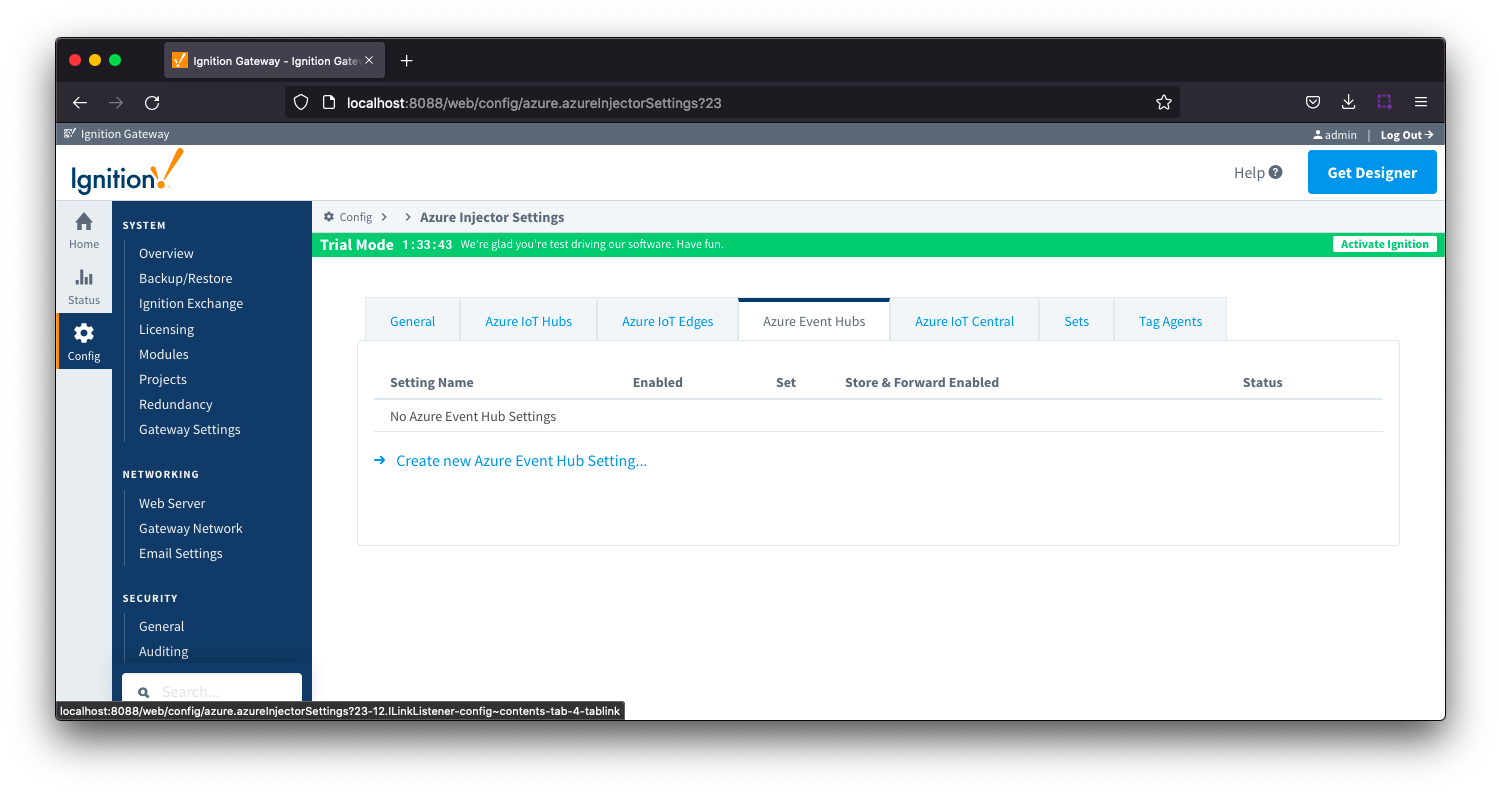
Clicking on the 'Create new Azure Event Hub ..' link will bring up the following form to add a new Azure Event Hub. The configuration sections available are Main, Store & Forward and Advanced
Azure Event Hub - Main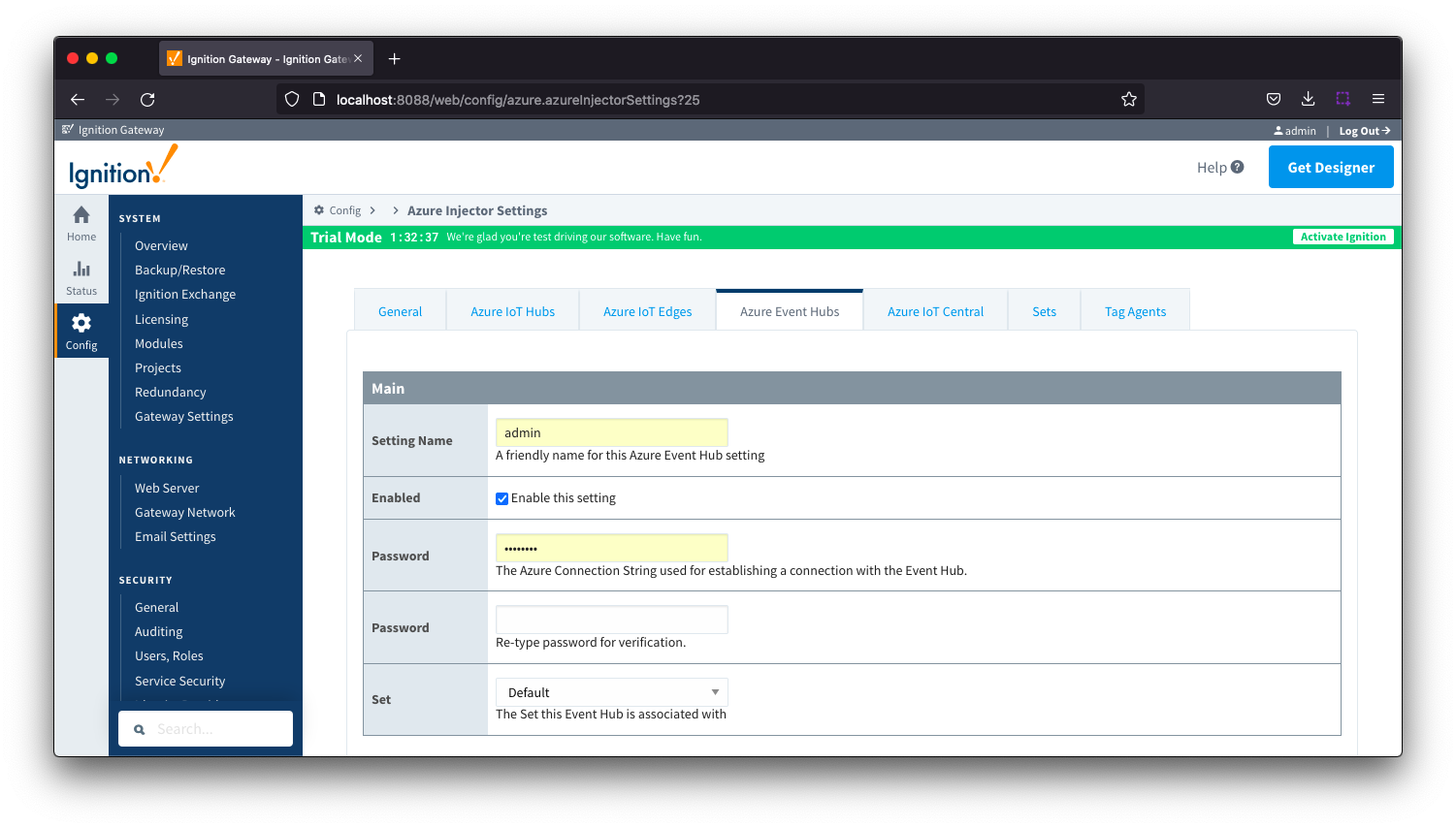
- Setting Name
- This is a friendly name of the Azure Event Hub used to easily identify it. This must also be unique.
- Enabled
- Whether or not this connection is enabled.
- Password/Connection String
- Set
- The Set to associate this Azure Event Hub connection with.
Azure Event Hub Settings - Store & Forward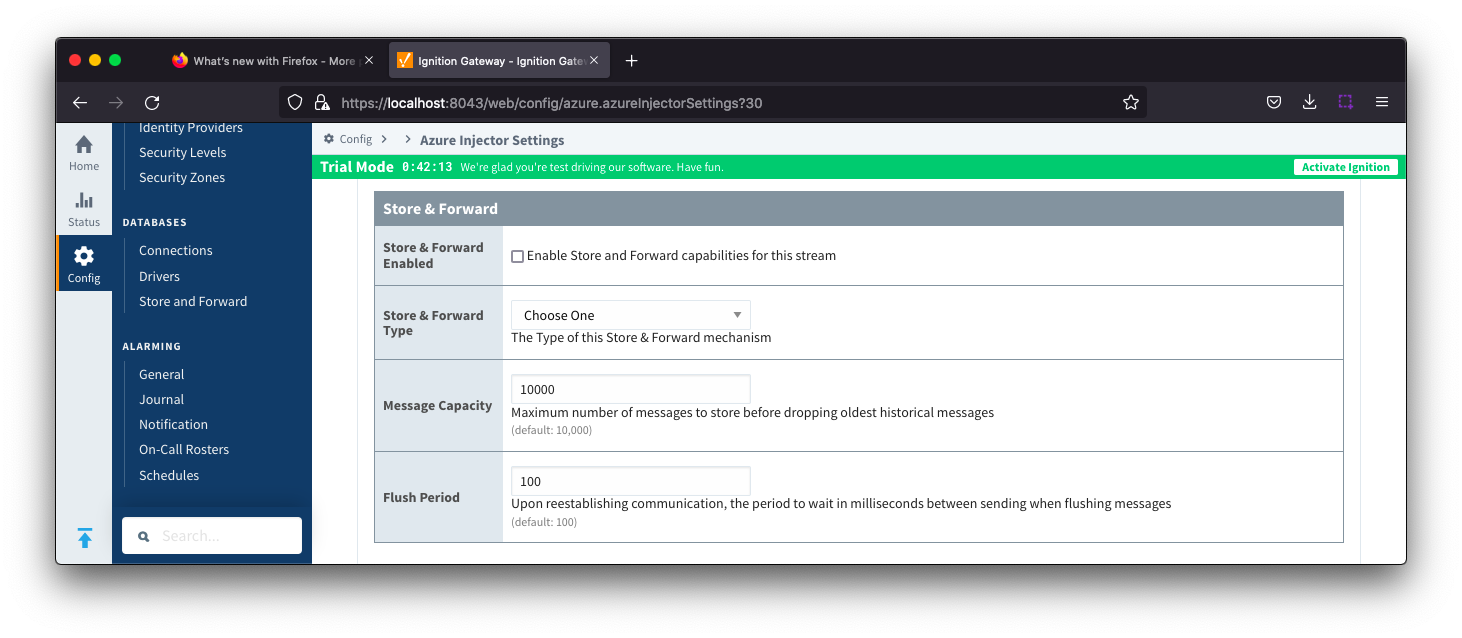
- Store & Forward Enabled
- Whether to enable Store & Forward capabilities for this endpoint
- Store & Forward Type
- The type of the Store & Forward mechanism
- Message Capacity
- The Maximum number of messages to store before dropping the oldest historical messages
- Flush Period
- The period of time to wait (in milliseconds) between sending when flushing messages
Azure Event Hub Settings - Advanced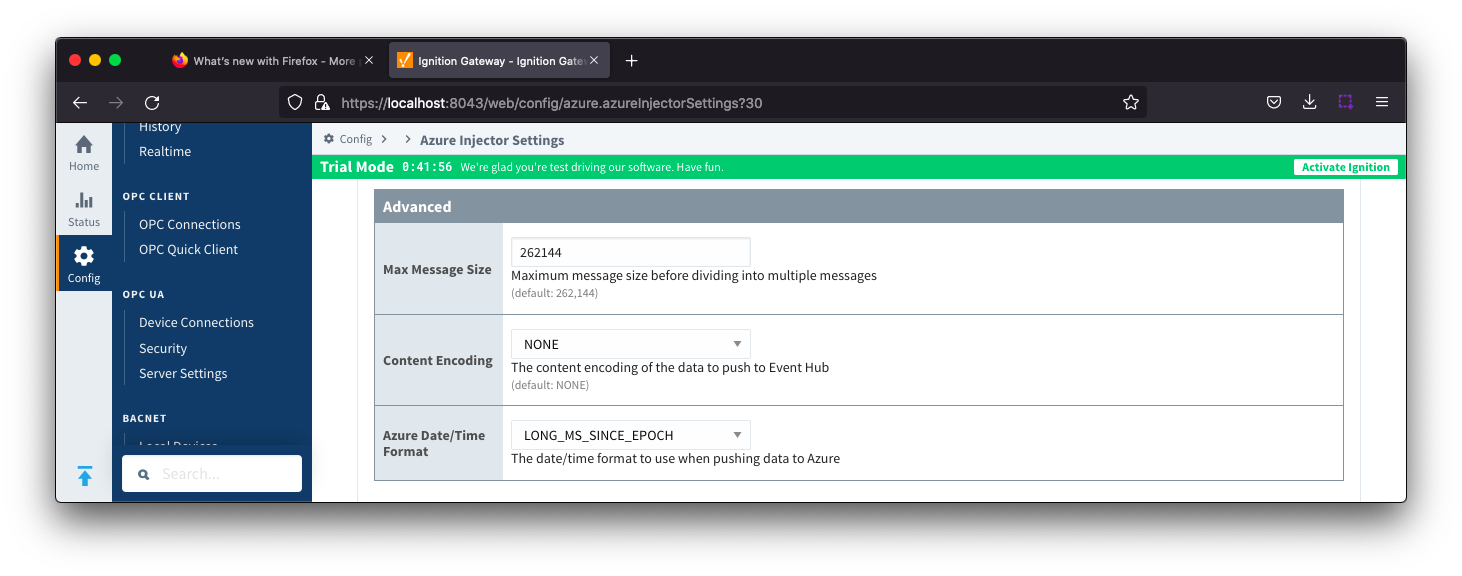
- Max Message Size
- The maximum message size for the Azure Event Hub. Default is 262144 bytes (256KB).
- EventHub Basic: 262144 bytes (256KB)
- EventHub Standard or better: 1048576 bytes (1MB)
- Content Encoding
- The content encoding of the data to push to Event Hub. Current option is In_Memory
- Azure Date/Time Format
- The date/time format to use when pushing messages to IoT Hub
- LONG_MS_SINCE_EPOCH (default) - The timestamp values will all be as numbers in milliseconds since epoch (Jan 1, 1970) in UTC
- STRING_AZURE_COMPAT - The timestamp will be pushed as described here. This is useful when wanting to use 'edge' timestamps in Azure Time Series insights.
- See Pushing Data to Azure Time Series Insights tutorial for more detail
Azure IoT Central
This tab provides a list of Azure IoT Central endpoints that the module should connect to to push tag data. One or more Azure IoT Central endpoints can be configured on this tab.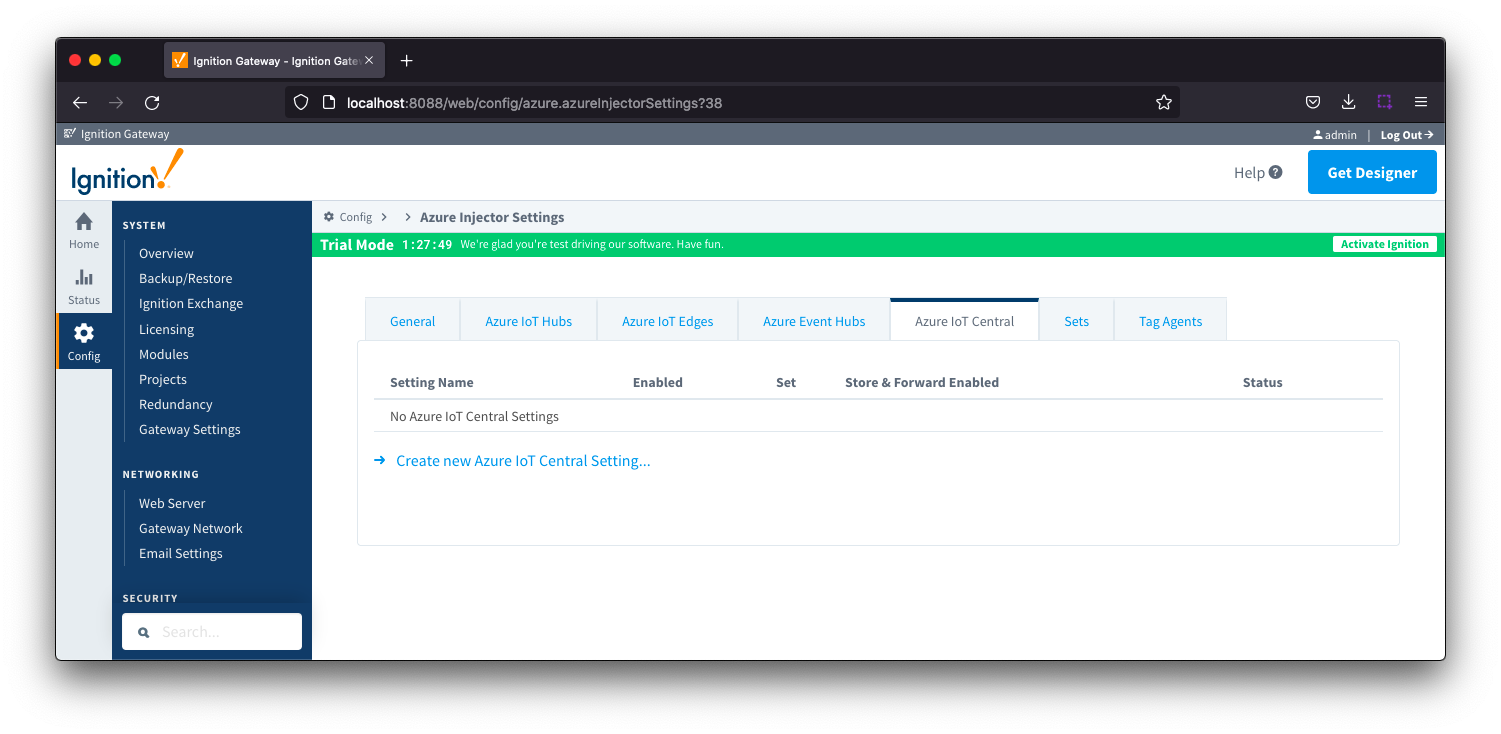
Clicking on the 'Create new Azure IoT Central Setting.." link will bring up the following form to add a new Azure IoT Central. The configuration sections available are Main, Store & Forward and Advanced.
Azure IoT Central - Main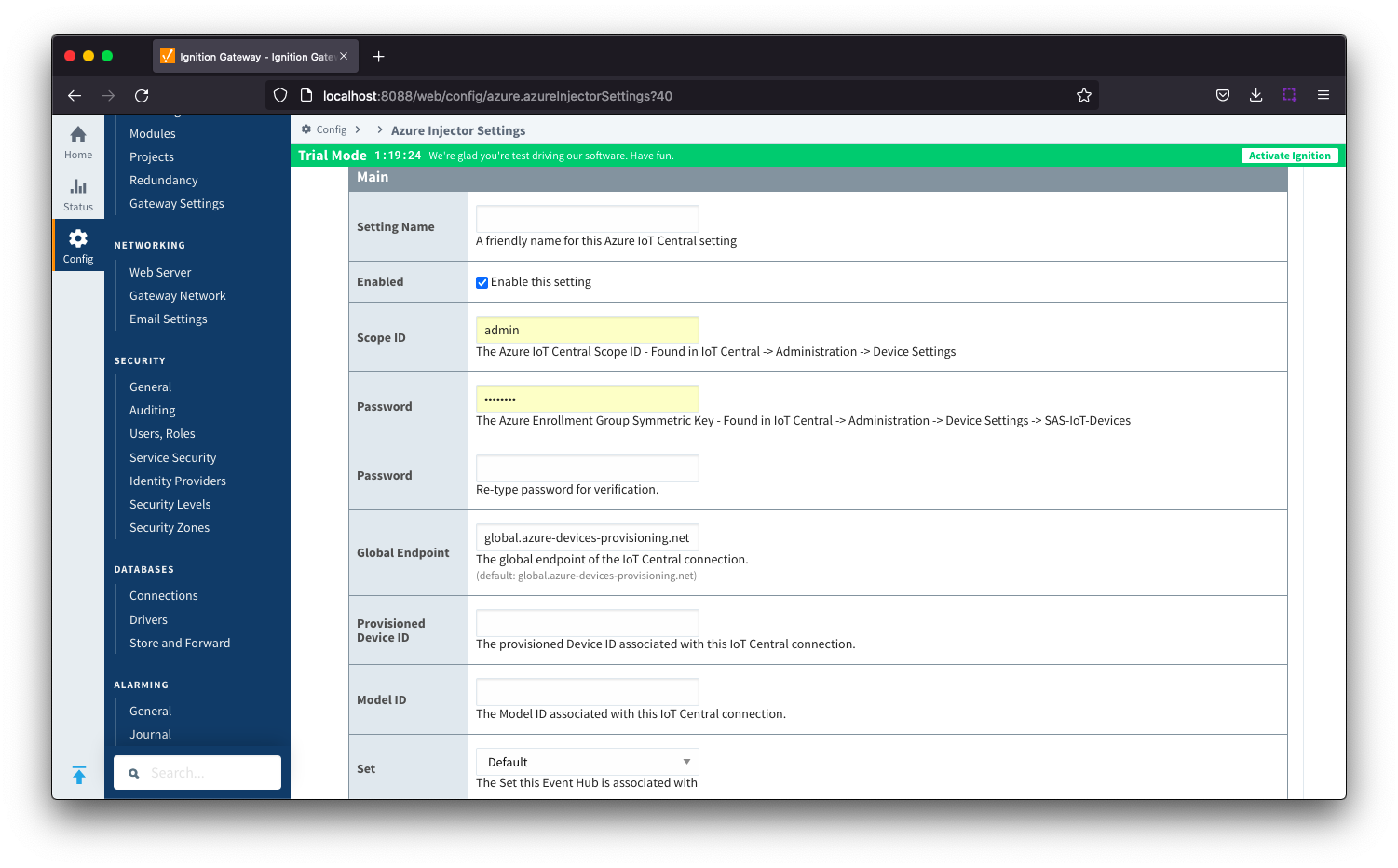
- Setting Name
- This a friendly name of the Azure IoT Central used to easily identify it. This must also be unique.
- Enabled
- Whether or not this connection is enabled.
- Scope ID
- The Azure IoT Central Scope ID.
- Found in the IoT Central -> Administration → Device Settings.
- Password
- The Azure Enrollment Group Symmetric Key.
- Found in the IoT Central -> Security -> Permissions -> Device Connection Groups -> [SAS-IoT-Devices] -> SAS -> Primary/Second key.
- Global Endpoint
- The global endpoint of the IoT Central connection. Default is global.azure-devices-provisioning.net
- Provisioned Device ID
- The provisioned Device ID associated with this IoT Central connection.
- Model ID
- The Model ID associated with this IoT Central connection.
- Set
- The Set associated with this IoT Central connection.
Azure IoT Central - Store & Forward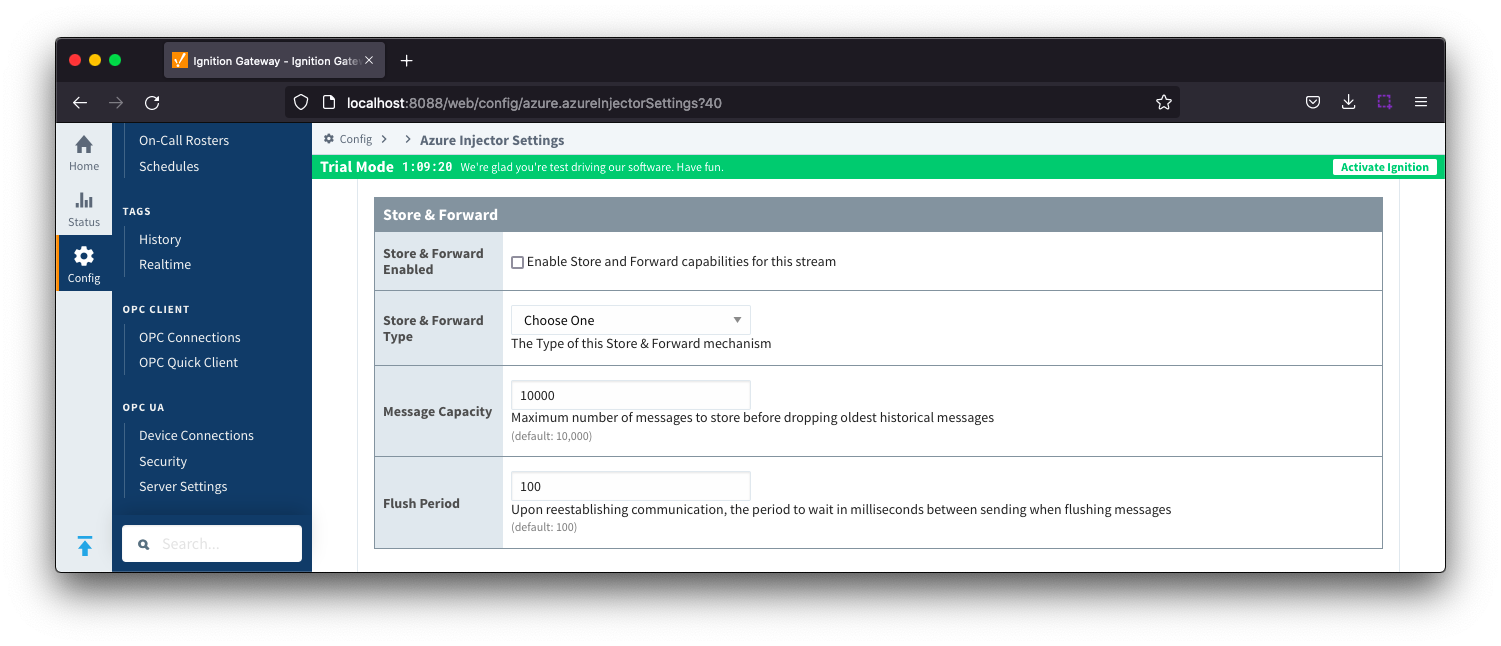
- Store & Forward Enabled
- Whether to enable Store & Forward capabilities for this endpoint
- Store & Forward type
- The type of Store & Forward mechanism
- Message Capacity
- The maximum number of messages to store before dropping the oldest historical messages. default is 10,000
- Flush Period
- The period of time to wait (in milliseconds) between sending when flushing messages. Default is 100
Azure IoT Central - Advanced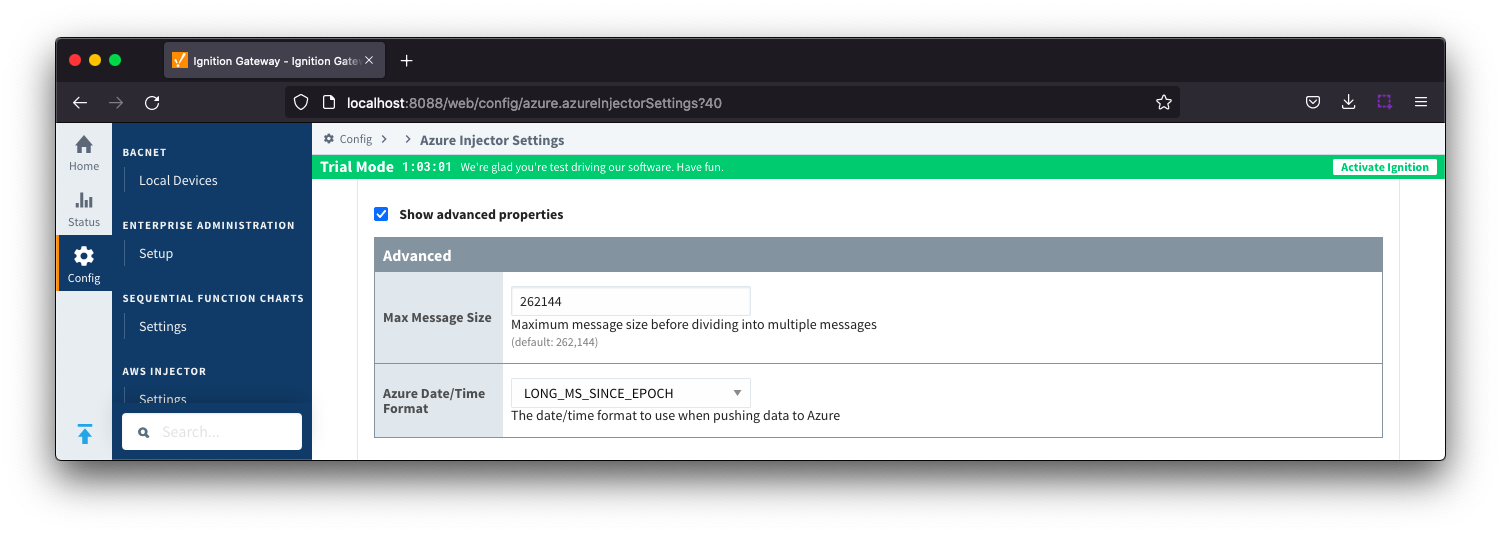
- Max Message Size
- The maximum message size in bytes that any message can be when pushing to IoT Central.
- Azure Date/Time Format
- The date/time format to use when pushing messages to IoT Hub
- LONG_MS_SINCE_EPOCH (default) - The timestamp values will all be as numbers in milliseconds since epoch (Jan 1, 1970) in UTC
- STRING_AZURE_COMPAT - The timestamp will be pushed as described here. This is useful when wanting to use 'edge' timestamps in Azure Time Series insights.
- See Pushing Data to Azure Time Series Insights tutorial for more details
Sets
This tab contains a list of Azure Sets. Each set represents a grouping of Azure IoT/Event Hub endpoints. When a set is referenced by a Tag Agent, the Agent will push Tag data to all Azure IoT/Event Hub endpoints contained within that Set.
Out of the box the Azure Injector module will have one "Default" set defined. Additional Sets can be configured for situations where multiple Tag Agents will need to push to different Azure IoT Hub endpoints.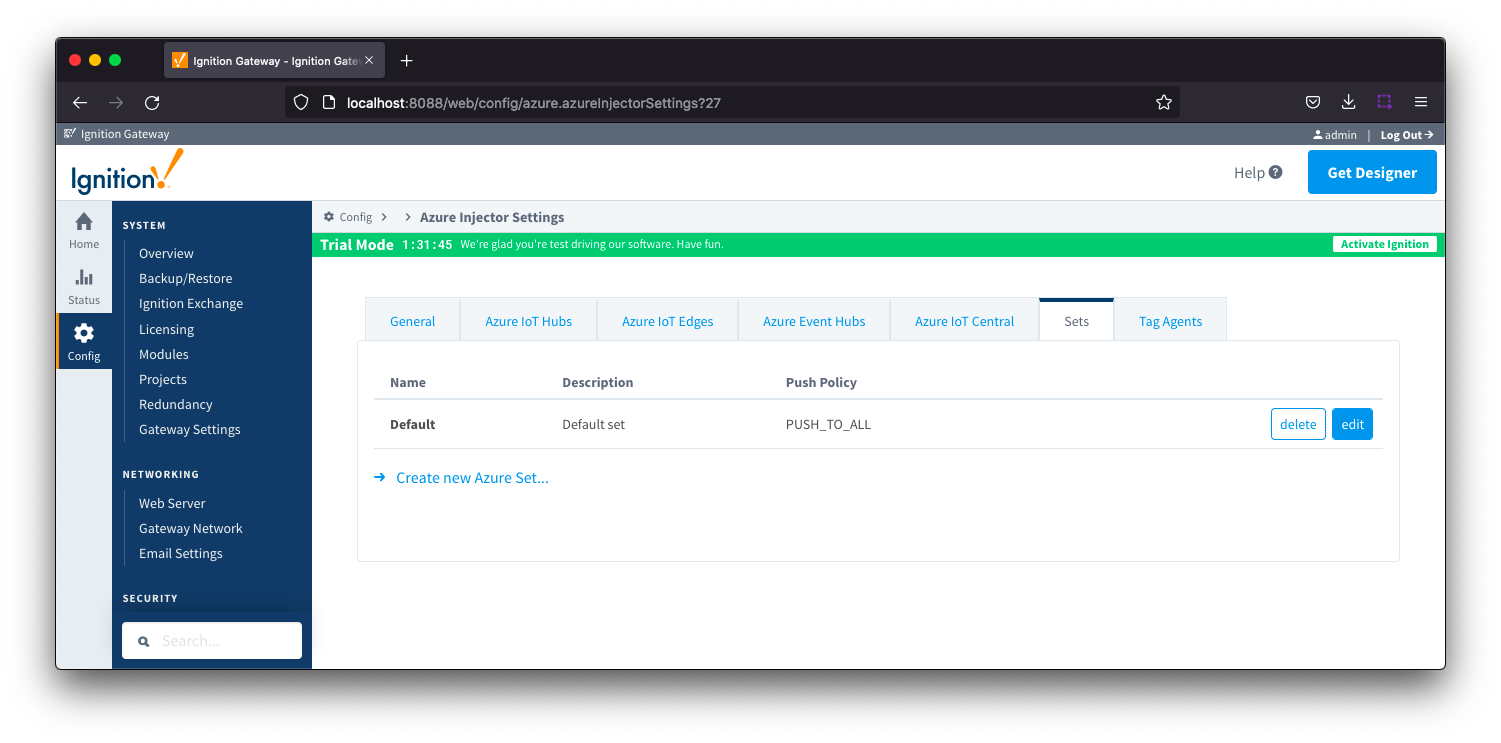
Clicking on the 'Create new Azure Set ..' link will bring up the following form to add a new Set. The configuration section available is Main
Sets - Main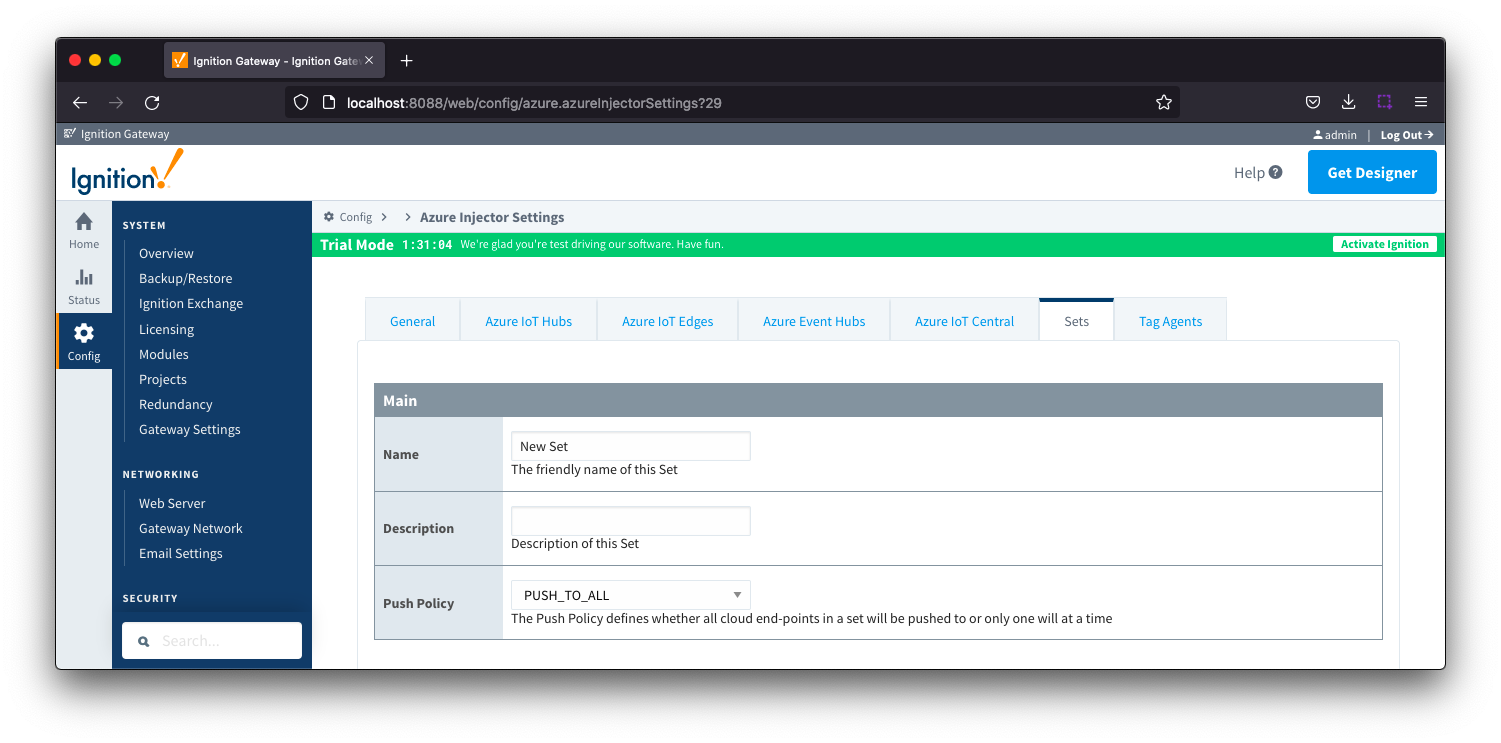
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the set used to easily identify it.
- Description
- This is a friendly description of the set.
- Push Policy
- This defines which endpoints to push to.
- If PUSH_TO_ALL is selected, every endpoint that is part of this set will receive all messages.
- If PUSH_TO_ANY is selected, only one of the endpoints that is part of this set will receive any given message. PUSH_TO_ANY is useful when adding endpoint configurations to increase the throughput of the Injector.
Tag Agents
Tag Agents are the workers within Azure Injector that monitor tag events, convert them to a JSON representation, and push them to one or more Azure IoT Hub endpoints. Out of the box the Azure Injector module will have one "default" Tag Agent defined.
Tag Agents are configured to point to a single folder. All Tags within that folder will be monitored by the Tag Agent. 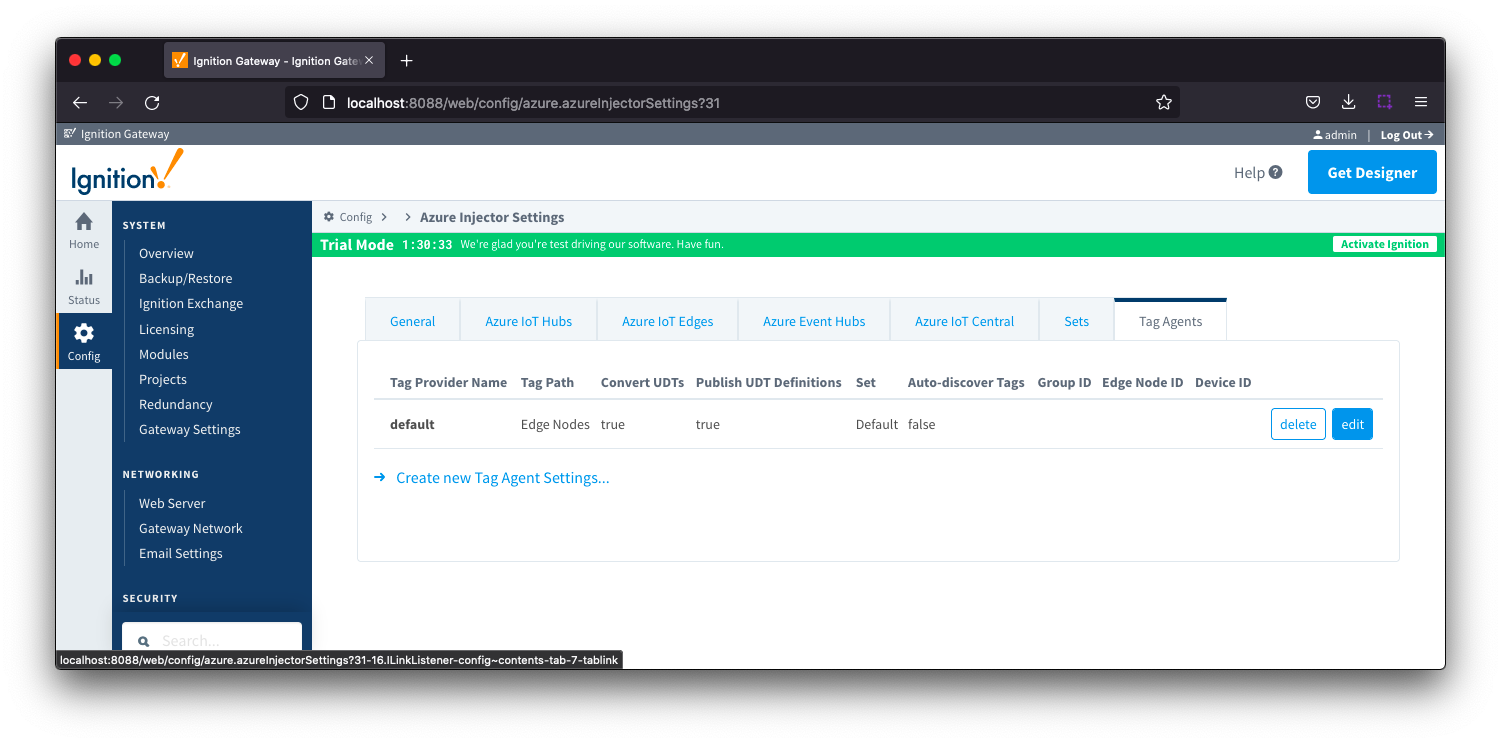
Clicking on the 'Create new Tag Agent Settings..' link will bring up the following form to add a new Tag Agent. The configuration sections available are Agent Settings, Sparkplug Settings and Advanced
Tag Agents - Agent Settings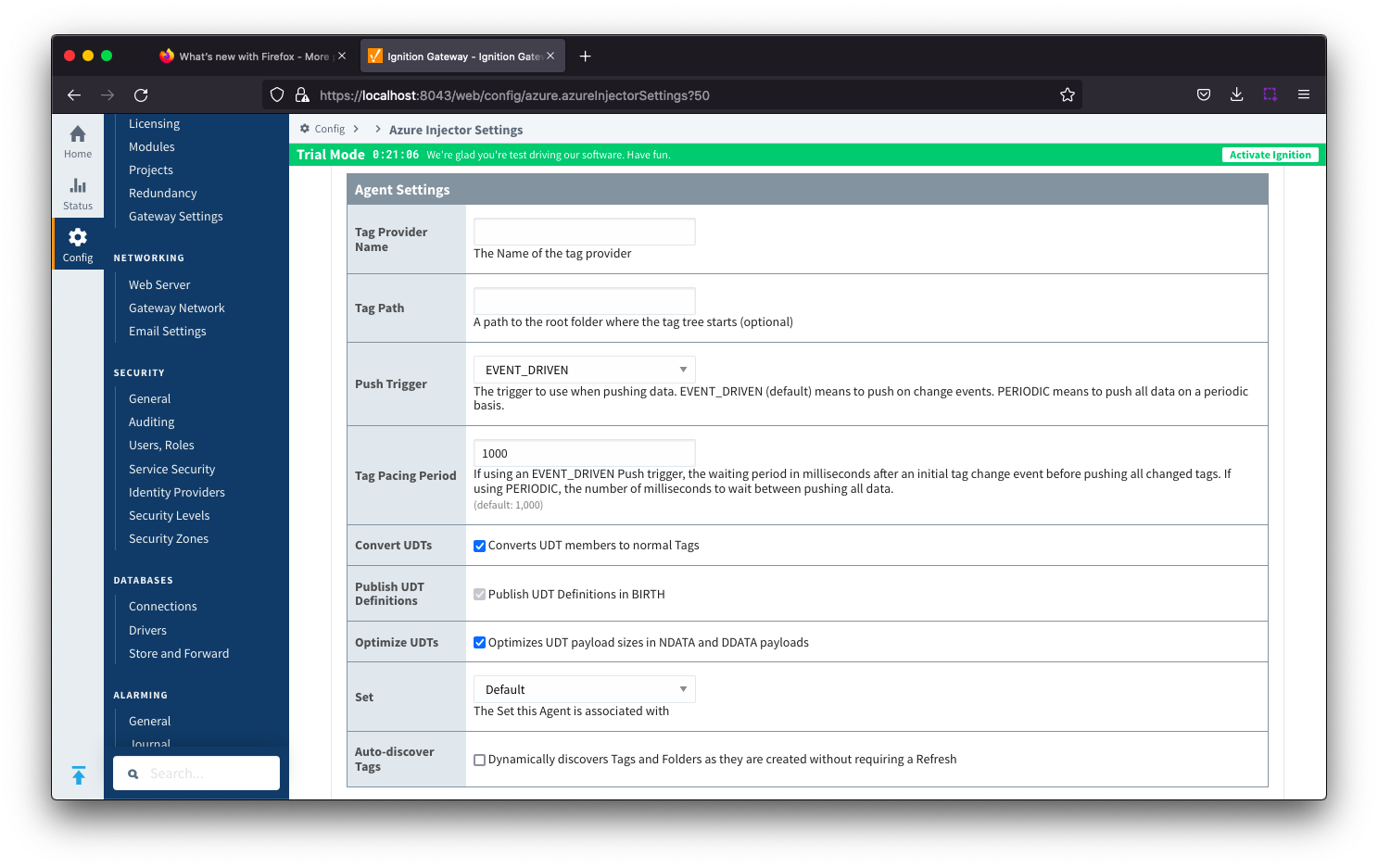
- Tag Provider Name
- The name of the Tag provider containing the tags.
- Tag Path
- An optional folder path under the Tag provider where the root folder of the Tags can be found.
- Push Trigger
- Defines what triggers a push to the cloud endpoint
- EVENT_DRIVEN (default) - when a tag change event (value or quality) occurs, and no pending push exists, tag events will be aggregated for the 'Tag Pacing Period' before being pushed.
- PERIODIC - will push the latest data for all tags associated with the Agent every 'Tag Pacing Period'. With this option, only one event per tag will be sent and tag change events will not be captured.
- Tag Pacing Period
- The buffer period, in milliseconds, that Tag events will be aggregated into a single payload before pushing.
- Convert UDTs
- Whether to convert UDT members to normal Tags before publishing. If enabled the Tags representing the UDT member will retain their member path prefixed by the UDT Instance name.
- Publish UDT Definitions
- This will only be used if 'Convert UDTs' is false
- Whether or not to push the UDT Definitions in the the NBIRTH messages
- Optimize UDTs
- This will only be used if 'Convert UDTs' is false
- Whether or not to 'convert UDTs' only for DATA messages.
- Set
- The Set of Azure IoT Hub endpoints that the Tag Agent will push to.
- Auto-discover Tags
- Whether newly added tags should be dynamically scanned and their values pushed. This field is disabled by default. It should remain disabled while manually editing tags and/or their configurations. It should only typically be enabled in systems where tags are created in real time.
Tag Agents - Sparkplug Settings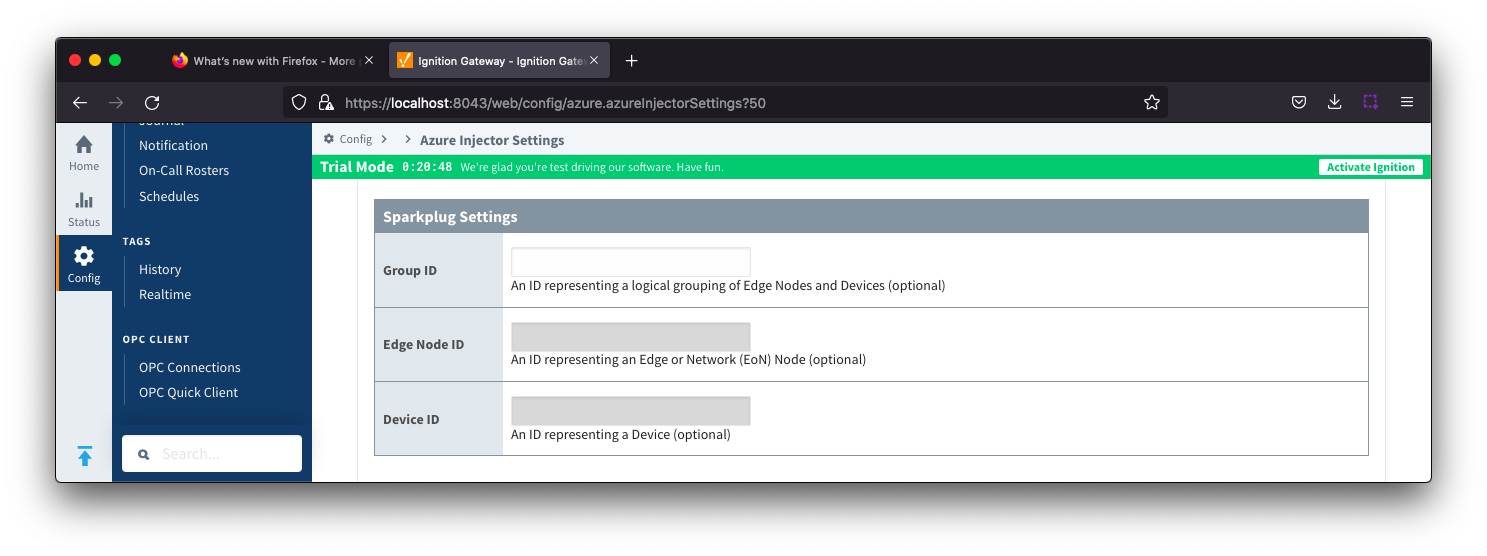
- Group ID
- An ID representing a logical grouping of MQTT Edge Of Network (EoN) Nodes and Devices into the infrastructure.
- Edge Node ID
- An ID that uniquely identifies the MQTT Edge Of Network (EoN) Node within the infrastructure.
- Device ID
- An optional ID that uniquely identifies a Device within the infrastructure.
The Sparkplug settings are optional and allow for an additional customization of how the Tag Agent scans and discovers tag within the specified Tag Path. Here is a brief description of how the Agent scans/discovers folders based on the different combinations of potential Sparkplug Settings.
- If all three IDs are left blank the Agent will assume the following folder structures follow the Tag Path:
- <groupFolder>/<edgeNodeFolder>/<deviceFolder>/<tags>
- <groupFolder>/<edgeNodeFolder>/<tags>
- If only the Group ID is specified the Agent will assume the following folder structure follows the Tag Path:
- <edgeNodeFolder>/<deviceFolder>/<tags>
- <edgeNodeFolder>/<tags>
- If the Group ID and the Edge Node ID are specified the Agent will assume the following folder structure follows the Tag Path:
- <deviceFolder>/<tags>
- <tags>
- If the Group ID, Edge Node ID, and the Device ID are specified the Agent will assume the following folder structure follows the Tag Path:
As you can see, the Sparkplug settings can be used to either hard-code these IDs, or leave them blank so that the Agent will scan and discover them based on the tag tree layout. For more information see MQTT Transmission Transmitters and Tag Trees document keeping in mind that MQTT Transmission Transmitters can be thought of like 'Agents' in Injectors with regard to Sparkplug IDs and tag trees.
Tag Agents - Advanced
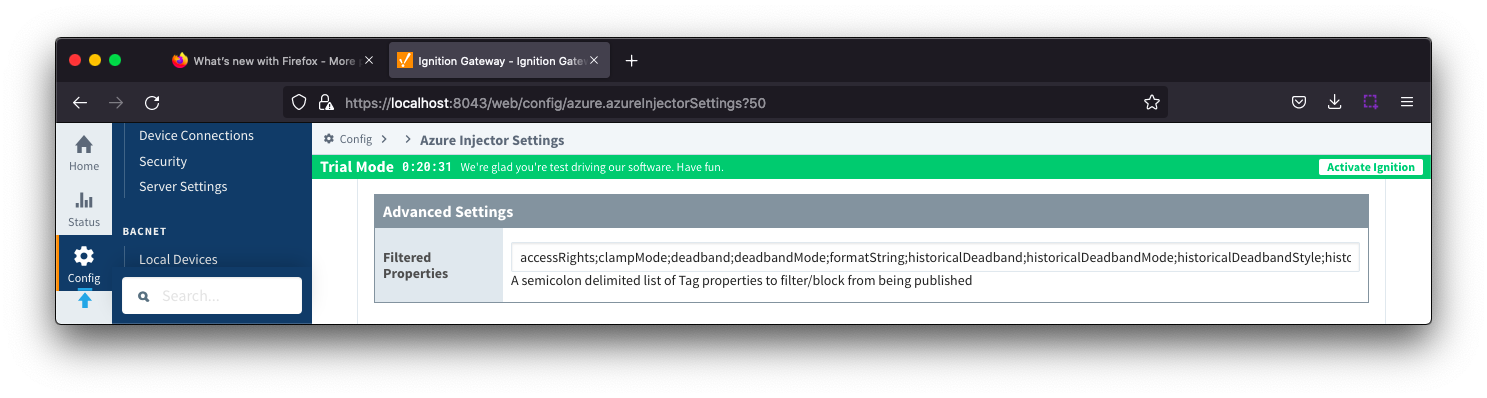
- Filtered Properties
- A semicolon delimited list of Tag properties to filter/block from being published. These should typically not be modified unless there is an explicit requirement that a specific property is needed to be added or removed from the default.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()