![]()
Prerequisites
Before being able to install and set up the Chariot MQTT Server you must have an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account. If you do not already have one you can create one here.
Summary
This process covers installing the Chariot MQTT Server into an AWS account as an EC2 instance. For reference, the Chariot MQTT Server Cloud Formation Template used to build the AWS infrastructure is here - chariot.yaml. Note this yaml file is here purely for reference to show exactly what is done during the cloud formation deployment. You do not need to manually deploy using the chariot.yaml file as this happens automatically when you deploy Chariot via the AWS Marketplace.
When you deploy Chariot through AWS Marketplace your license will be installed and activated.
Chariot Installation on AWS via Marketplace
Before deploying Chariot you must create create an AWS EC2 key pair which will ultimately allow you to SSH into the EC2 instance that gets created as part of the process. Information on how to create the key pair can be found here. The key pair must be created in the AWS Region that you intend to deploy Chariot into.
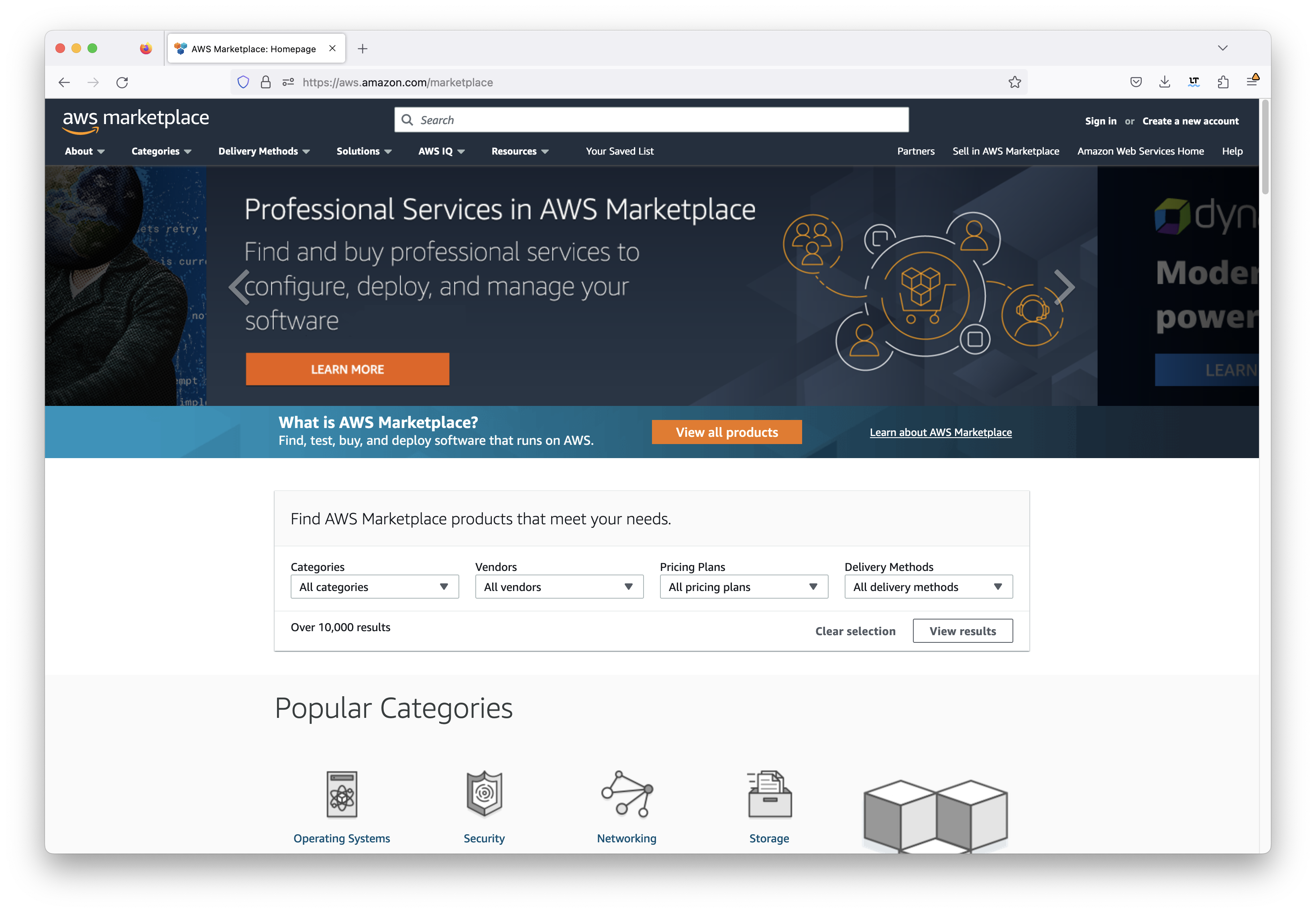
Chariot is installed using the AWS Marketplace 1-click procedure. Begin by browsing to this site: https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace. Log in using your AWS account credentials. After doing so, you will see something similar to what is shown below.
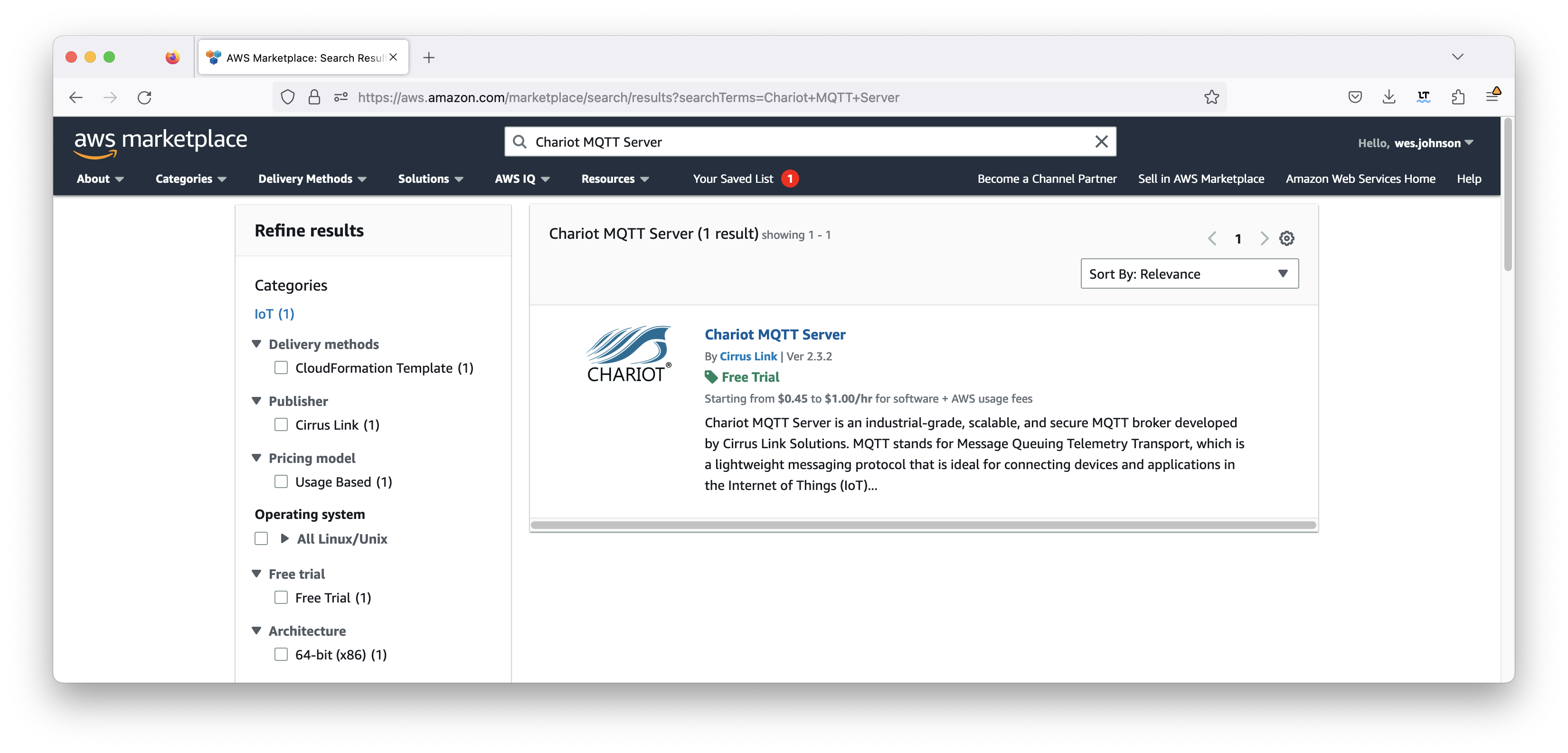
In the search bar, type in 'Chariot MQTT Server' and hit enter. This should show the following.
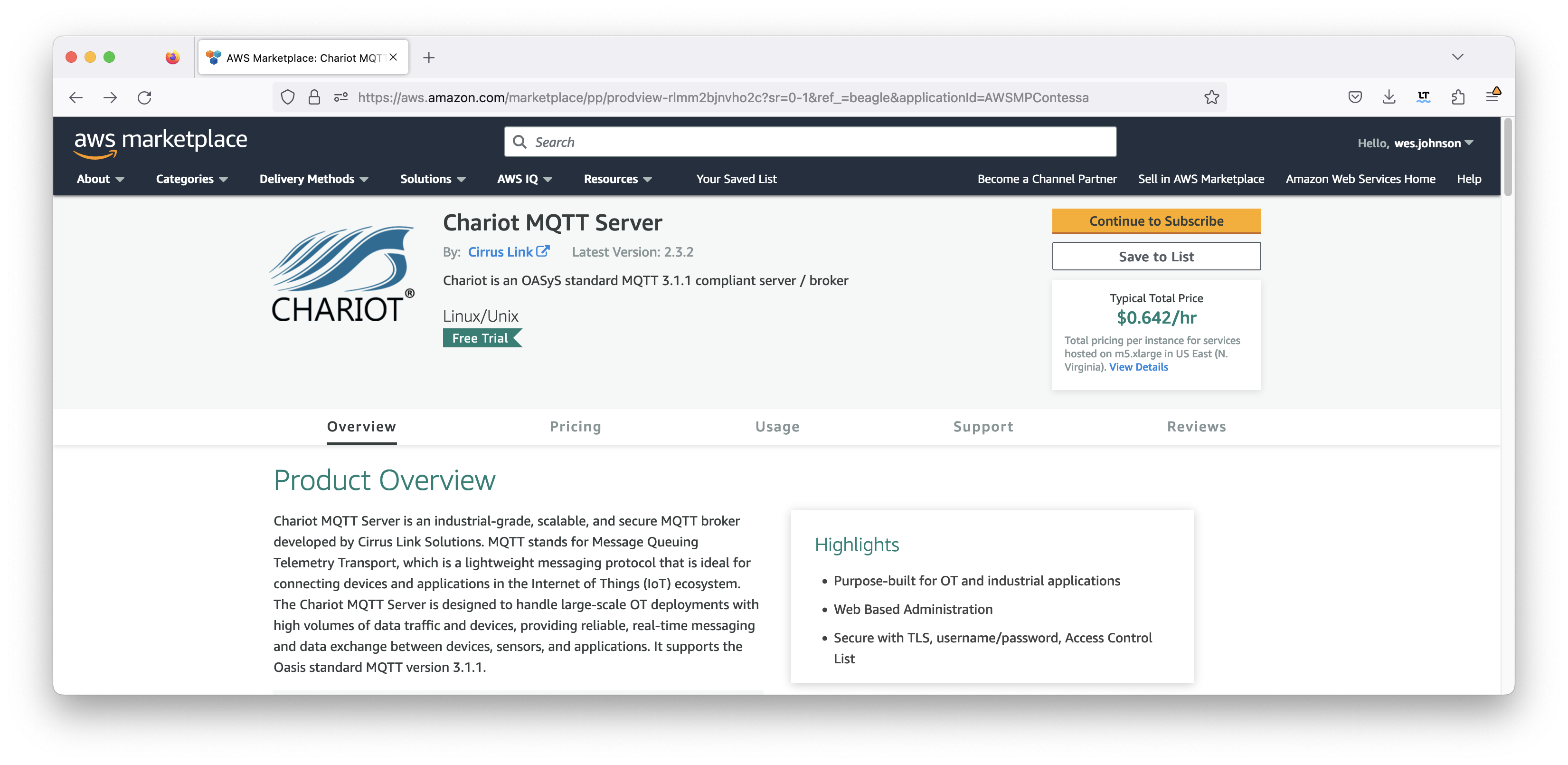
Then click on Chariot MQTT Server by Cirrus Link. After doing so, you should see the following.
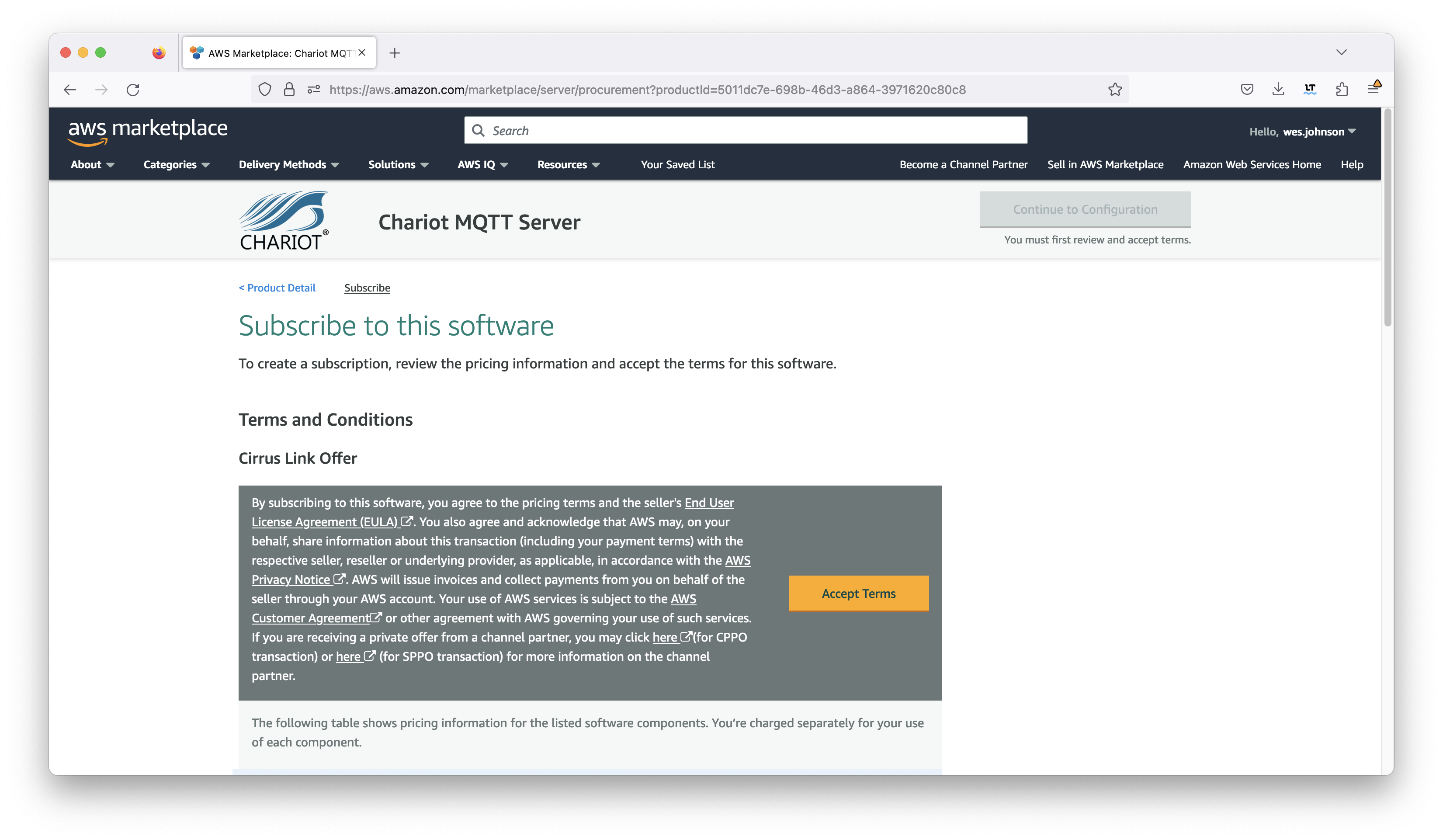
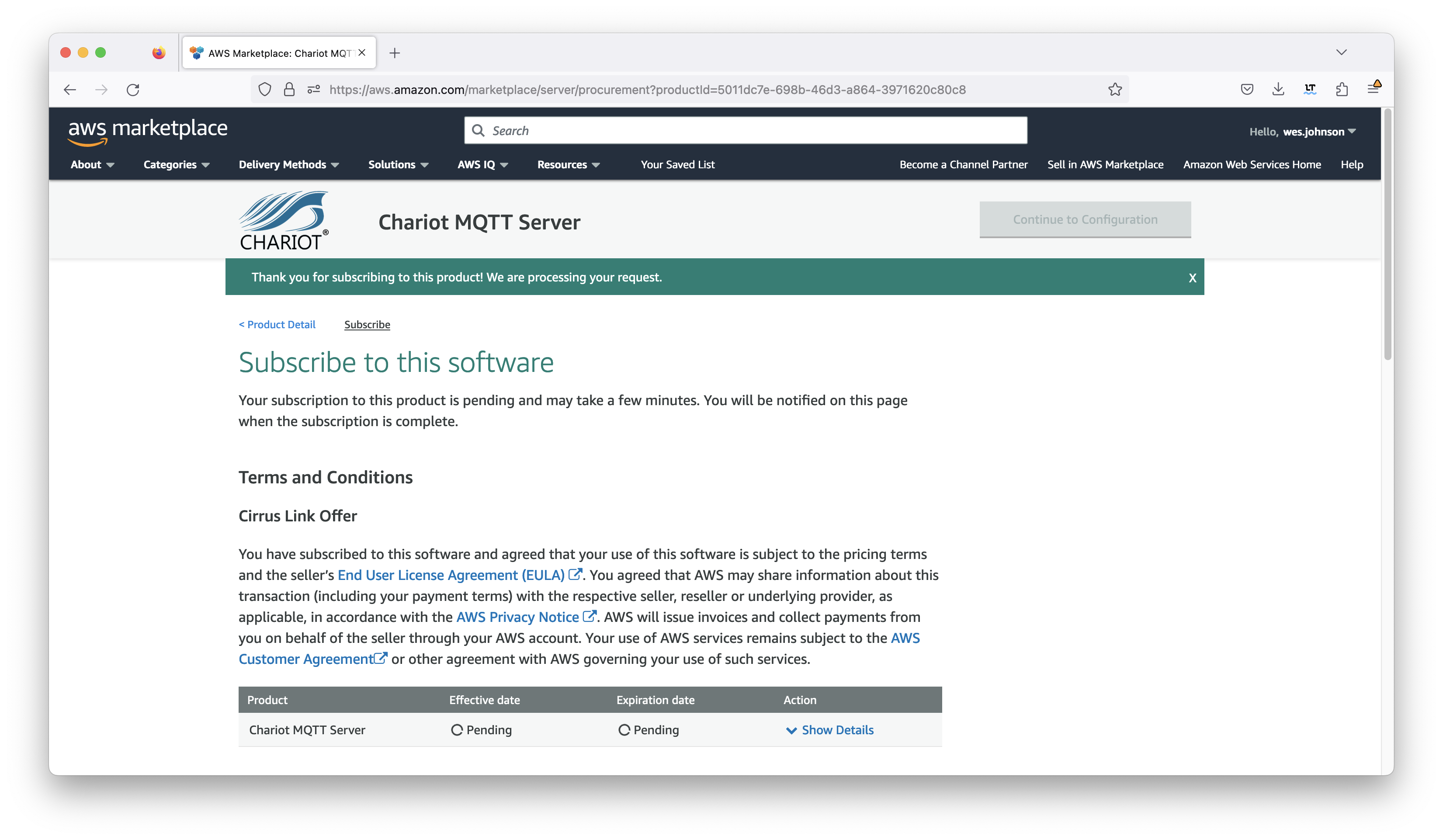
Click the yellow 'Continue to Subscribe' button near the top of the screen. This will bring up the following page:
Now click the orange 'Accept Terms' button if you agree to the terms. This will bring up the following screen.
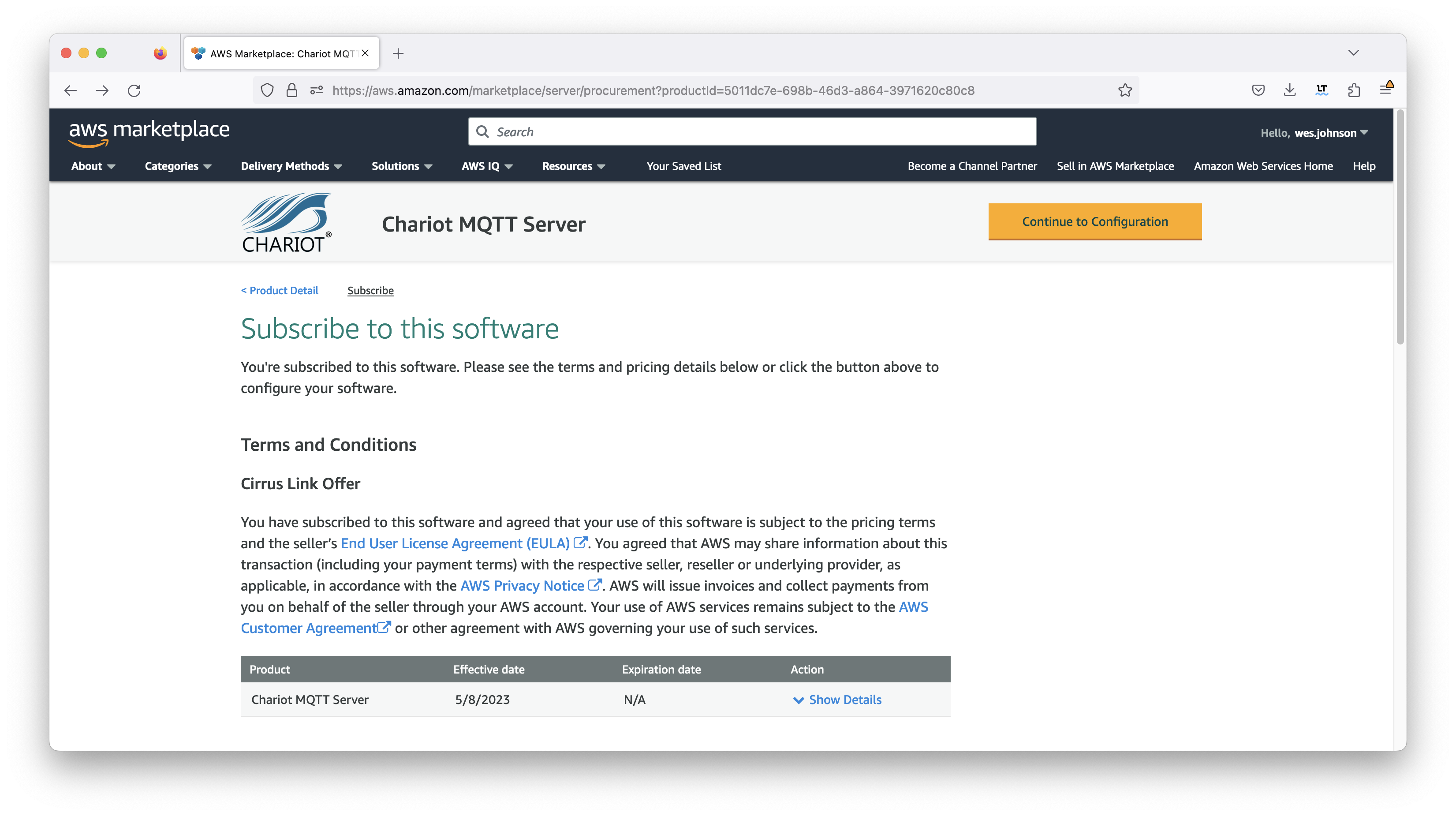
It will take some time and within a few minutes the effective date and expiration date should get set. Once this is done, click the orange 'Continue to Configuration' button in the upper right section of the screen as shown below.
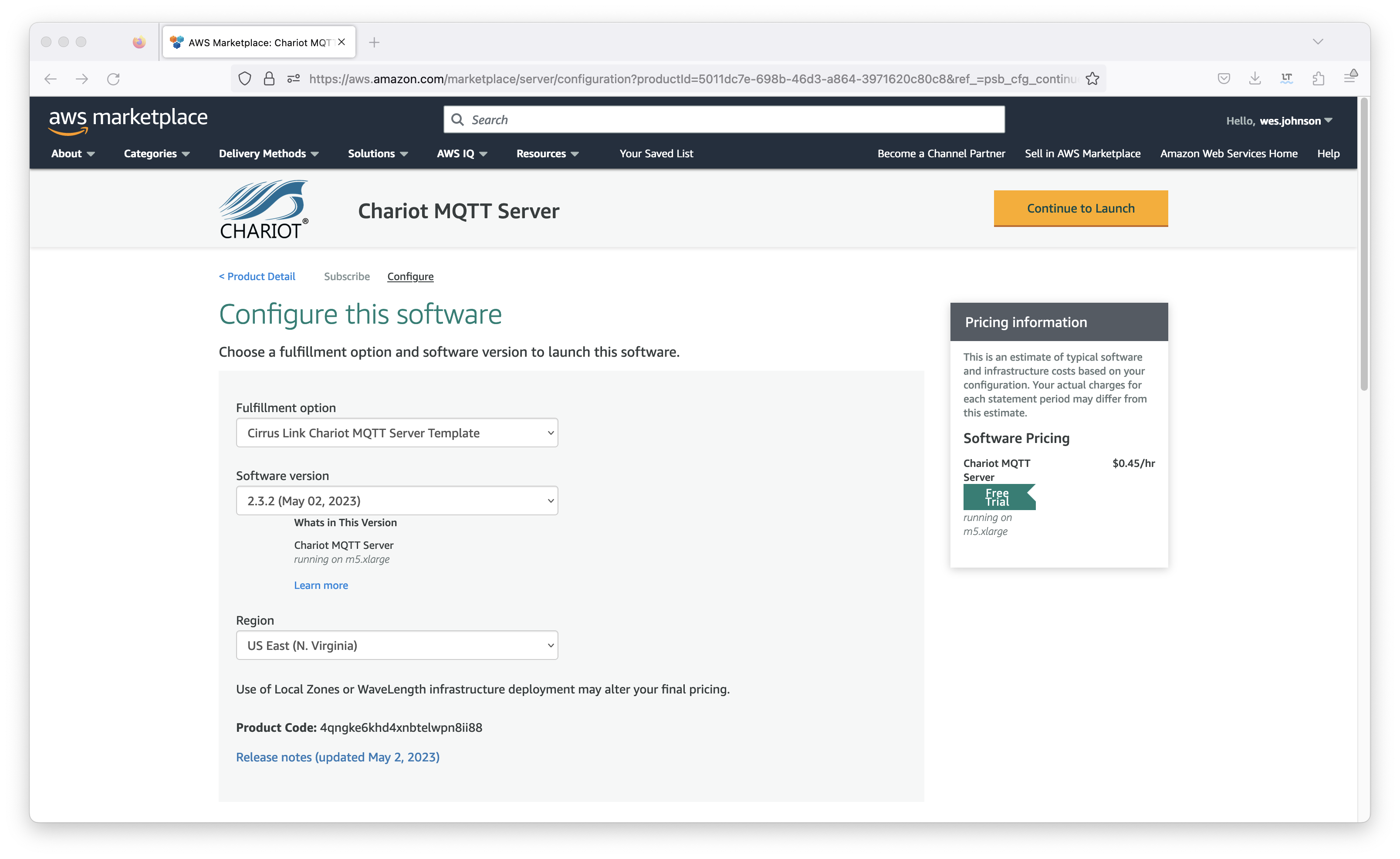
Now in the 'Fulfillment option' field, select 'CloudFormation Template' as shown below. This will set up the defaults including the 'Chariot MQTT Server Template' field, the version, and the region. Select your preference for the region also as shown below.
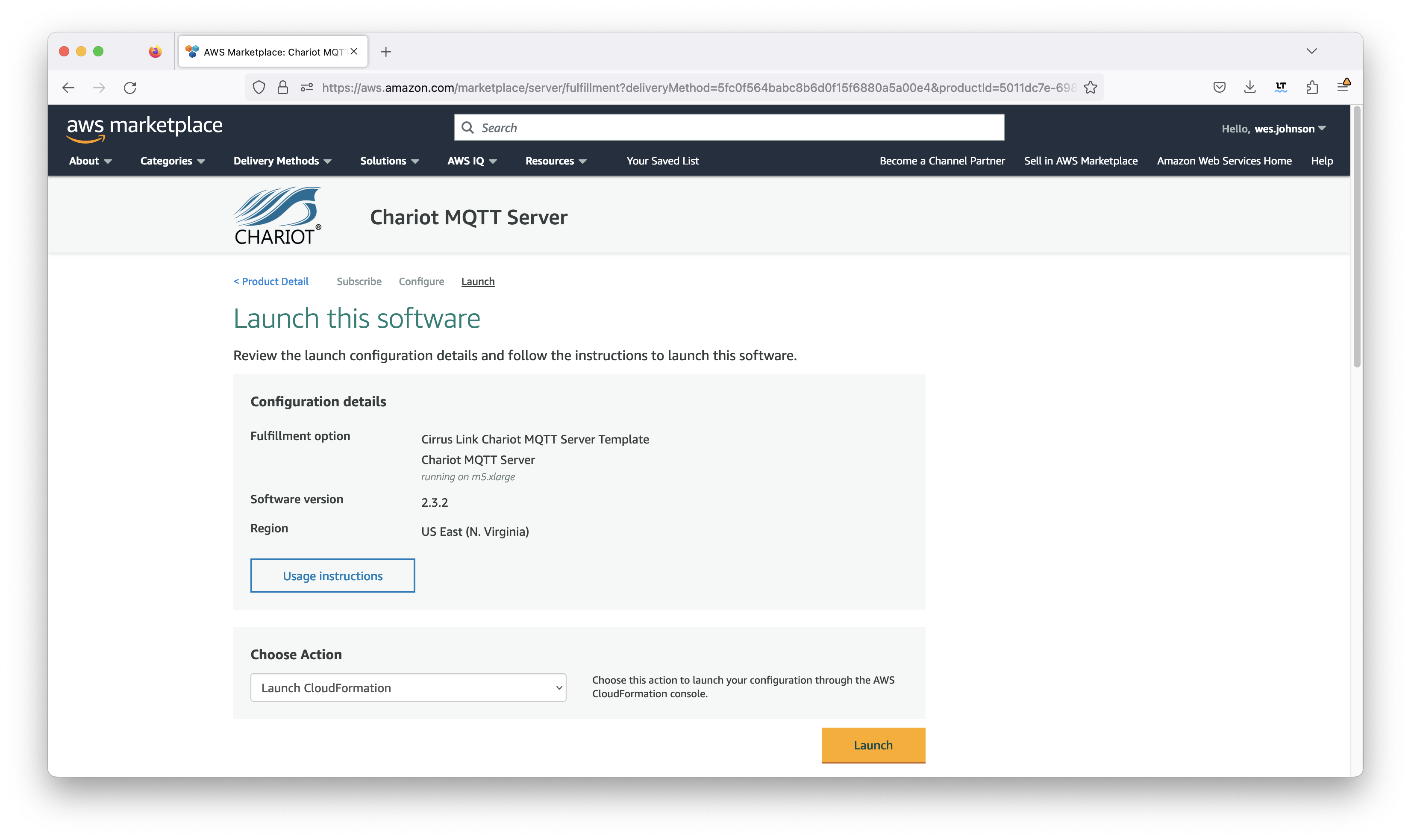
Now click the orange 'Continue to Launch' button in the upper right corner. This will bring up the following screen.
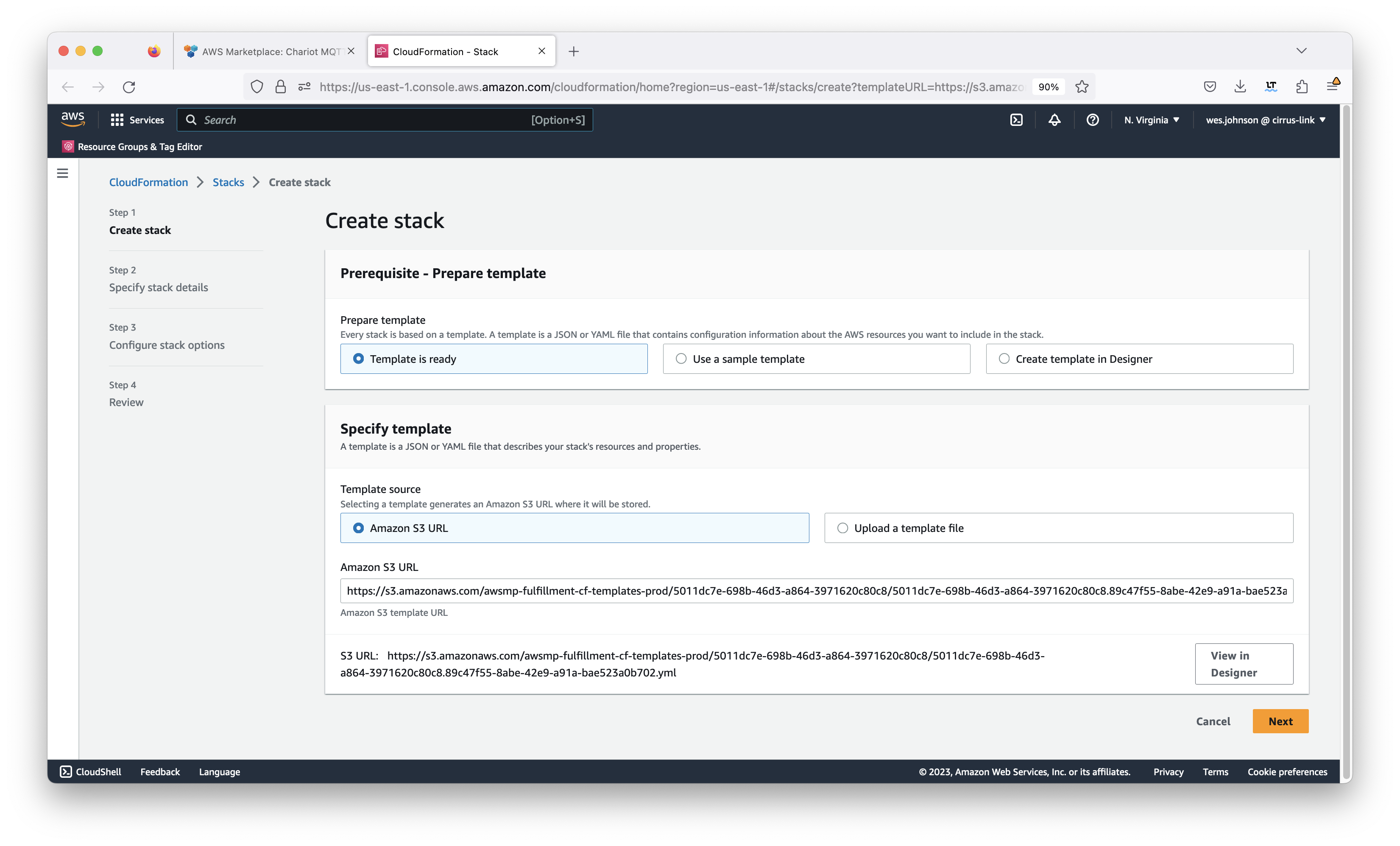
Finally, click the orange 'Launch' button shown in the screenshot above. This will bring up the CloudFormation stack creation page shown below. Note the template associated with the Chariot MQTT Server is automatically populated for you. This is also shown below.
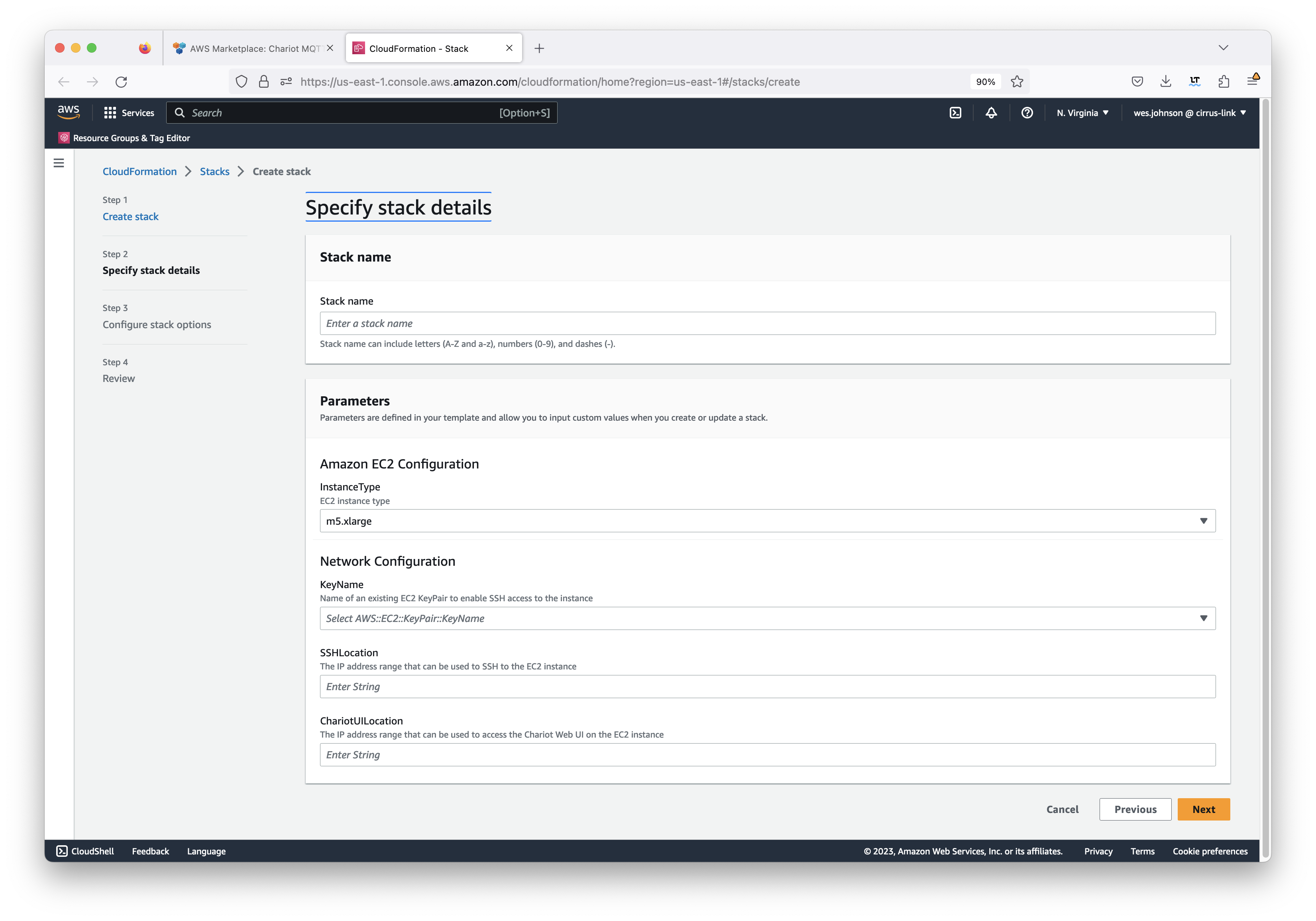
Click 'Next' in the lower right in the screen capture above. This will bring up the stack configuration page shown below.
Set the following properties for the stack:
- Stack Name
- This is a friendly name that will allow you to easily identify the stack in your AWS account
- Instance Type
- The instance size to use for the deployment. Note the size will affect the costs associated with your deployment.
- KeyName
- This is the EC2 keypair that you created at the beginning of this process. If you missed it, instructions to create it are here.
- SSH Location
- This is the IP address or addresses that will be whitelisted to allow SSH access to the EC2 instance. The example '0.0.0.0/0' will allow SSH access from anywhere. This is not recommended for production environments but will allow access from anywhere initially. This can be changed later as well. A more secure option would be to use your IP address. For example, '47.123.53.23/32' would be used if your IP address is '47.123.53.23'.
- Chariot UI Location
- This is the IP address or addresses that will be whitelisted to allow HTTP access to the EC2 instance. The example '0.0.0.0/0' will allow access from anywhere. This is not recommended for production environments but will allow access from anywhere initially. This can be changed later as well. A more secure option would be to use your IP address. For example, '47.123.53.23/32' would be used if your IP address is '47.123.53.23'.
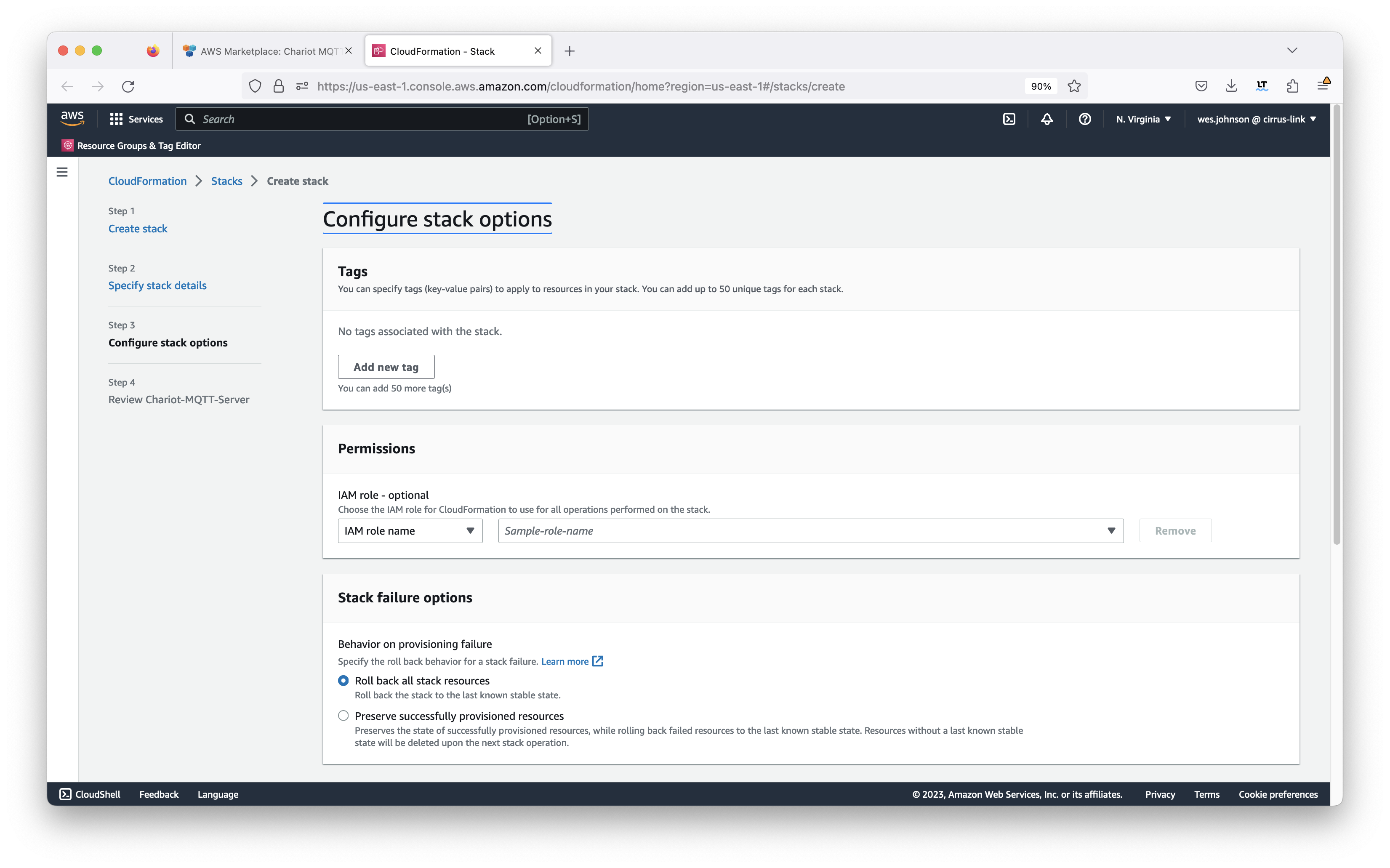
After setting the properties, click the 'Next' button in the lower right of the Window. This will bring up the following screen.
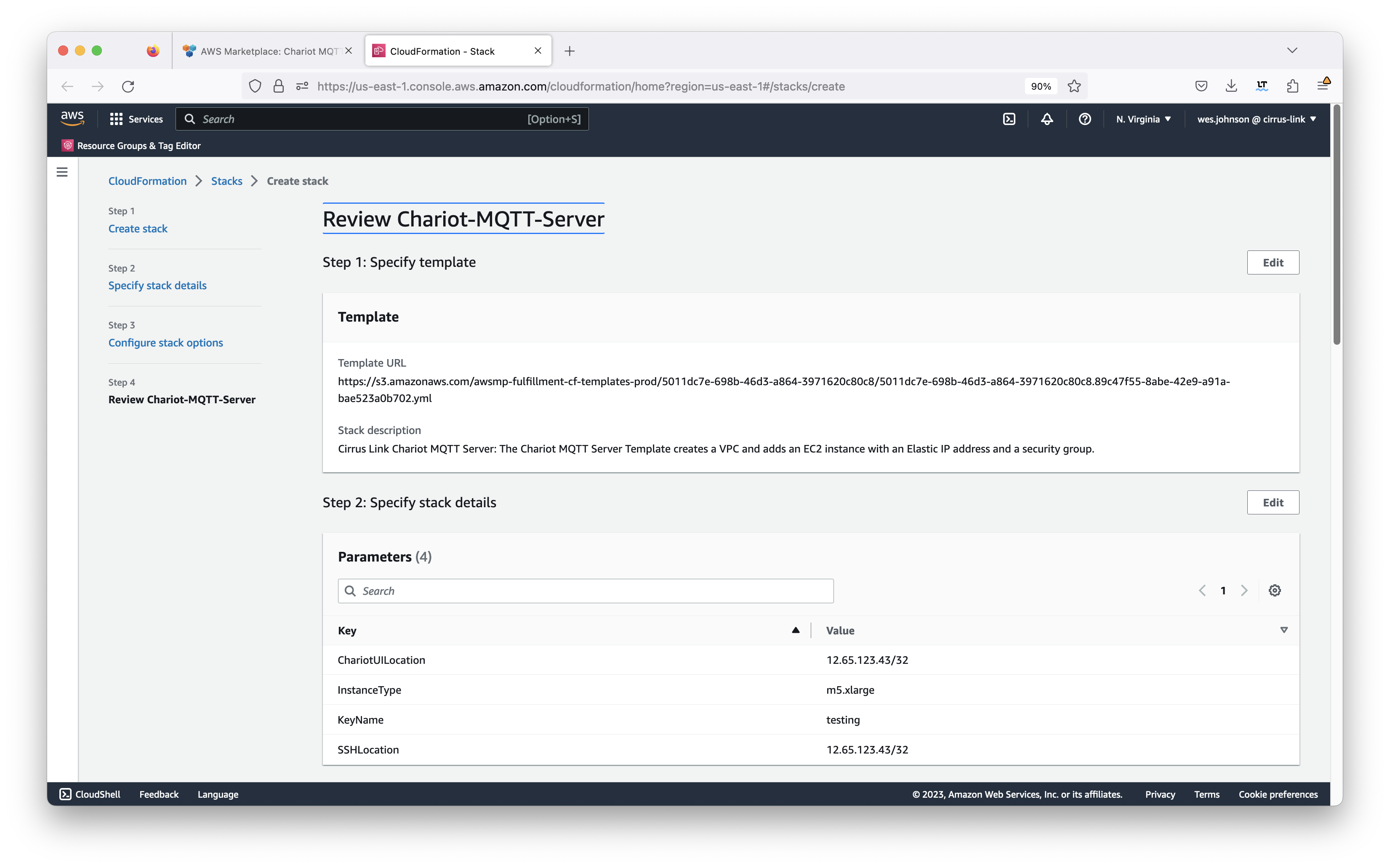
Configure anything else that may be required here. Generally, nothing must be set here given that the user you are logged in as has the permissions to create everything that will created as part of the Cloud Formation deployment. Also, the 'Roll back all stack resources' should be selected in case there is a failure in deployment. This will ensure no resources get created and left in place should any portion of the stack creation fail. After setting any additional configuration here, click the 'Next' button in the lower right corner. This will bring up the review screen as shown below.
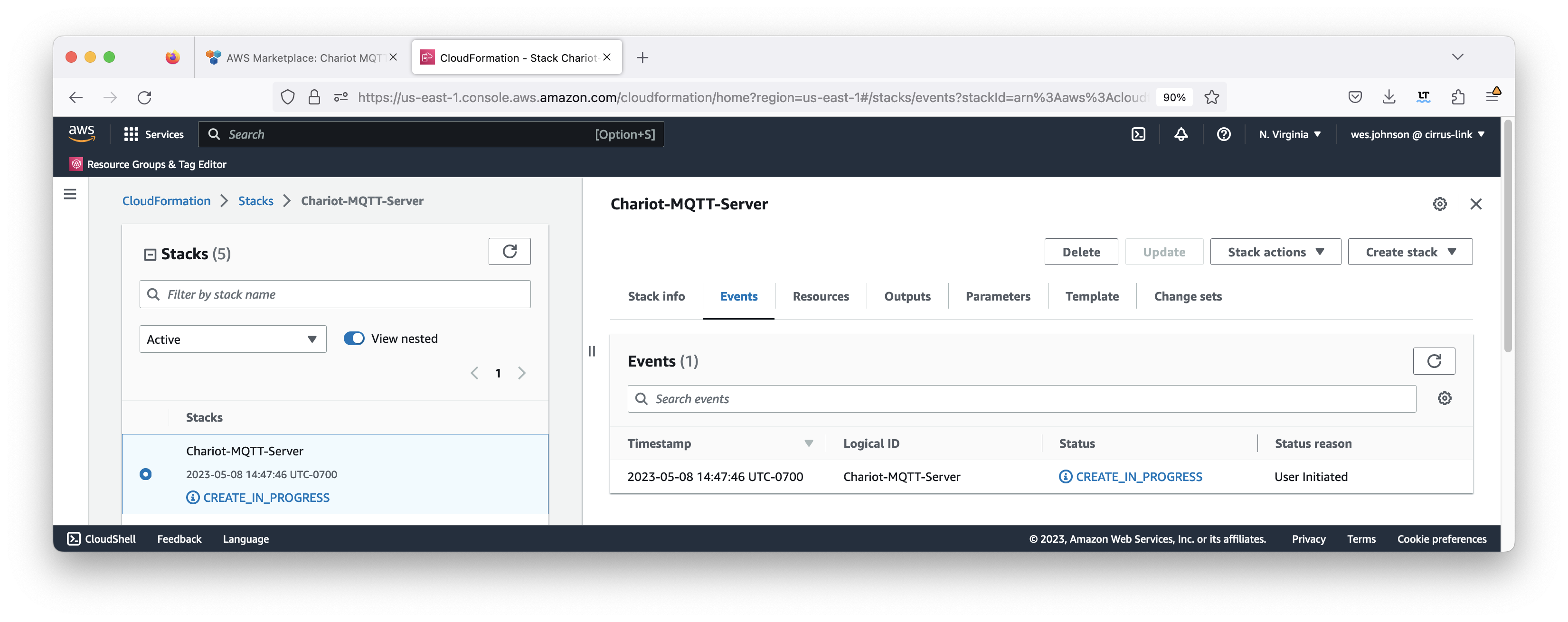
Double-check the configuration and finally click 'Submit' in the bottom right corner of the screen to kick off the stack creation. You should now see the 'CREATE_IN_PROGRESS' status as shown below.
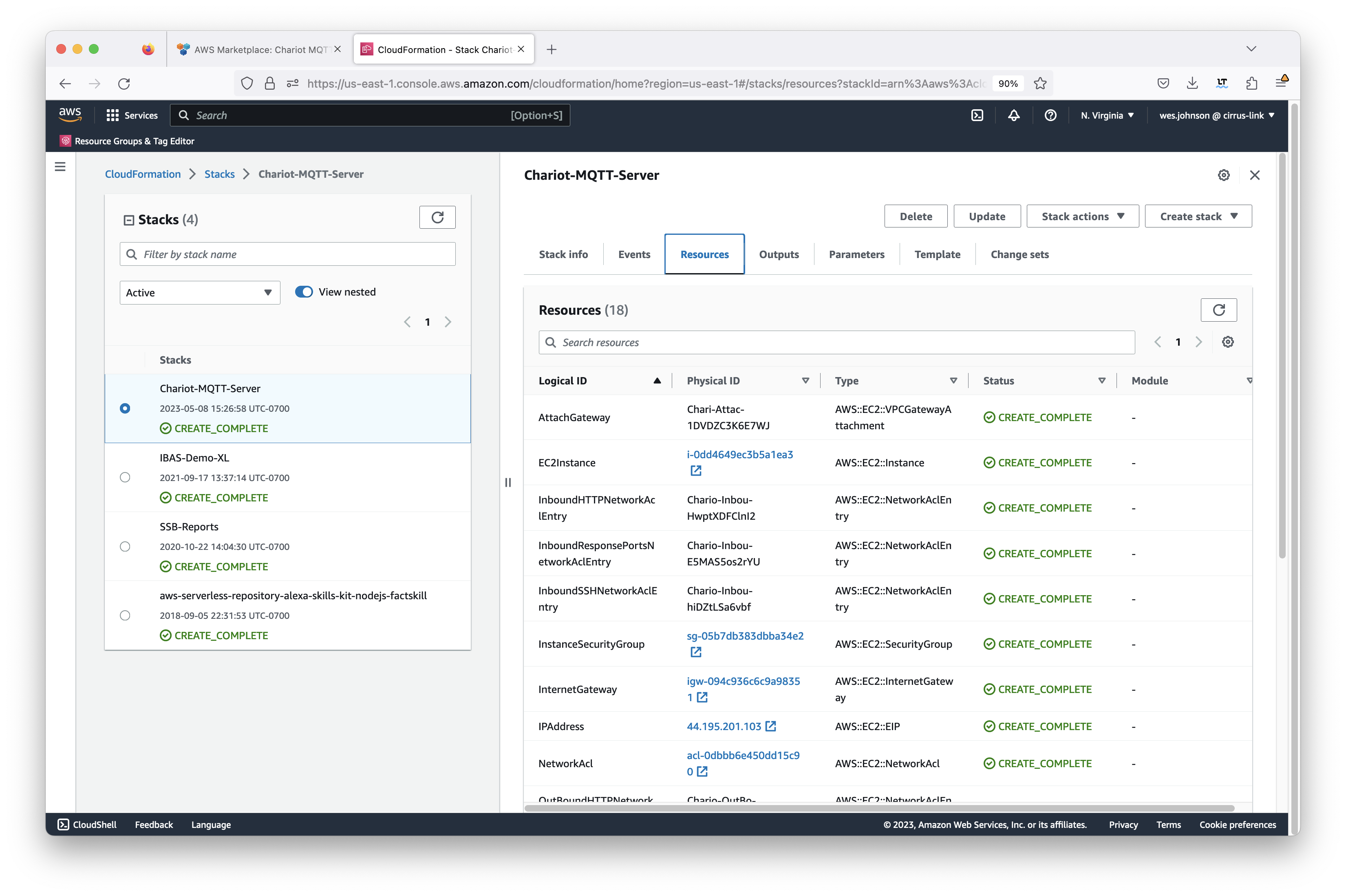
This will begin the stack deployment. You can check on the progress by clicking both the Events and Resources tab as shown below. Deployment takes a few minutes to complete. When it completes, you should see something similar to what is shown below with all of the resources showing 'CREATE_COMPLETE' for the status.
Deployments can fail for multiple reasons, including AWS account resource limitations. By clicking the 'Events' page, you can see more information about what failed during deployment.
If this happens during deployment, note the 'Status reason' column on the right side of the events tab. Typically, the following steps are necessary to resolve the issue.
- Delete the stack using the 'Delete' button at the top of the stack's page
- Resolve the issue resulting in the failure. Often these are AWS account resource limits. If so, request an AWS resource limit increase via an AWS support ticket.
- Repeat this procedure to deploy the stack.
After the AWS Infrastructure has been deployed via the AWS Marketplace 1-click procedure, the application must be configured. In order to configure the application, you must be able to access the Chariot MQTT Server Web UI using your web browser. Use the following URL and credentials to login into your Chariot MQTT Server Web UI:
- URL: http://<chariot-url-or-ip>:8080
- Default admin user
- username: admin
- password: your EC2 instance ID
- example: i-0049ac1e13e558b70
We recommend changing your Chariot admin password upon first login.
More information on configuring the Chariot MQTT Server can be found here.
Information on accessing the EC2 instance via SSH can be found here.
Chariot Configuration
For configuration details, please see: Chariot MQTT Server: Configuration