MQTT Engine provides a configuration section to the Ignition Gateway and this can be seen in the left side bar of the Ignition Gateway web UI.
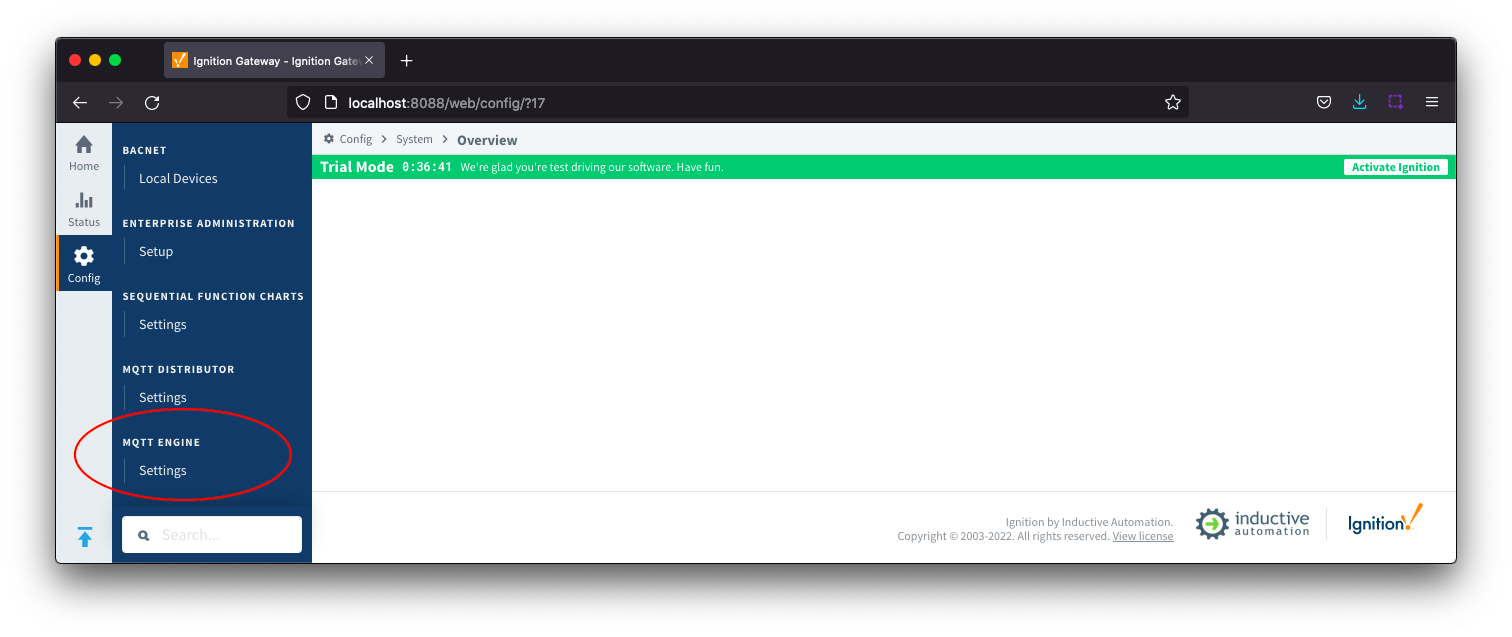
The configuration options for each of the three tabs - General, Servers, and Namespaces - are detailed below.
General
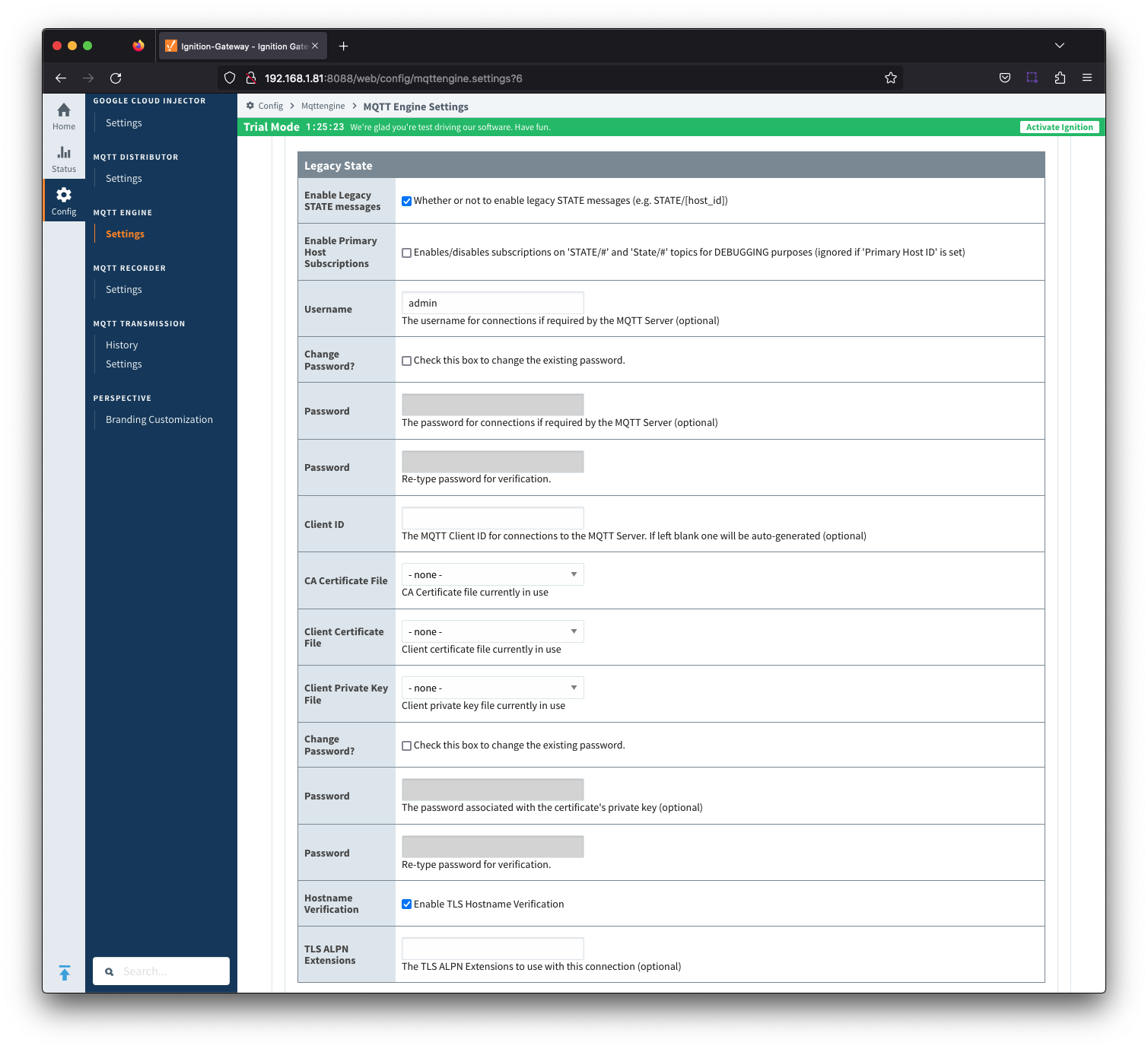
The configuration sections available are Main, Miscellaneous and Advanced.
General - Main
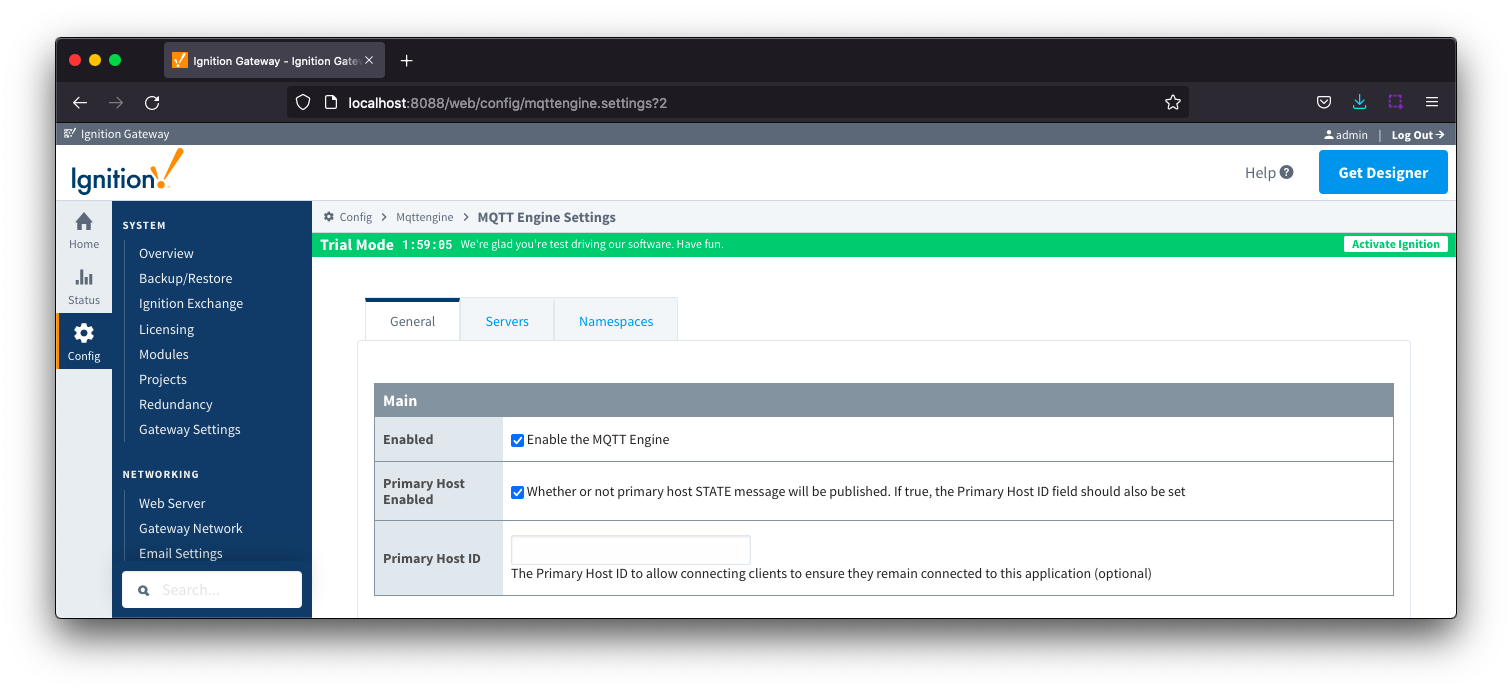
Enabled
- Whether or not the MQTT Engine module is enabled and connecting to configured MQTT Servers.
- Primary Host Enabled
- Whether or not primary host STATE message will be published. If true, the Primary Host ID must also be set.
- When enabled, the MQTT Engine will publish it's connection state on a topic that contains the Primary Host ID. In the event that MQTT Engine becomes disconnected from the server, a death certificate will be published on the same topic, setting the state to 'offline'. Any connecting client that subscribes on the state topic will then be notified of the MQTT Engine state and walk to the next server is MQTT Engine is offline.
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to allow connecting clients to ensure they remain connected.
- This must contain only letters, numbers, or any of the following special characters: . $ % @ ! - _ ^ *
General - Miscellaneous
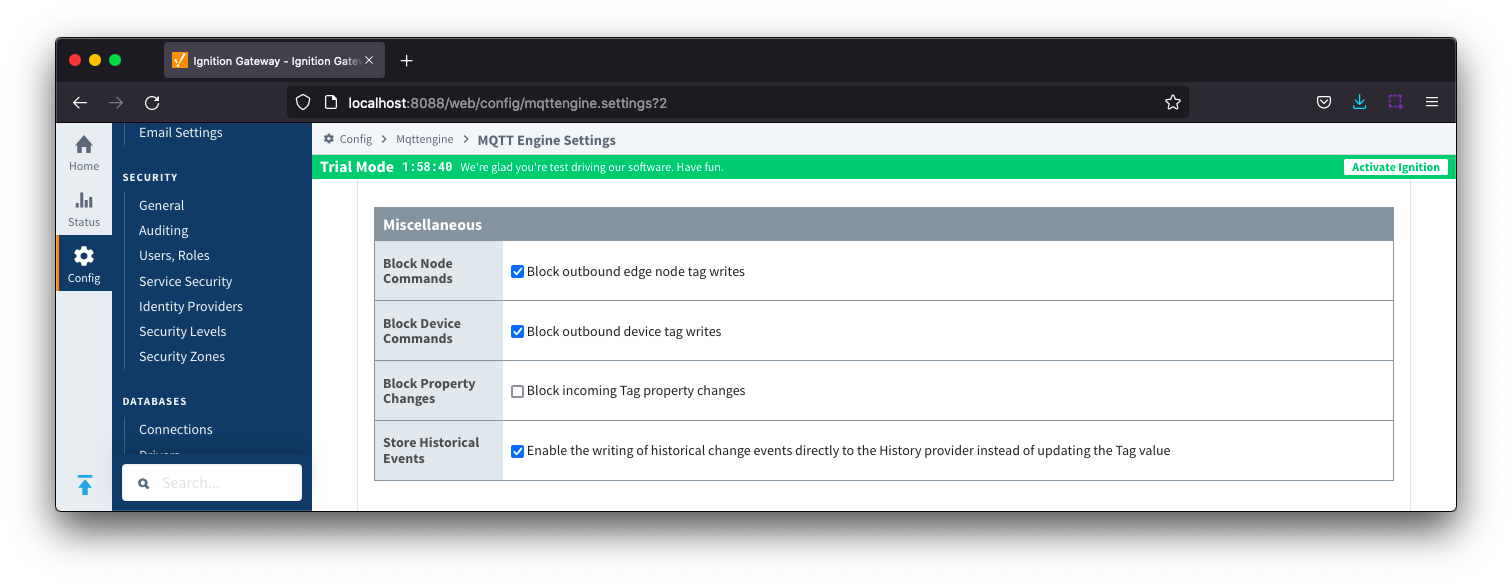
- Block Node Commands
- Whether or not to block outgoing commands from MQTT Engine to Edge Nodes. This is true by default and provides a security mechanism for preventing accidental outgoing commands from MQTT Engine.
- Block Device Commands
- Whether or not to block outgoing commands from MQTT Engine to Devices. This is true by default and provides a security mechanism for preventing accidental outgoing commands from MQTT Engine.
- Block Property Changes
- Whether or not to block incoming properties from modifying MQTT Engine tag properties. This is false by default so property changes will be applied if not included in the Filtered Property list under 'Advanced'.
- Store Historical Events
- Whether or not to write historical change events directly to the Historian (if history is enabled on a Tag) instead of updating the live Tag value.
- Note: Store and Forward does not guarantee all data is stored and forwarded. There are some edge cases that are not currently handled with regard to data loss in the event of connection failures related to MQTT keep alive timeouts. This window of potential missed data can be reduced by decreasing MQTT Transmission and MQTT Engine configurable keep alive timeouts.
General - Advanced
These are advanced settings/features and they should be left with default values in almost all cases. Please be careful when changing these settings from their default values.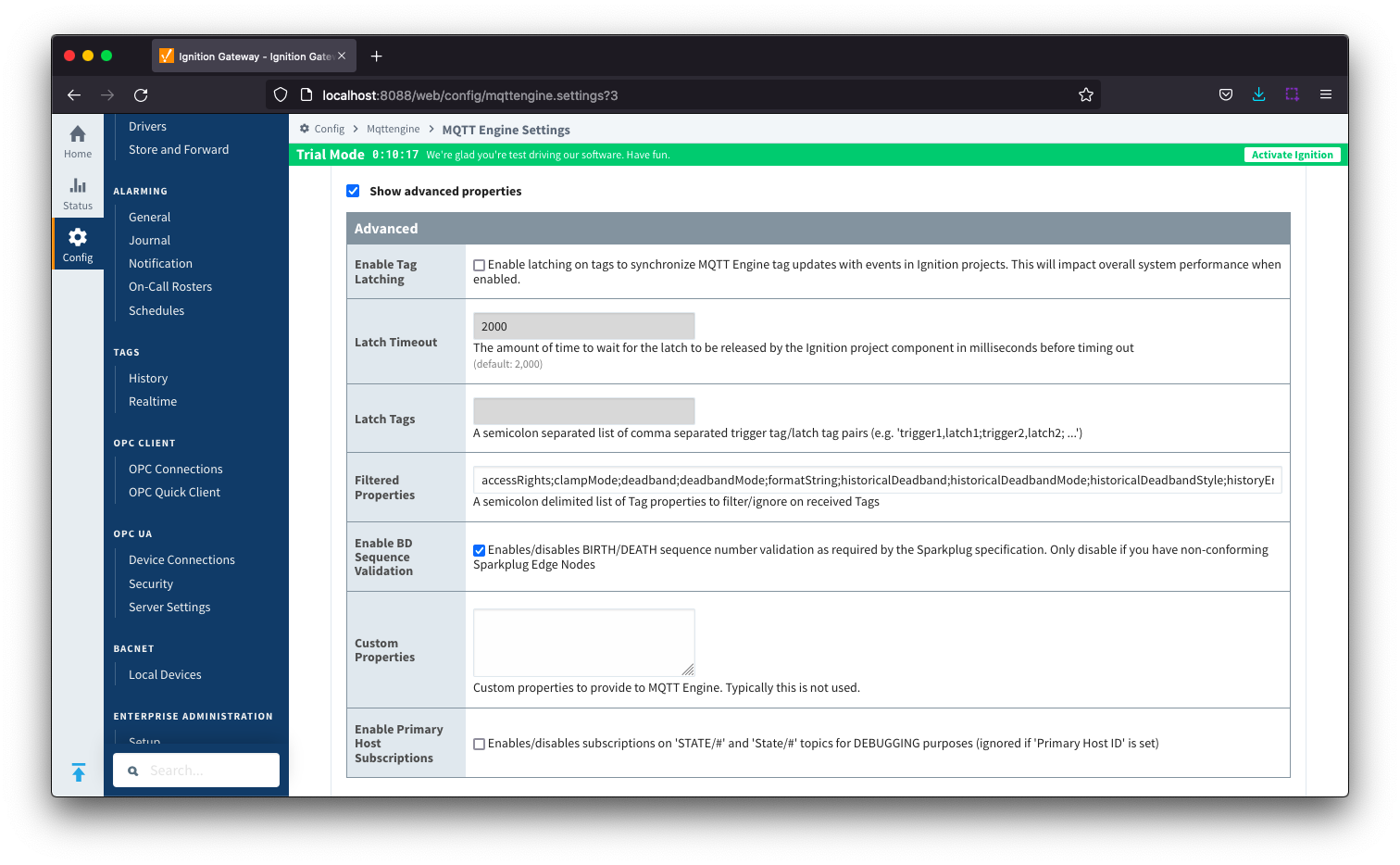
The Servers tab has two parts - Settings and Certificates
Servers - Settings
This tab provides a list of the MQTT Servers that MQTT Engine should connect to. By default, MQTT Engine is configured to connect to the local MQTT Distributor based MQTT Server and is set up to connect to localhost, port 1883, using the default username/password.
Additional or alternative MQTT Servers can be configured in MQTT Engine - often times more than one will be configured to handle fail-over in redundant or geographically distributed systems. Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server' link will bring up a form for adding a new MQTT Server setting.
The connection status of each server can be seen in the 'Status' column.
The configuration sections available are Main, TLS and Advanced.
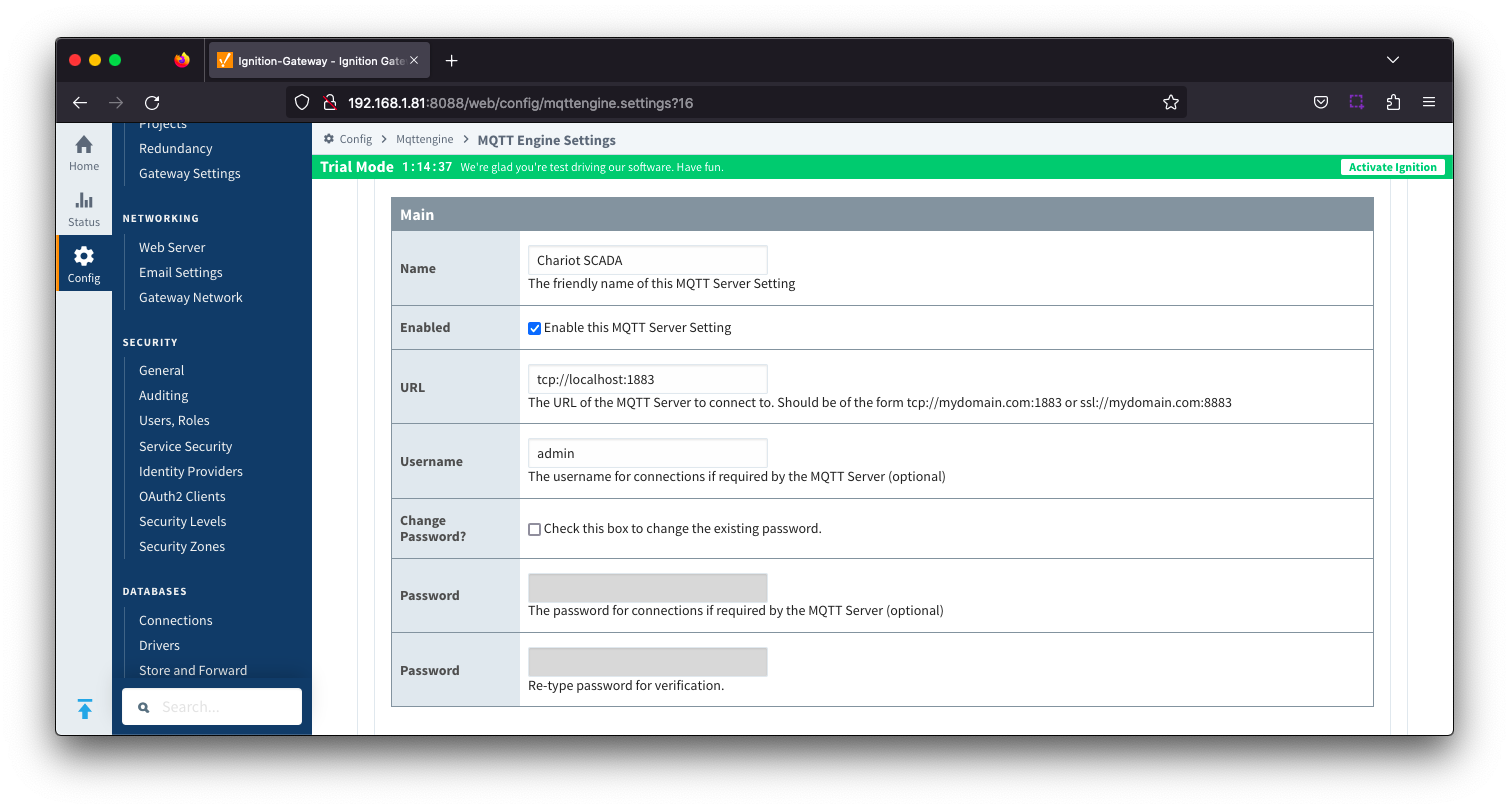
Server Settings - Main
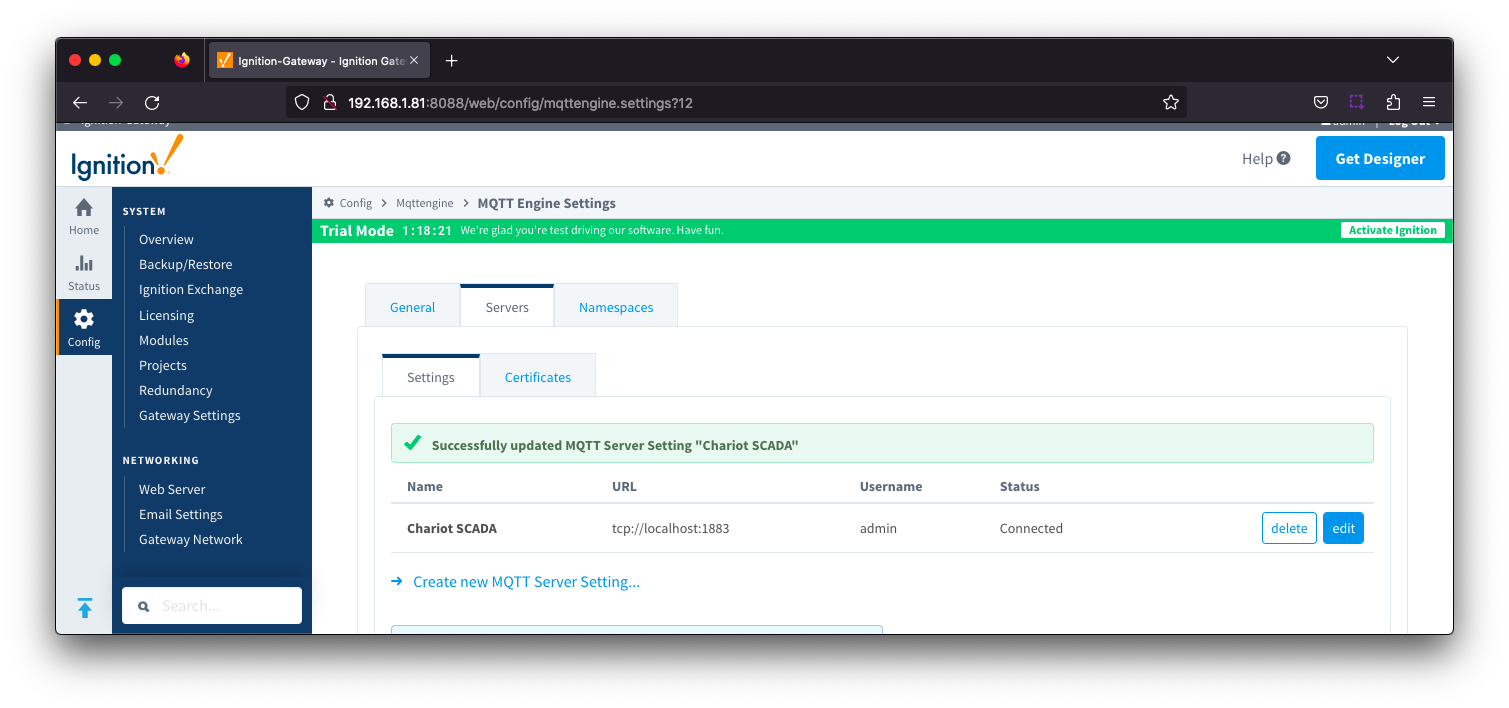
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the MQTT Server used to easily identify it.
- Enabled
- Whether or not connections to this MQTT Server are enabled.
- URL
- This is the URL of the MQTT server. Its format is as follows: [protocol]://[location]:[port]. Each of these are shown below.
- protocol - Either tcp or ssl
- location - The server location. e.g. localhost, myserver.chariot.io, mydomain.com, etc
- port - The port the MQTT Server is listening on. Generally this is 1883 if using TCP or 8883 if using SSL
- Username
- Optional MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Password
- Optional MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
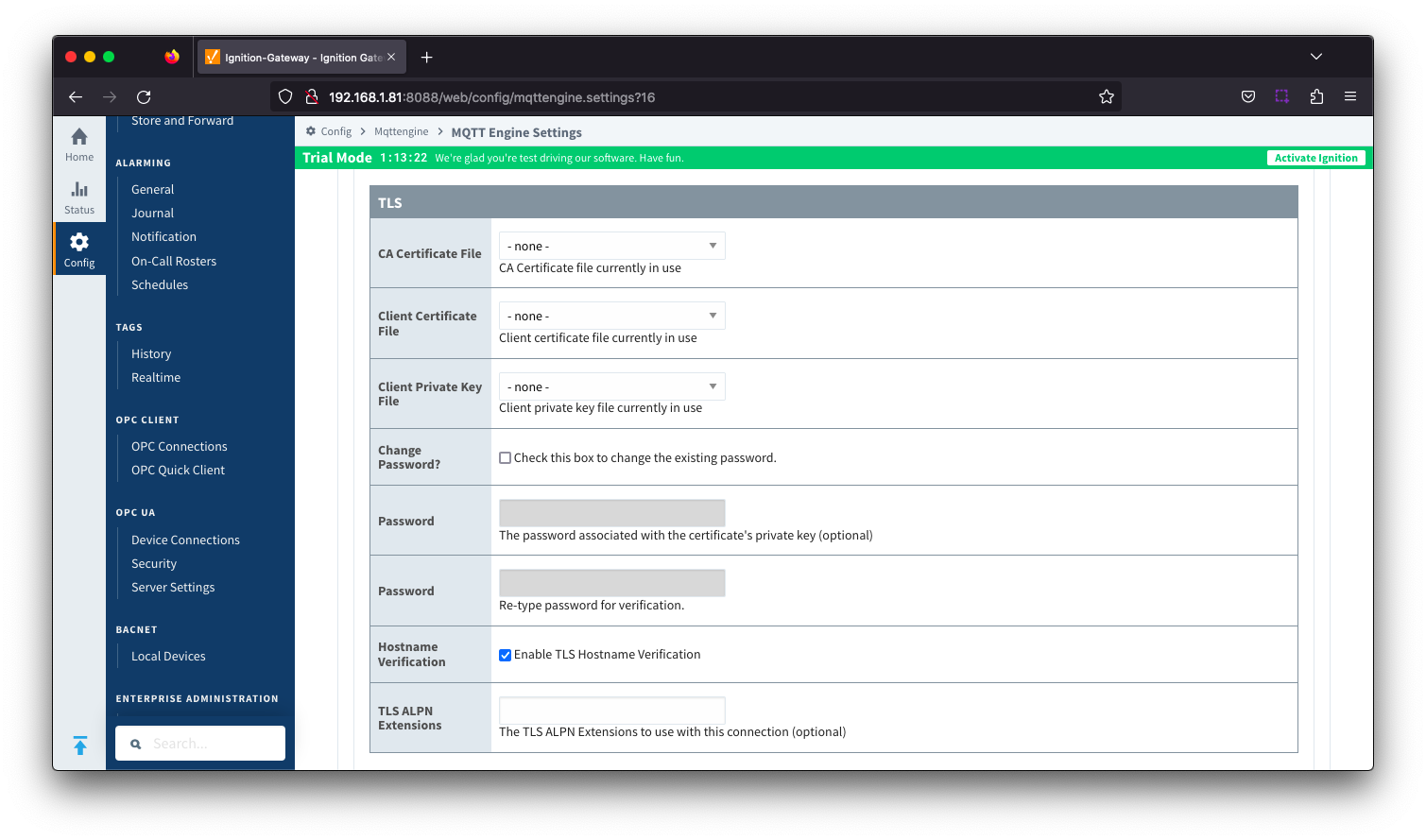
Server Settings - TLS
See this document for TLS configuration: Configuring Secure MQTT Communication
- CA Certification File
- CA Certification file currently in use.
- Client Certification File
- Client Certification file currently in use.
- Client Private Key File
- Client Private Key file currently in use
- Password
- Optional password associated with the certificate's private key.
- Hostname Verification
- Enable TLS Hostname Verification. This is true by default.
- TLS ALPN Extensions
- Optional TLS ALPN Extensions to use with this connection
Server Settings - Advanced
- Client ID
- Optional MQTT client ID to use. If specified this will be used in the MQTT Engine connect packet when connecting to the server. If left blank, a random client ID will be create of the form 'IgnitionTarget-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx'. Caution: MQTT Clients IDs must be unique and if two clients attempt to connect with the same client ID, one will be forcefully disconnected from the server to allow the other client to connect.
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT client keep alive time (in seconds).
- Filtered Namespaces
- A comma separated list of namespaces that will be filtered/disabled for connections to this MQTT Server.
Servers - Certificates
This tab provides a list of the certificate or private key files if loaded and available for TLS configuration.
The Certificates tab contains a single Main section.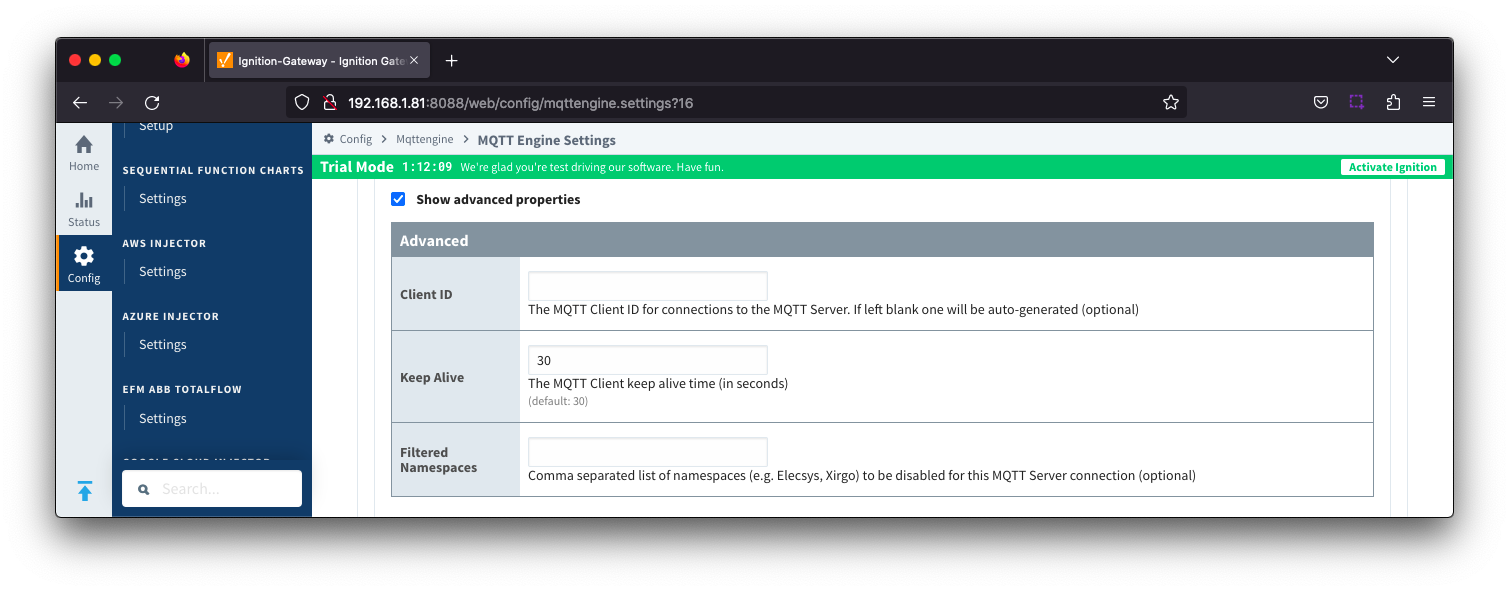
Servers Certificates - Main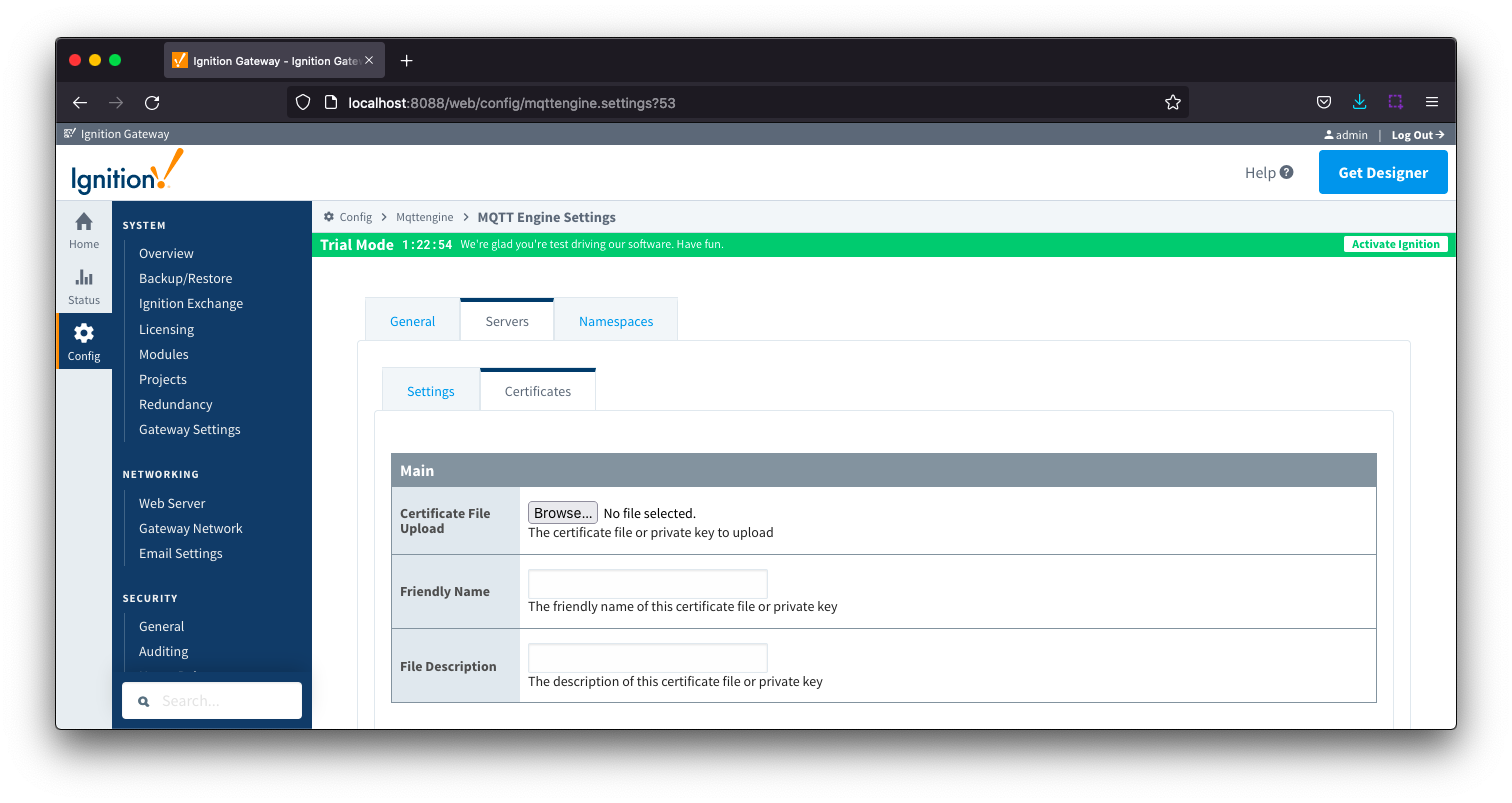
- Certificate File Upload
- Browse to the certificate file or private key to upload.
- Friendly Name
- The friendly name of the certificate file or private key.
- File Description
- The description of the certificate file or private key.
Namespaces
The third tab is used for configuring namespaces. Each namespace configuration represents a family of devices and/or data that MQTT Engine will support. A namespace defines the topics that each MQTT Engine client will subscribe on as well as indicates how the payload will be handled.
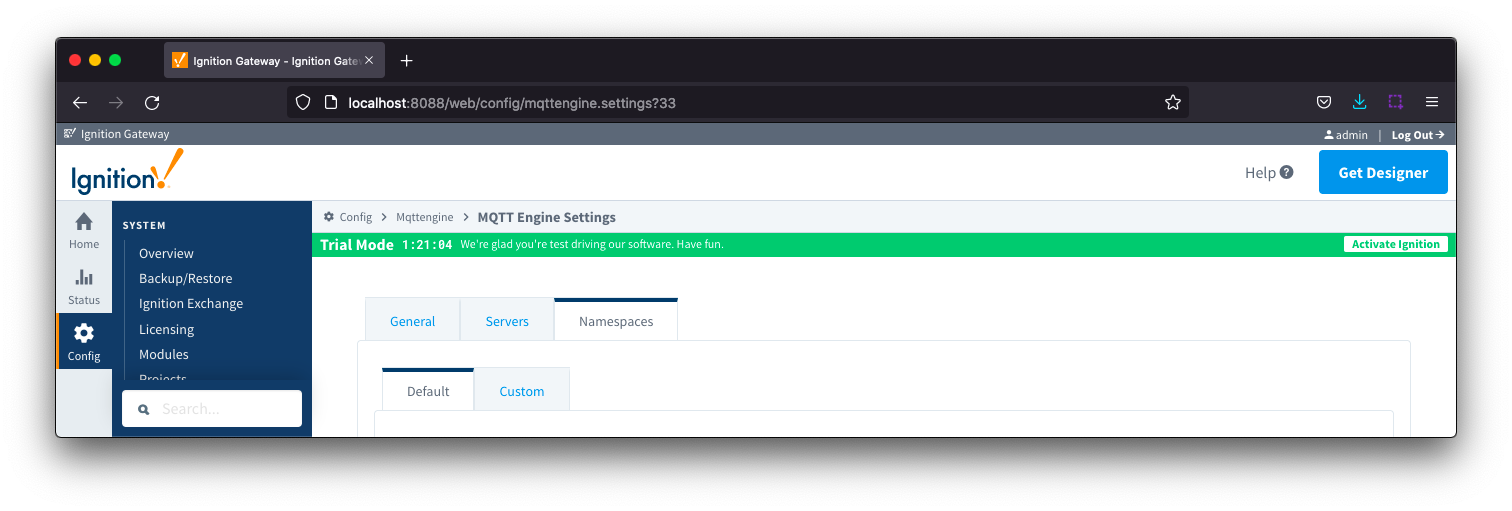
The Namespace tab has two parts - Default and Custom.
Namespaces Default
Default namespaces are provided out of the box and can simply be enabled or disabled. When MQTT Engine is first installed, all default namespaces are enabled.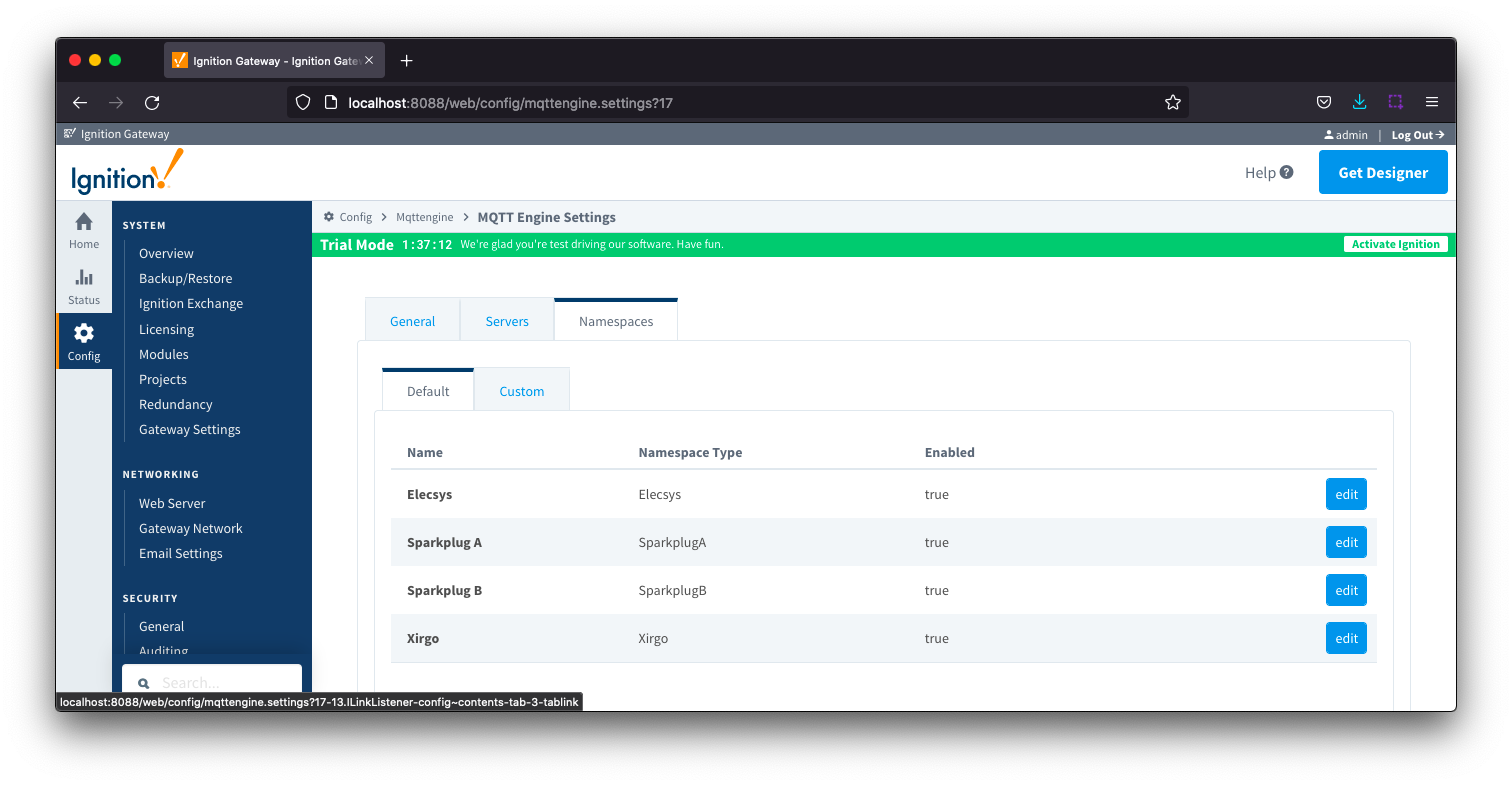
The Default tab has two parts - General and Filters.
Namespaces Default - General
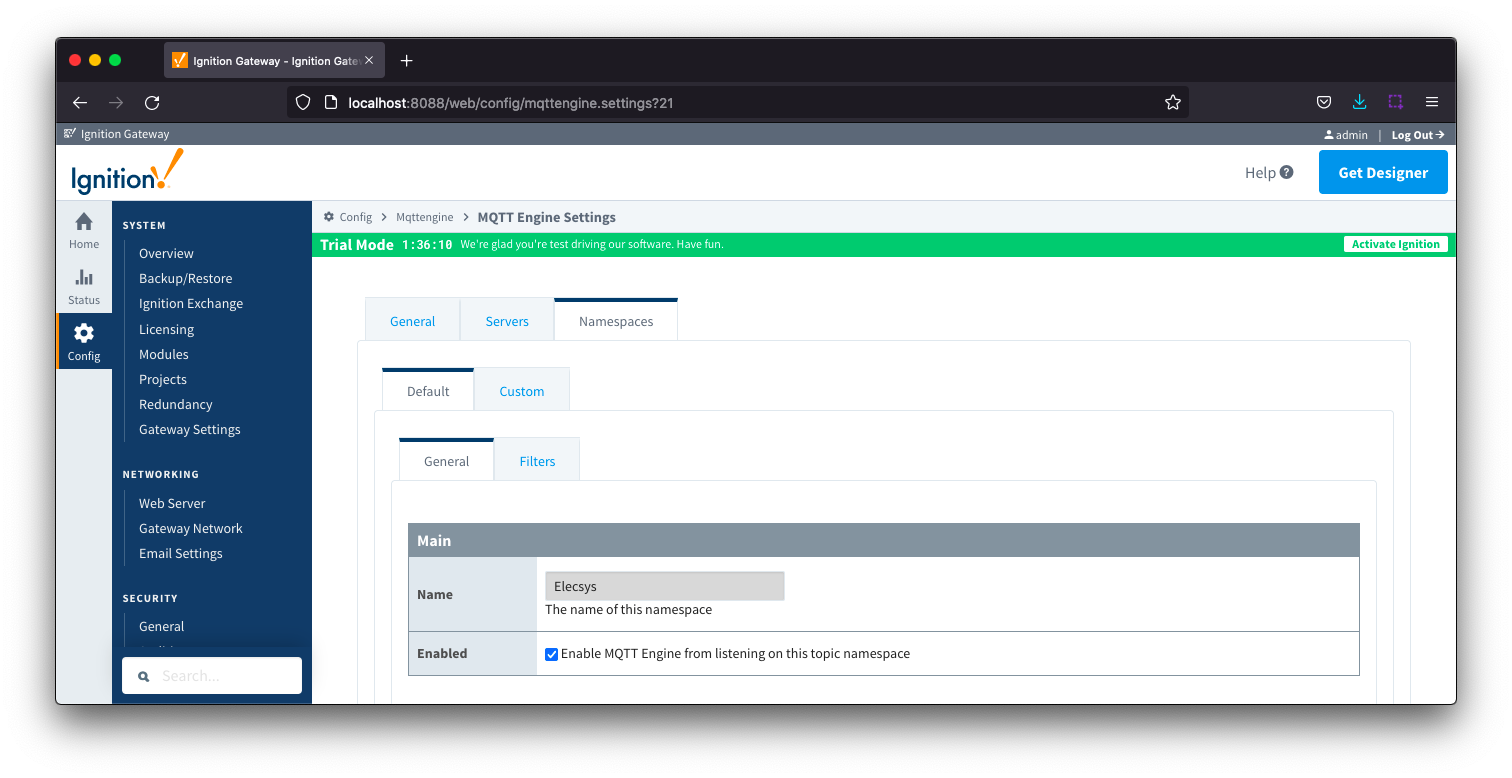
- Name
- A friendly name of the namespace to easily identify it.
- Enabled
- Whether or not the namespace is enabled. This is true by default.
- If enabled, MQTT Engine will subscribe to the topics necessary to provide support for devices and data associated with that namespace. If disabled, MQTT Engine will unsubscribe from those topics and no longer support the devices and data associated with that namespace.
Namespaces Default - Filters
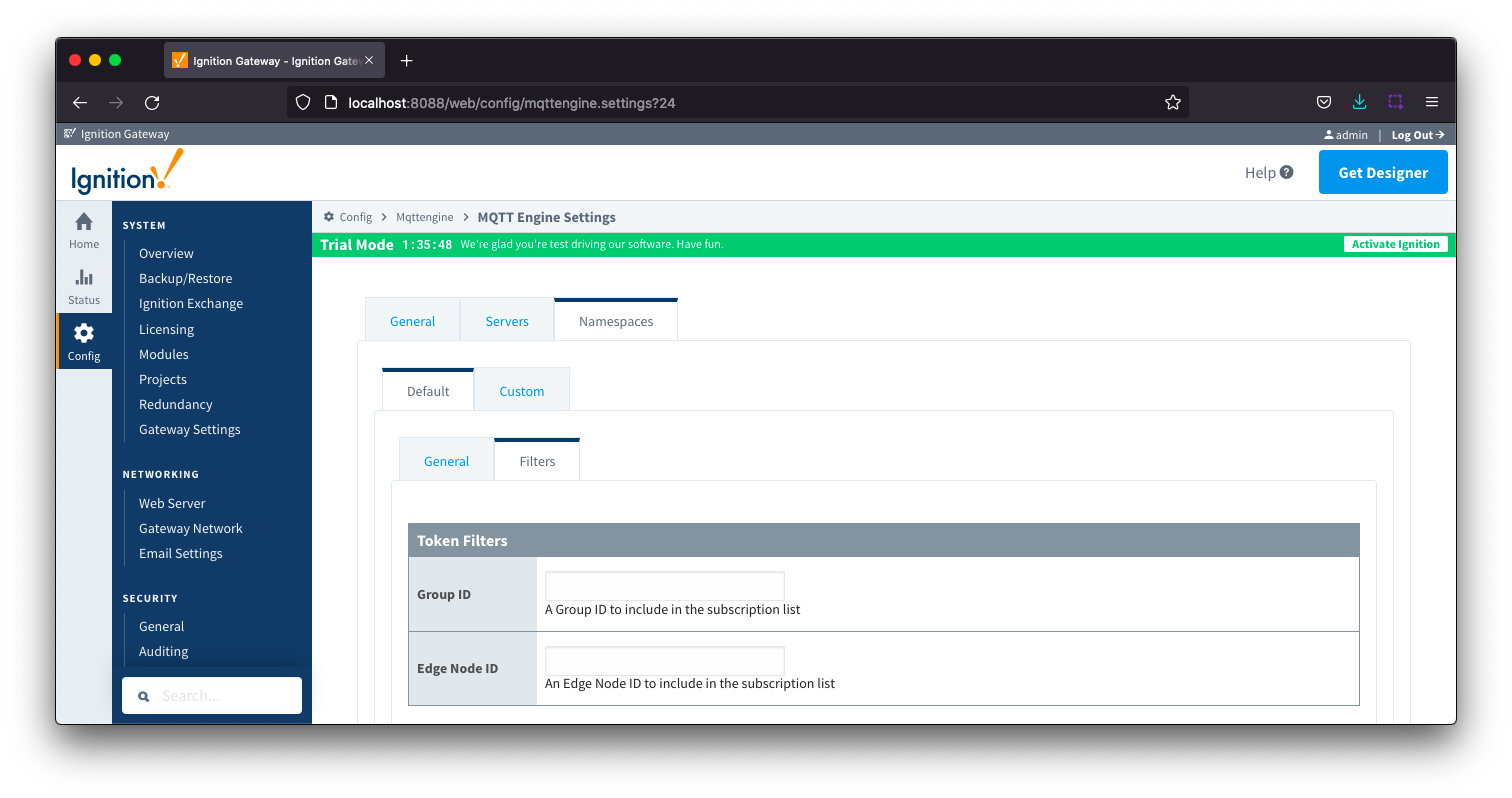
- Group ID
- Edge Node ID
- Edge Node ID to be filtered
Additional detail on the default namespaces is available here.
Namespaces Custom
Custom namespaces are used to provide support for generic MQTT messages with string based payloads. If a custom namespace is configured MQTT Engine will convert all messages received to tags. The topic of each message will directly translate into the tag's path. The payload of the message will be that tag's value. 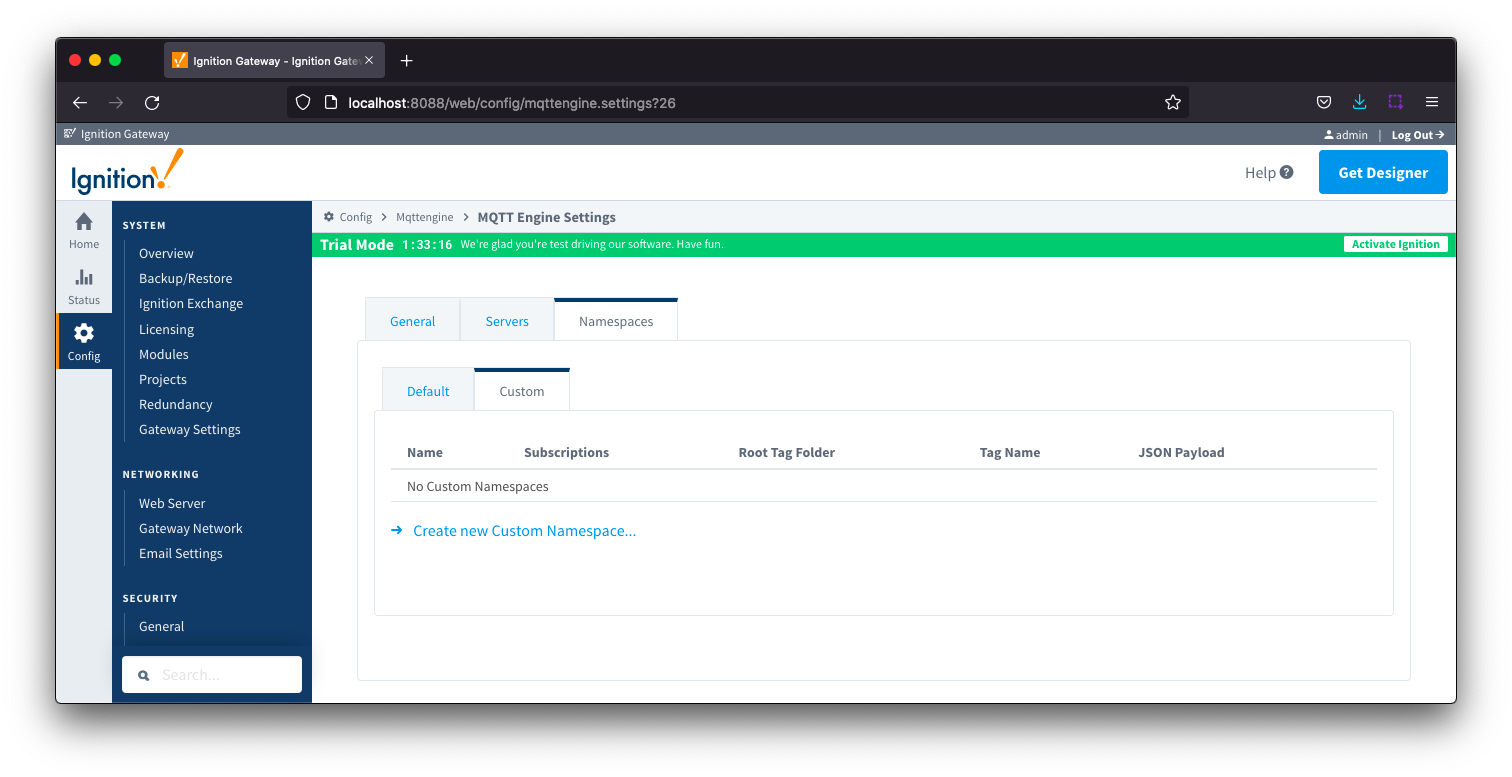
The configuration sections available are Main, Optional and Advanced.
Namespaces Custom - Main
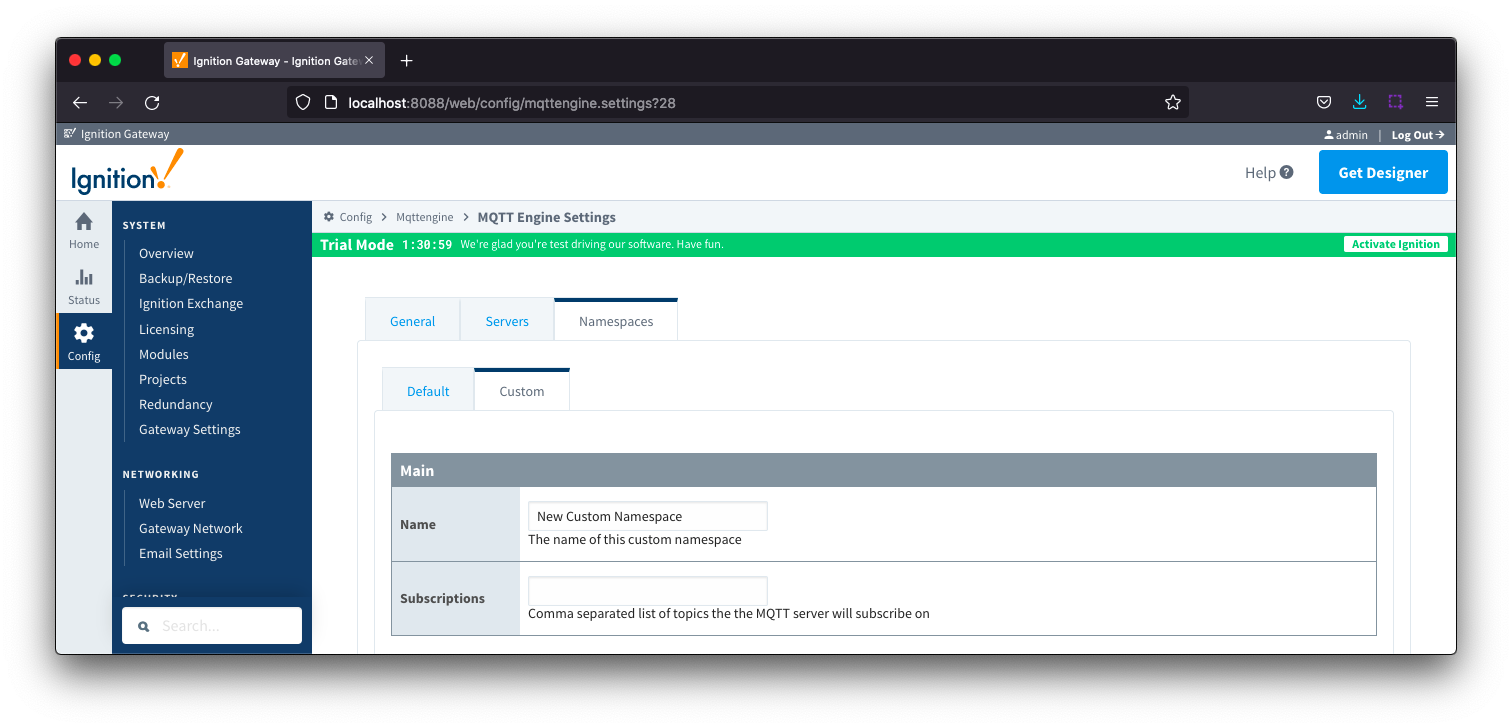
- Name
- A friendly name of the namespace to easily identify it.
- Subscriptions
- A comma separated list of subscriptions.
Namespaces Custom - Optional
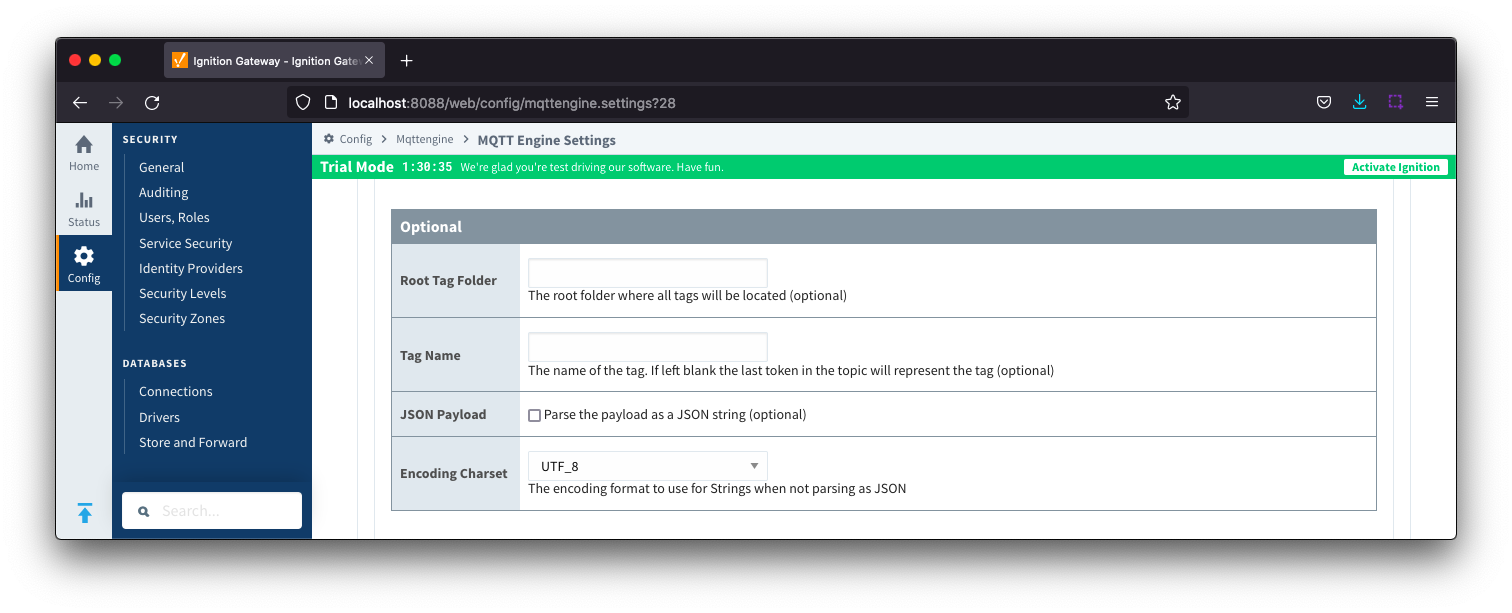
- Root Tag Folder
- A name of a folder where all tags will be stored. If configured, this folder will be the base folder where all tag paths will start.
- Tag Name
- A tag name to be used for all tags. If not configured, the last token in the topic will represent the tag.
- JSON Payload
- Optional flag to indicate that the content of the string based payload is a JSON object.
- Encoding Charset
- The encoding format to use when not parsing as JSON.
Namespaces Custom - Advanced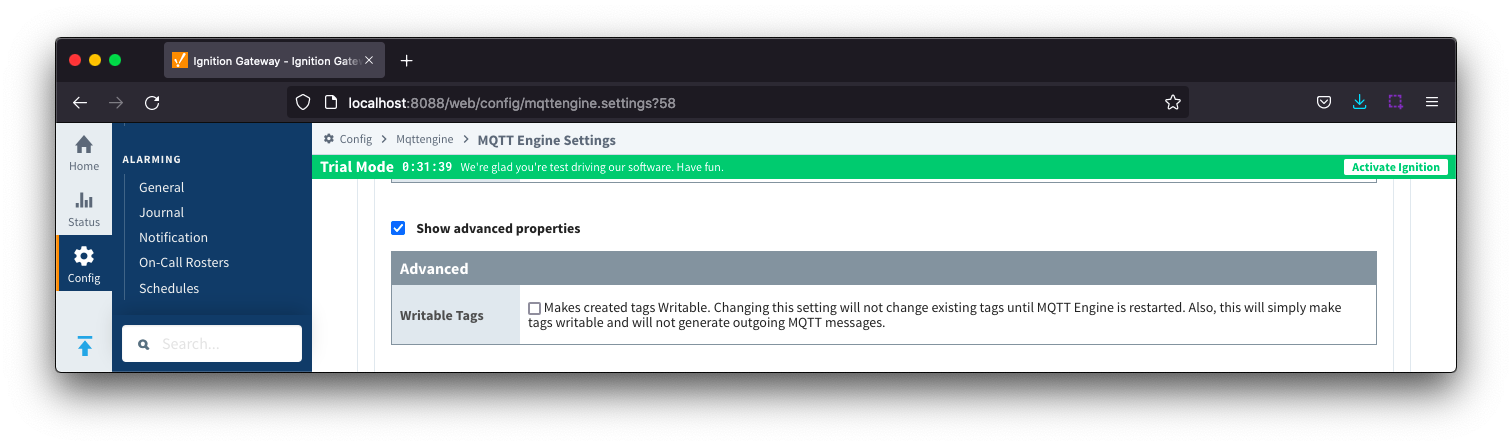
- Writable Tags
- Enables writes on tags created by the Custom Namespace. Note: This will only make the tags writable; it will not result in outgoing MQTT messages.
Please read the MQTT Engine Custom Namespace tutorial for more information.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()