To enable history configuration is required at MQTT Engine, at each MQTT tag, and at the MQTT Transmission module. In addition, a History Store must also be defined for MQTT Transmission.
MQTT Transmission History Store
- Define and enable an MQTT Transmission History Store
- Config your transmitter to consume the enabled History Store
- Store and forward controls whether or not a tag is stored in the configured History Store when Transmission is offline. By default the global setting of "Enable History Storage by Default" is selected for all tags. To override , individual tags will require a custom tag property 'StoreAndForward' (type: boolean) to be created and set to the reverse state of the global setting.
MQTT Engine Tags
- History *must* be enabled on the MQTT Engine Tag and the history settings for that tag must be as follows:
- History Enabled: true
- Storage Provider: Must be set to an existing Storage Provider
- Sample Mode: On Change
- Min Time Between Samples: 0 ms
- This is required in cases where historical metrics flushed from the Edge have very high resolution; e.g., the historical metrics have timestamps 1 ms apart for a single tag.
See the Ignition documentation Configuring Tag History for additional help.
Historical Event Processing
There are two ways that MQTT Engine historical event processing can result in historical inserts into the database:
- Engine is configured to write historical events directly to the database, via the Historian, bypassing the Tag.
- Engine is configured to write historical events to the Tag instead of directly to the Historian.
Writing historical events directly to the database, via the Historian, bypassing the tag
The configuration parameters required to write historical events directly to the database, via the Historian, bypassing the Tag are detailed below.
MQTT Engine
Under the MQTT Engine Settings General Tab, navigate to the Miscellaneous Settings and ensure Store Historical events is selected

MQTT Transmission
Under the MQTT Transmission Settings for your transmitter, navigate to the History Settings and ensure that In-Order History is de-selected.

Writing historical events directly to tag
There are several reasons why you might need to write directly to the tag which include:
- To have Tag Events scripts fire when applicable
- If indirectly referencing MQTT Engine tags
- To have alarms triggered when applicable
The configuration parameters required to write historical events to the Tag instead of directly to the Historian are detailed below.
MQTT Engine
Under the MQTT Engine Settings General Tab, navigate to the Miscellaneous Settings and ensure Store Historical events is de-selected

MQTT Transmission
Under the MQTT Transmission Settings for your transmitter, navigate to the History Settings and ensure that In-Order History is selected. This ensures that when the Edge side client comes back online and flushes history, it will flush the oldest historical events first (in order) before sending live Tag changes events to Engine.

History Configuration Persistence
However, deleting MQTT Engine tags can be required in certain cases. One example is if UDTs are being propagated from the Edge and the UDT definition on the Edge has been updated. This requires one to delete all instances of the UDT under MQTT Engine and delete the corresponding UDT definition so that it can be recreated/updated at MQTT Engine for the Edge side changes to take affect.
There are two options for persisting history configuration in this case and they are as follows:
- Use Reference tags to indirectly reference MQTT Engine tags such that history configuration can be persisted on the Reference tag when the underlying MQTT Engine tags are deleted. This is the recommended way of configuring history on MQTT Engine tags (indirectly) so history configuration persists.
- Use Ignition scripting to reapply history configuration directly on MQTT Engine tags on demand. This is a bit more cumbersome as there must be some mechanism to "trigger" the script execution.
History and Indirect References to MQTT Engine Tags
Configuring history on tags indirectly referencing MQTT Engine tags will work properly if the referencing tag is a Reference tag only. Derived, Expression and OPC tags (expose MQTT Engine tag provider through OPCUA server) will not properly store history when MQTT Engine tags are updated with historical data at a high rate of speed. This is a limitation within the Ignition platform and may be addressed in a future release.
If using an Ignition release before v8.1.4 with MQTT Engine - In order for historical tag changes at the MQTT Engine tag to propagate to the referencing tag, MQTT Engine must be configured to write historical data directly to its tags and MQTT Transmission must be configured to flush history in-order. See this section above for more details on these configuration requirements.
If using an Ignition v8.1.4 or later with MQTT Engine - Historical back-fill support was added in Ignition which allows Reference Tags in Ignition to be updated even if history arrives out of order. See the following document for details: MQTT History Back-Fill with Reference Tags
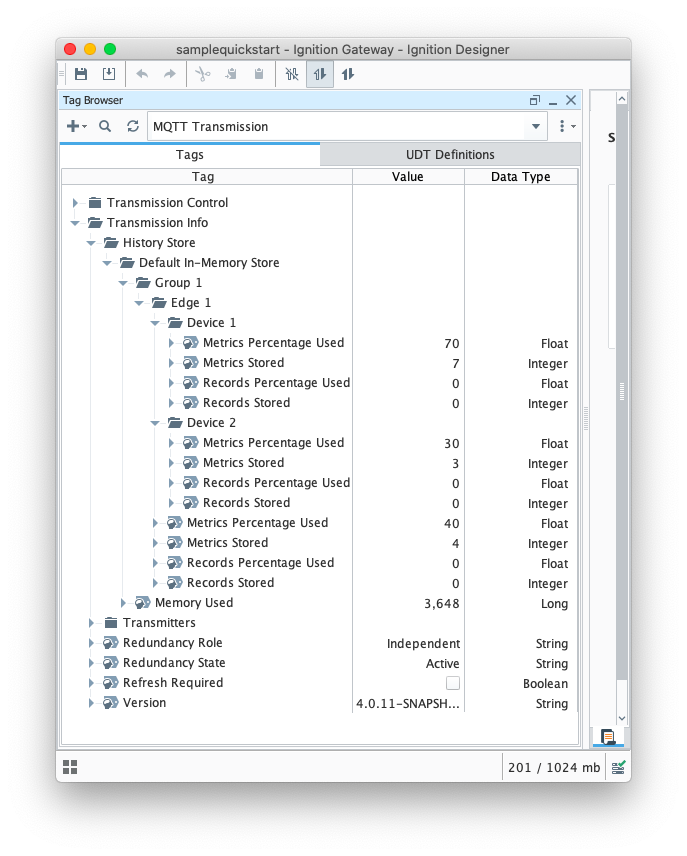
History Stores Metrics & Flushing History
One can determine the current size of the History Store by examining the History Store metric tags under [MQTT Transmission]Transmission Info/History Store. These tags will show the number of historical metrics stored per edgenode/device and how much memory/disk is being consumed by these metrics. These tags update live (count down) as historical data is flushed.
Additional Resources
- Inductive Automation's Ignition download with free trial
- Cirrus Link Solutions Modules for Ignition
- Support questions
- Sales questions
- About Cirrus Link
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()




