MQTT Transmission provides a configuration section to the Ignition Gateway and this can be seen in the left side menu bar of the Ignition Gateway web UI.
There are two configuration pages "History" and "Settings".
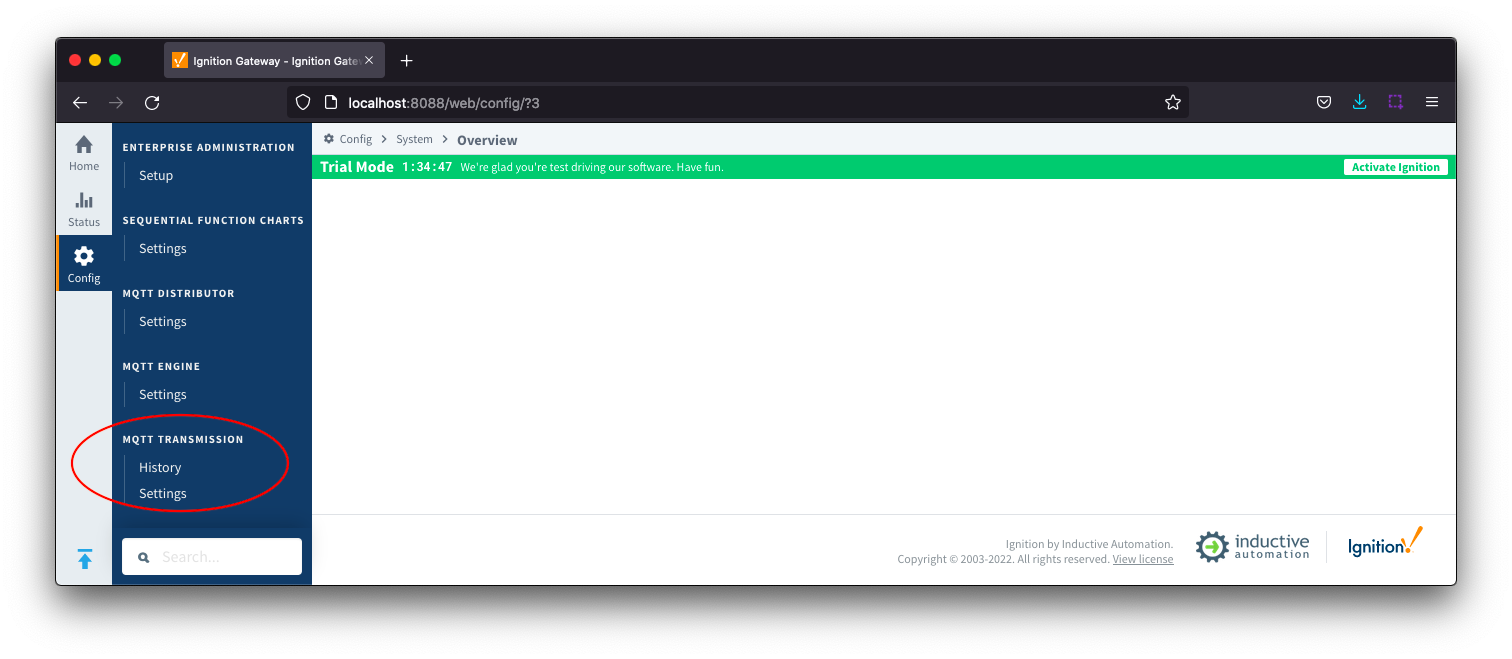
Settings
The configuration options for each of the six tabs - General, Servers, Sets, Transmitters, Records and Files - are detailed below.
General
The General Settings tab contains a single Main section.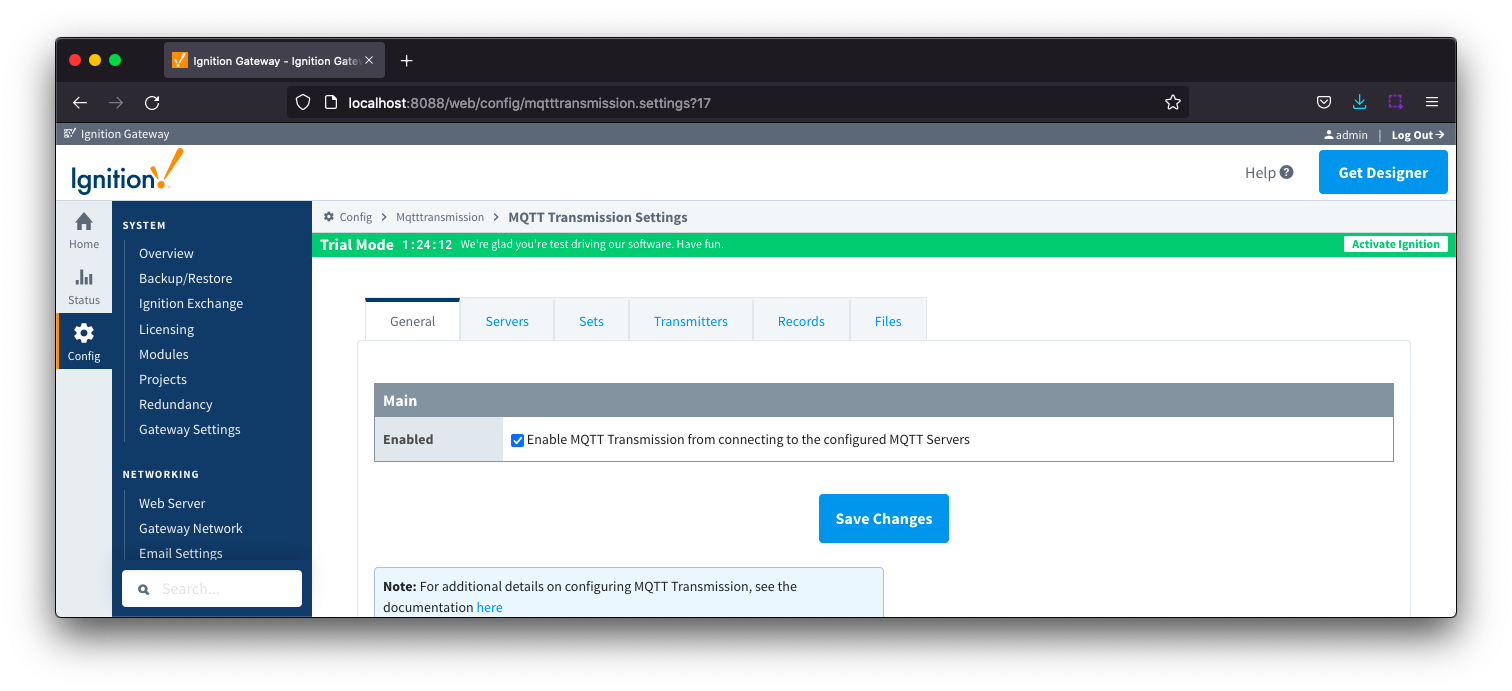
General - Main
- Enabled
- Whether or not to enable or disable MQTT Transmission from connecting to the configured MQTT Servers.
The Servers tab has two parts - Settings and Certificates
This tab provides a list of the MQTT Servers that MQTT Transmission should connect to. By default, MQTT Transmission is configured to connect to the local MQTT Distributor based MQTT Server and is set up to connect to localhost, port 1883, using the default username/password.
Additional or alternative MQTT Servers can be configured in MQTT Transmission - often times more than one will be configured to handle fail-over in redundant or geographically distributed systems. Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server' link will bring up a form for adding a new MQTT Server setting.
The 'Connected' column will show the connection status of each MQTT Client with the MQTT Server.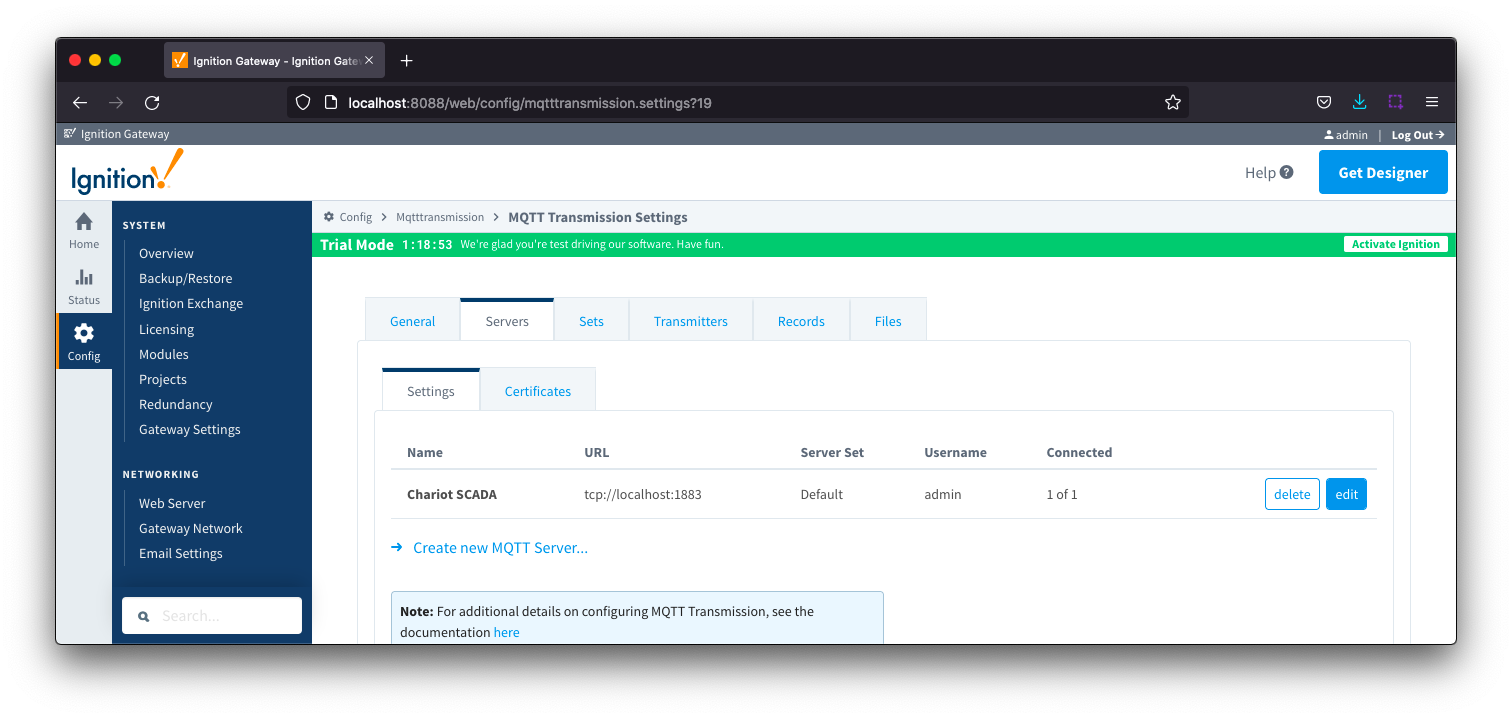
The configuration sections available are Main, TLS, and Advanced.
Server Settings - Main

- Name
- This is the friendly name of the MQTT Server used to easily identify it
- URL
- This is the URL of the MQTT server. Its format is as follows: [protocol]://[location]:[port]. Each of these are shown below
- protocol - Either tcp or ssl
- location - The server location. e.g. localhost, myserver.chariot.io, mydomain.com, etc
- port - The port the MQTT Server is listening on. Generally this is 1883 if using TCP or 8883 if using SSL
- Server Set
- The Set that this server is a member of.
- Username
- Optional MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
Change Password?
- Check box to enable changing of the optional password
- Password
- Optional MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
Server Settings - TLS
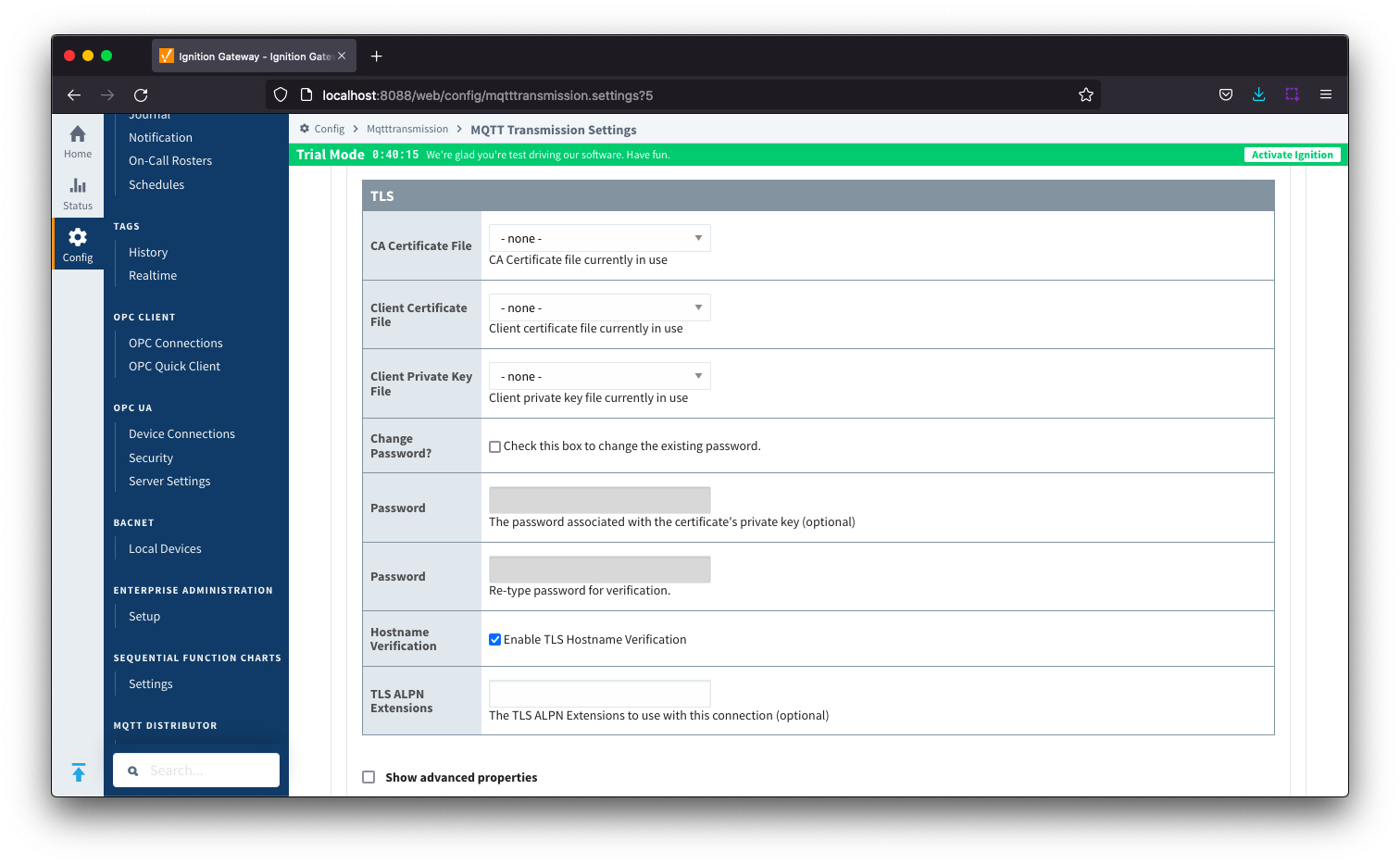
See this document for TLS configuration: Configuring Secure MQTT Communication
- CA Certification File
- CA Certification file currently in use.
- Client Certification File
- Client Certification file currently in use.
- Client Private Key File
- Client Private Key file currently in use
- Change Password?
- Check box to enable changing of the optional password.
- Password
- Optional password associated with the certificate's private key.
- Hostname Verification
- Enable TLS Hostname Verification. This is true by default.
- TLS ALPN Extensions
- Optional TLS ALPN Extensions to use with this connection
Server Settings - Advanced
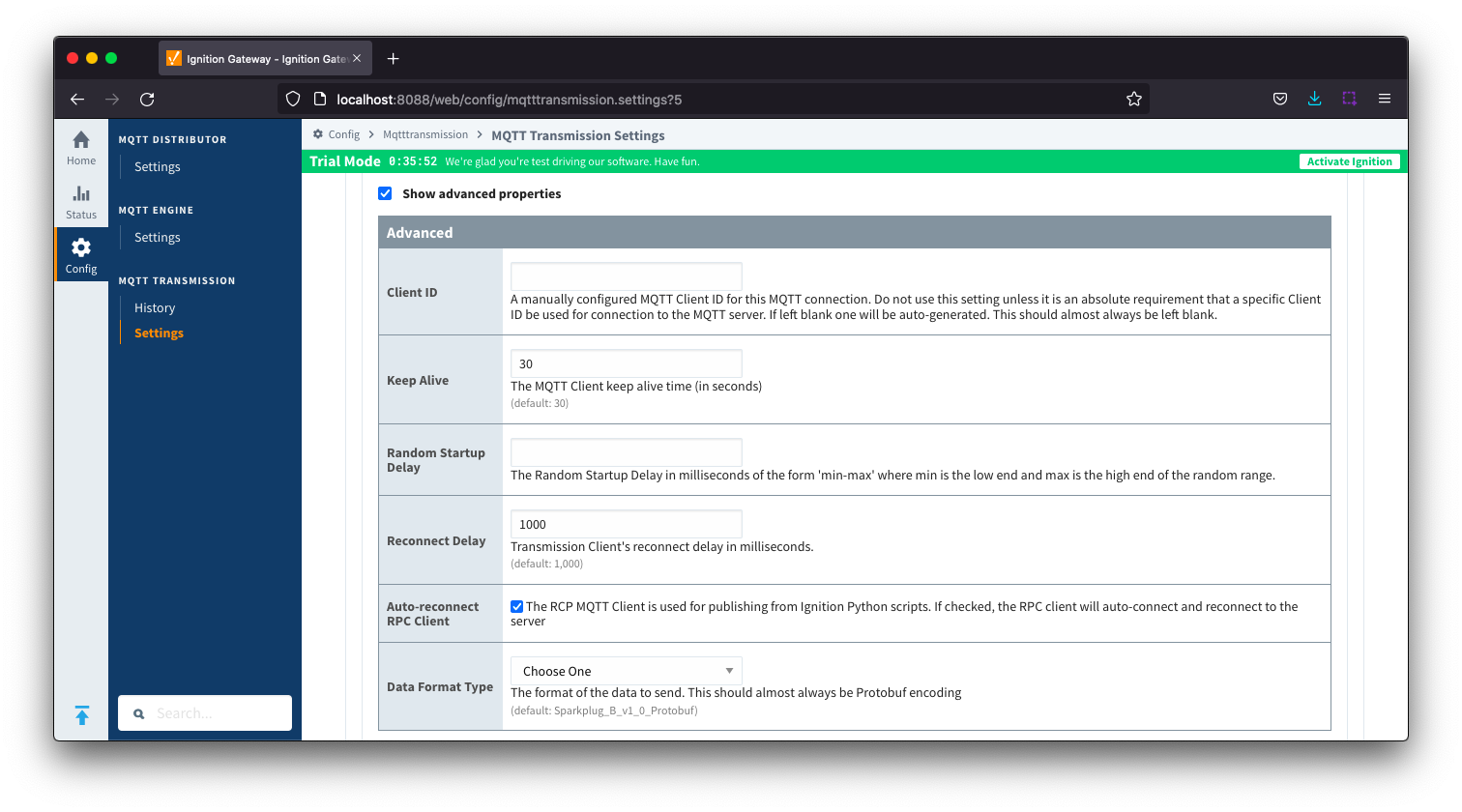
- Client ID
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT client keep alive time (in seconds).
- Random Startup Delay
- The Random Startup Delay in milliseconds of the form 'min-max' where min is the low end and max is the high end of the random range. e.g. '10-1000'.
- Reconnect Delay
- The clients reconnect delay in millisecond.
- Auto-reconnect RPC Client
- Allow the RPC Client to auto connect and reconnect when publishing from Ignition Python scripts.
- Data Format Type
- The format of the data to send. Default is Sparkplug_B_v1_0_Protobuf with JSON as an option.
Servers - Certificates
This tab provides a list of the certificate or private key files if loaded and available for TLS configuration.
The Certificates tab contains a single Main section.
Server Certificates - Main
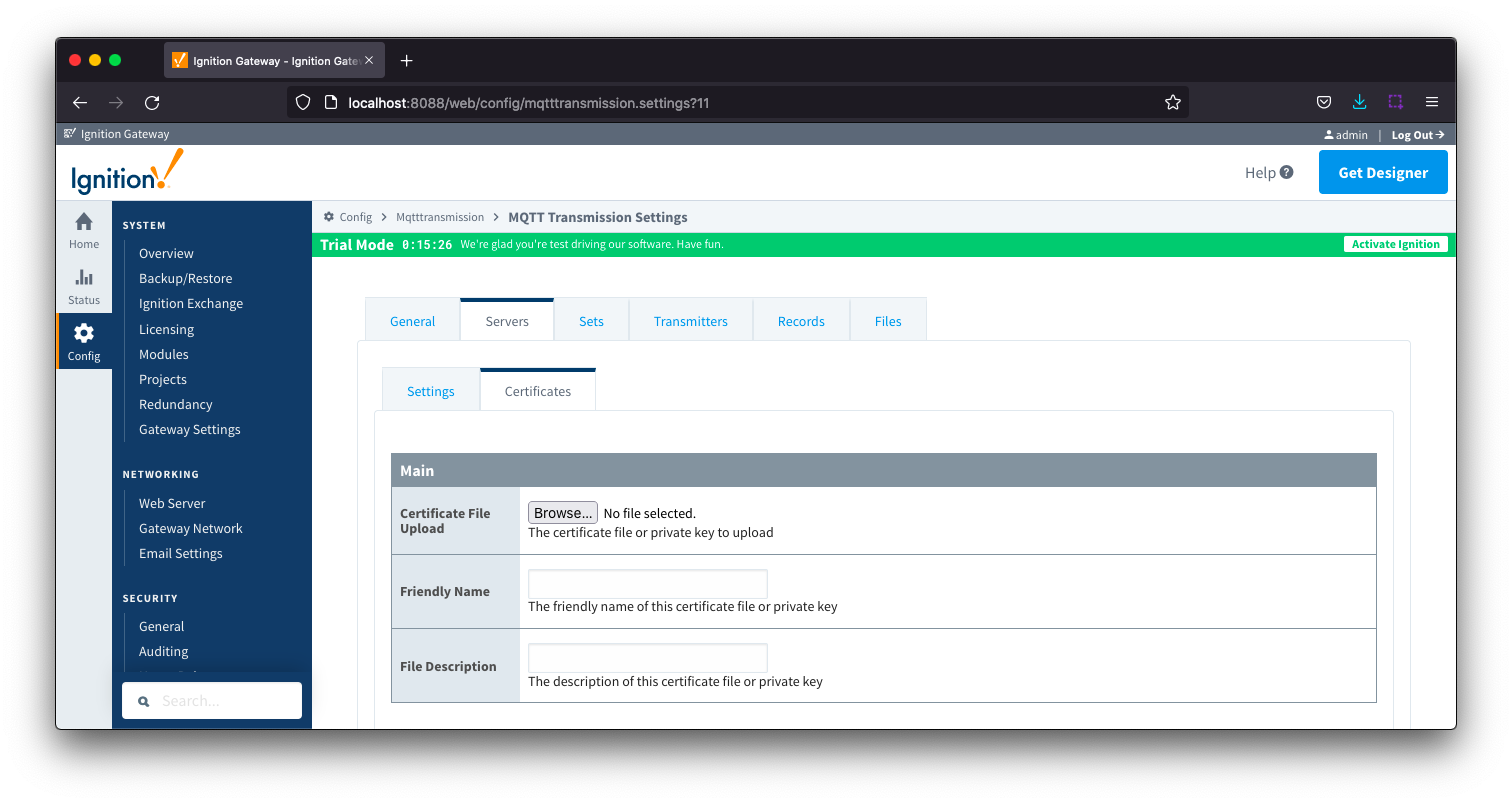
- Certificate File Upload
- Browse to the certificate file or private key to upload.
- Friendly Name
- The friendly name of the certificate file or private key.
- File Description
- The description of the certificate file or private key.
Sets
The Sets tab contains a list of server sets. Each set represents a logical grouping of MQTT servers. When a set is referenced by a Transmitter configuration, a single connection to one of the servers in the set will be maintained. The other servers will act as failover in the case that a connection with the first is lost. Server sets cannot have common elements meaning that a single MQTT server cannot be in more than one set.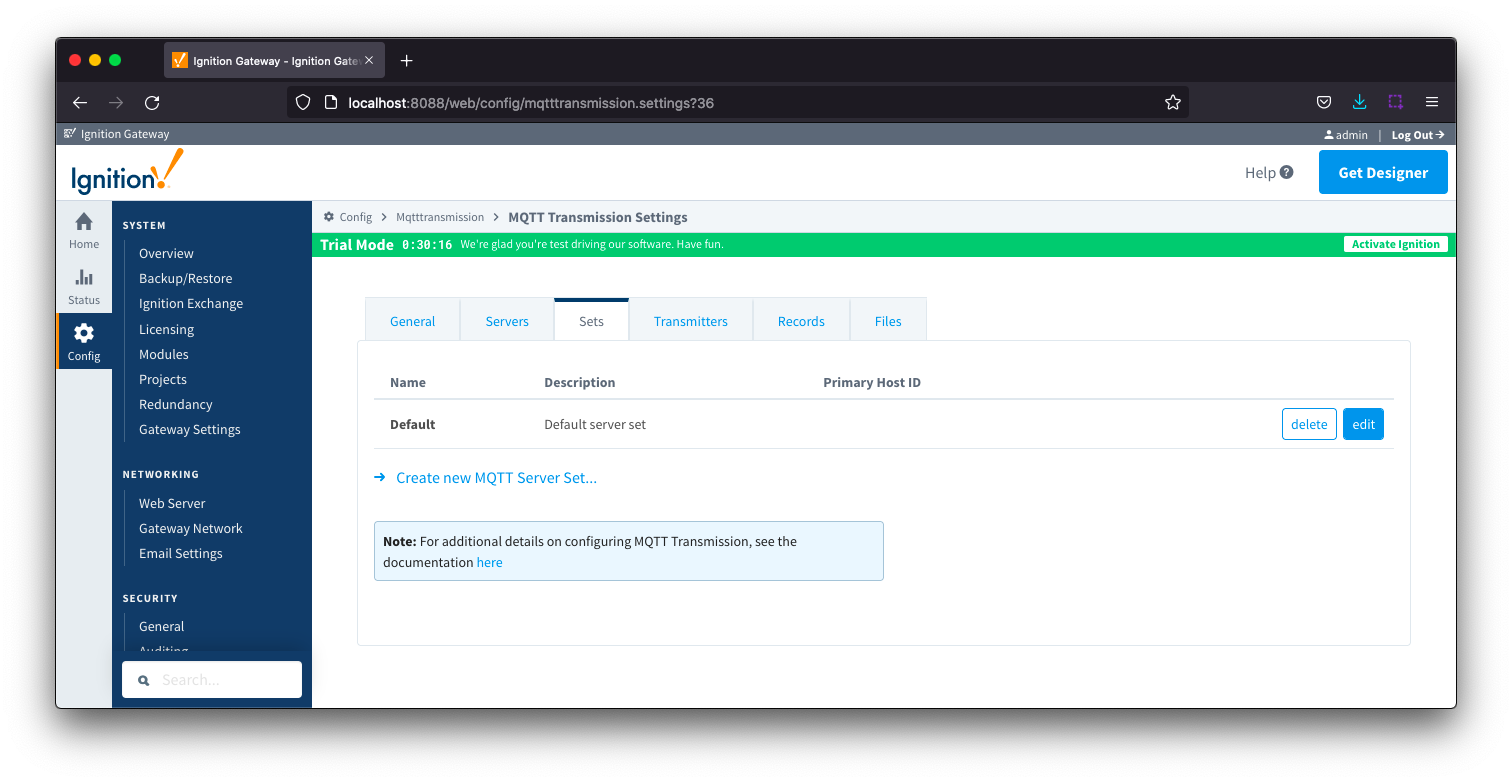
The Sets tab contains a single Main section.
Sets - Main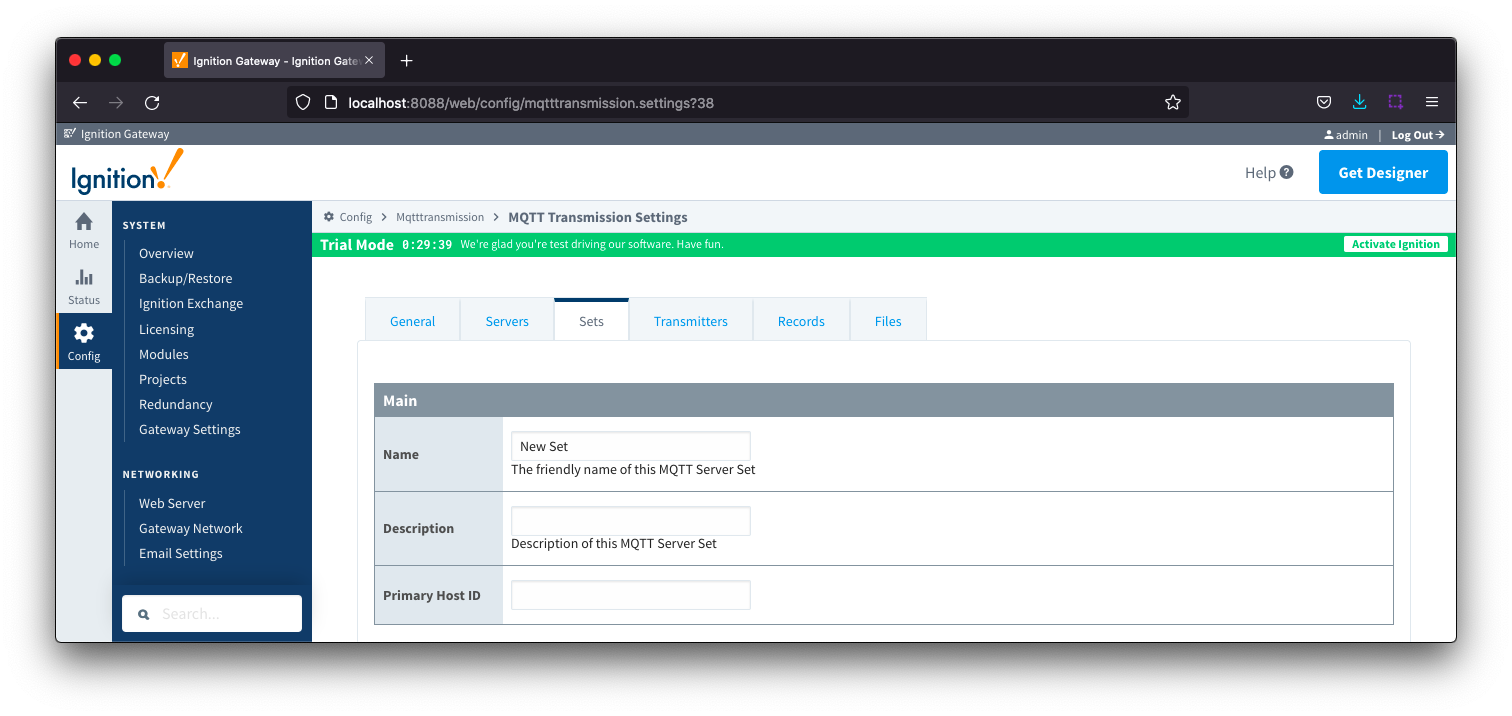
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the set used to easily identify it.
- Description
- This is a friendly description of the set.
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to use for 'state' notifications. These notifications are used to notify MQTT Transmission if the primary backend application loses connection with the MQTT Server, meaning it has gone 'offline'. If MQTT Transmission is notified that the primary backend application has gone 'offline', it will close it's client connection with the MQTT server and walk to the next MQTT server defined in the set. If the primary host ID is not set, MQTT Transmission will not subscribe on the notification topics and not receive any 'state' notifications.
- This must contain only letters, numbers, or any of the following special characters: . $ % @ ! - _ ^ *
Transmitters
Transmitters are the agents within MQTT Transmission that monitor tags, convert them to Sparkplug Messages, and publish them to an MQTT Server. Each transmitter is configured with a server Set and will attempt to maintain an MQTT client connection with one server in that Set at all times.
Transmitters will monitor tags from a specific Tag Provider and, optionally, a specific Tag Path. If the tag folder hierarchy has been constructed as Group ID, Edge Node ID, and Device ID, then these will automatically be used when building up the MQTT message payload that will represent the Tags as follows:
[TagProvider]<TagPath>/<GroupID>/<EdgeNodeID>/<DeviceID>
If your tag folder hierarchy does not conform to this structure, you can explicitly define these required elements under the SparkPlug Settings section and the elements will be prepended to your tag string.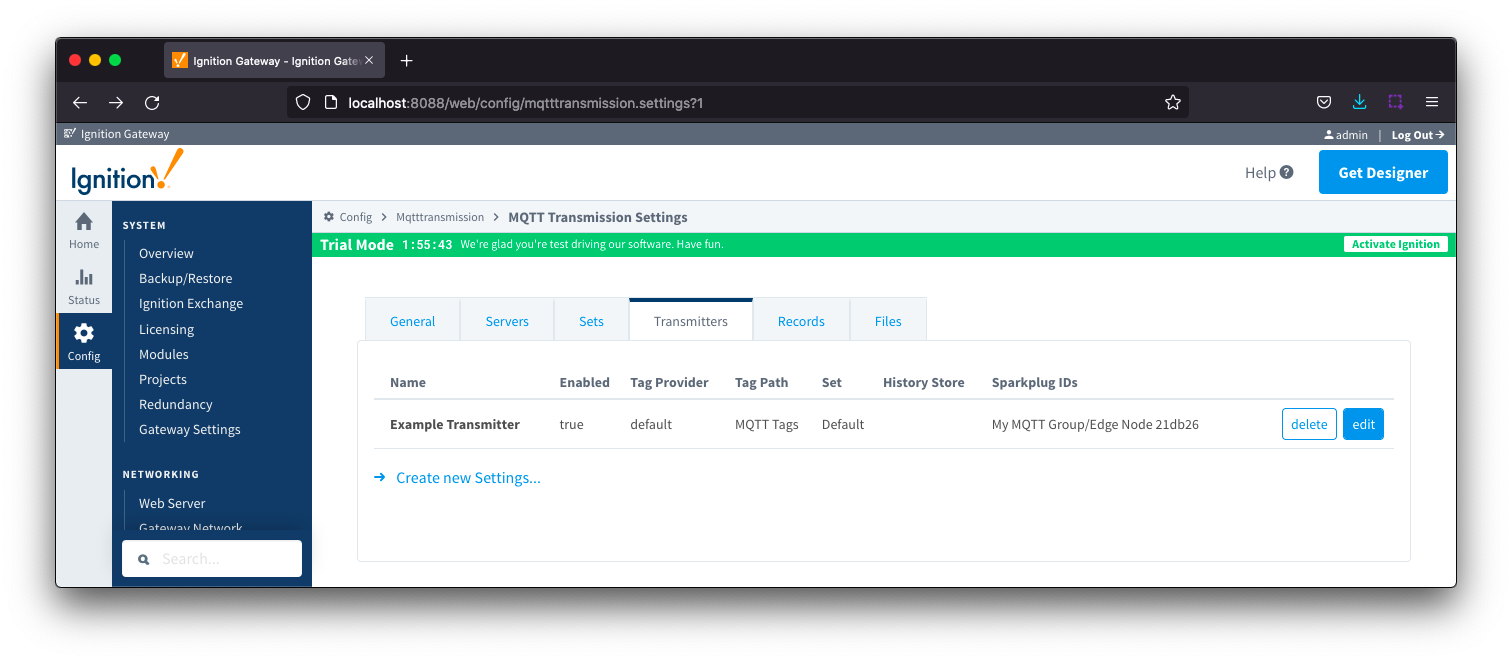
The configuration sections available are Tag Settings, Command Settings, History Settings, Sparkplug Settings and Advanced Settings.
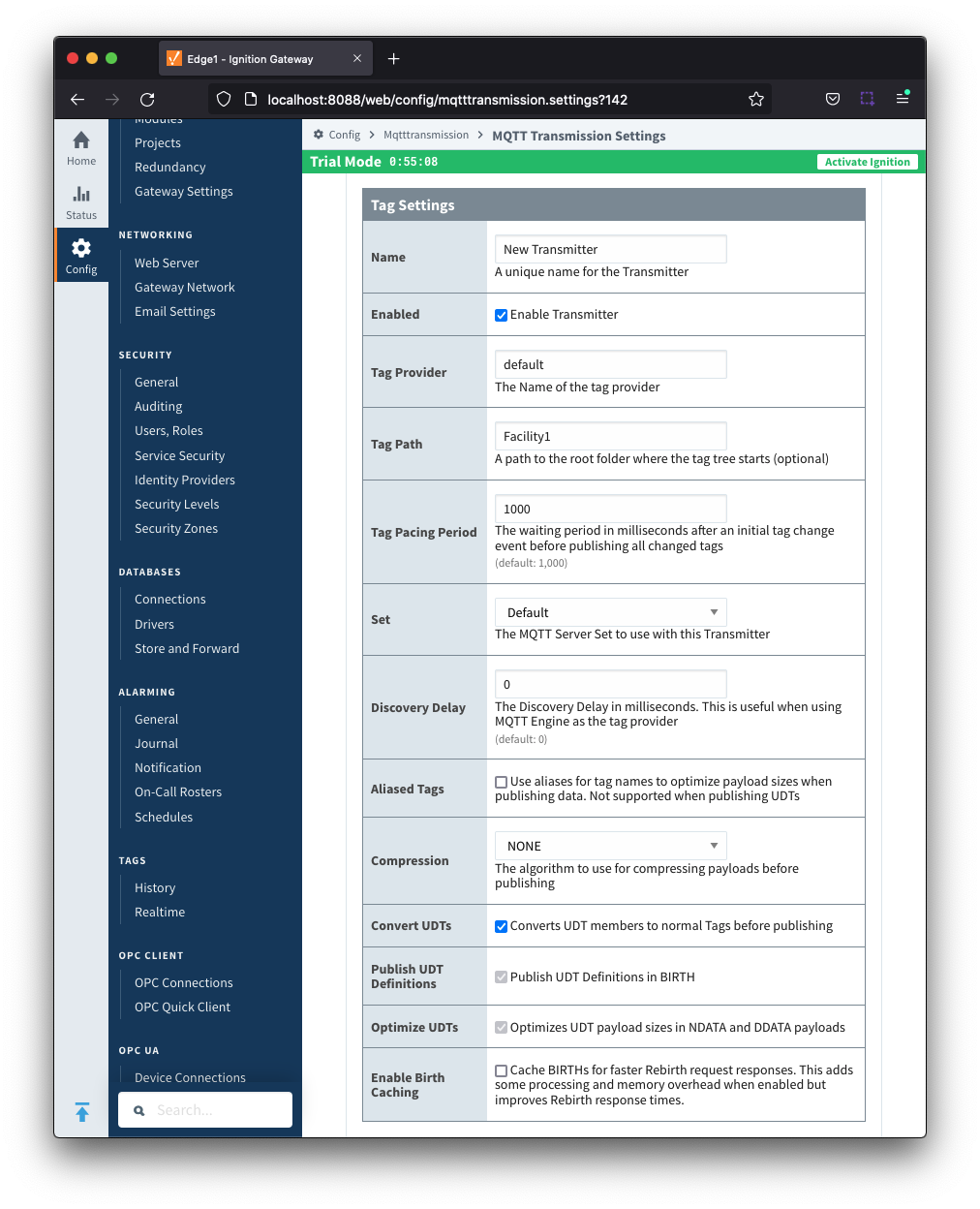
- Name
- Unique name for the Transmitter
- Enabled
- Checkbox to enable/disable the Transmitter. Selected by default.
- Tag Provider
- The name of the tag provider that Transmission will monitor. By default this is the Ignition 'default' provider.
- Tag Path
- Optional path to the root folder where the tag tree starts.
- Transmitters also support a multi-tag path configuration. Reference the Transmitters with Multi-Tag Paths tutorial for configuration assistance.
- Tag Pacing Period
- The buffer period for outgoing Transmission messages in milliseconds. The default is 1000ms. This means when a tag change event is detected 1000ms will elapse before an MQTT message is sent. This allows additional tag change events to be buffered and put into the message and in turn reduce the number of generated MQTT messages.
- Set
- The Set that the default MQTT Transmission client will connect to.
- Discovery Delay
- An optional startup delay, in milliseconds, to wait before scanning for Tags to monitor. This is useful when Tags are dynamically created on initial startup, as is the case when using the MQTT Engine module.
- Aliased Tags
- Checkbox to enable/disable using aliases for tag names when published data messages as tag values change in order to optimize payload size when publishing data. Not selected by default.
- Compression
- The algorithm to use to compress payloads before they are published to the MQTT Server. If 'NONE' is selected then compression is disabled.
- Convert UDTs
- Checkbox to enable/disable converting UDT members to normal Tags before publishing. If enabled the Tags representing the UDT member will retain their member path prefixed by the UDT Instance name. Selected by default.
- Publish UDT Definitions
- Checkbox to enable/disable publishing UDT Definitions in BIRTH. Selected by default and not editable.
- Optimize UDTs
- Checkbox to enable/disable optimizing UDT payload sizes in NDATA and DDATA payloads. Selected by default and not editable.
- Enable Birth Caching
- Checkbox to enable/disable caching birth requests for faster rebirth request response. Not selected by default.
Transmitters - Command Settings
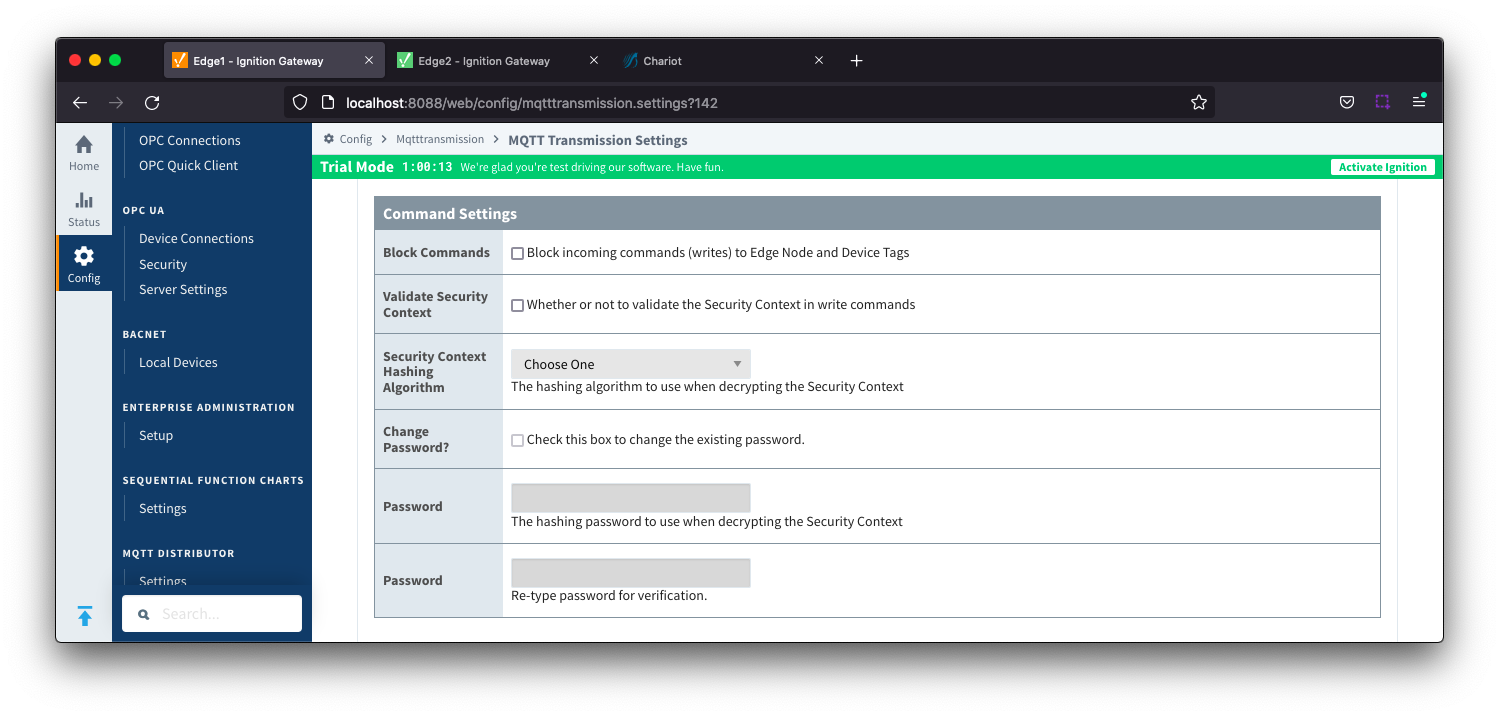
- Block Commands
- Checkbox to enable/disable the ability to block commands and tag writes received as messages from the MQTT server. Not selected by default.
- Validate Security Context
- Checkbox to enable/disable the ability to validate the Security Context in write commands. Not selected by default.
- Reference the Ignition MQTT Security Context HowTo for additional details on how to use this configuration.
- Security Context Hashing Algorithm
- The hashing algorithm to use when decrypting the Security Context. Available if "Validate Security Context" is enabled.
- Change Password?
- Checkbox to allow existing password to be changed
- Password
- The hashing password to use when decrypting the Security Context. Available if "Validate Security Context" is enabled.
Transmitters - History Settings

Note: Store and Forward does not guarantee all data is stored and forwarded. There are some edge cases that are not currently handled with regard to data loss in the event of connection failures related to MQTT keep alive timeouts. This window of potential missed data can be reduced by decreasing MQTT Transmission and MQTT Engine configurable keep alive timeouts.
- History Store
- The MQTT Transmission History Store to use with the Default Transmitter.
- Enable History Storage by Default
- Checkbox to enable/disable store and forward for all tags. Selected by default.
- Store and forward controls whether or not a tag is stored in the configured History Store when Transmission is offline. To override the global setting, individual tags will require a custom tag property 'StoreAndForward' (type: boolean) to be created and set to the reverse state of the global setting.
- In-Order History
- Checkbox to enable/disable the flush history in-order (synchronously) before live data resumes. Not selected by default.
- Group ID
- An ID representing a logical grouping of MQTT Edge Of Network (EoN) Nodes and Devices into the infrastructure.
- Edge Node ID
- An ID that uniquely identifies the MQTT Edge Of Network (EoN) Node within the infrastructure.
- Device ID
- An optional ID that uniquely identifies a Device within the infrastructure.
Note that if a 'Device ID' is not specified, any folder within the folder specified by the Tag Path will be considered a device folder and any Tags within it will be published as device Tags.
Transmitters - Advanced Settings
- Filtered Properties
- A semicolon delimited list of Tag properties to filter/block from being published
- Rebirth Debounce Delay
- The amount of time, in milliseconds, to delay before processing Rebirth NCMD requests after one has been processed. Default of 5000 milliseconds.
Records
The 'Records' tab allows user to create a table of custom records. Each record defines a folder (under specified tag provider) in which user can create a number of tags that will be published as a record by clicking the 'Publish' checkbox. The 'Publish' tag will be created automatically in the folder specified.

The configuration sections available are Tag Settings, Sparkplug Settings and Advanced Settings.
- Tag Provider
- The name of the tag provider (i.e. default)
- Tag Folder Path
- The path to the tag folder under specified tag provider
- Record Type
Records - Sparkplug Settings
- Group ID
- An ID representing a logical grouping of MQTT Edge of Network (EoN) Nodes and Devices into the infrastructure.
- Edge Node ID
- An ID that uniquely identifies the MQTT Edge of Network (EoN) Node within the infrastructure.
- Device ID
- An Optional ID that uniquely identifies a Device within the infrastructure.
Records - Advanced Settings
- Override Publish Tag
- Checkbox to override the default 'Publish Tag' in the Record defined folder path
- Publish Tag Path
- Overrides the default 'Publish Tag' in the Record defined folder path
Files
The 'Files' tab allows for the configuration to publish files which are transferred using Sparkplug over MQTT.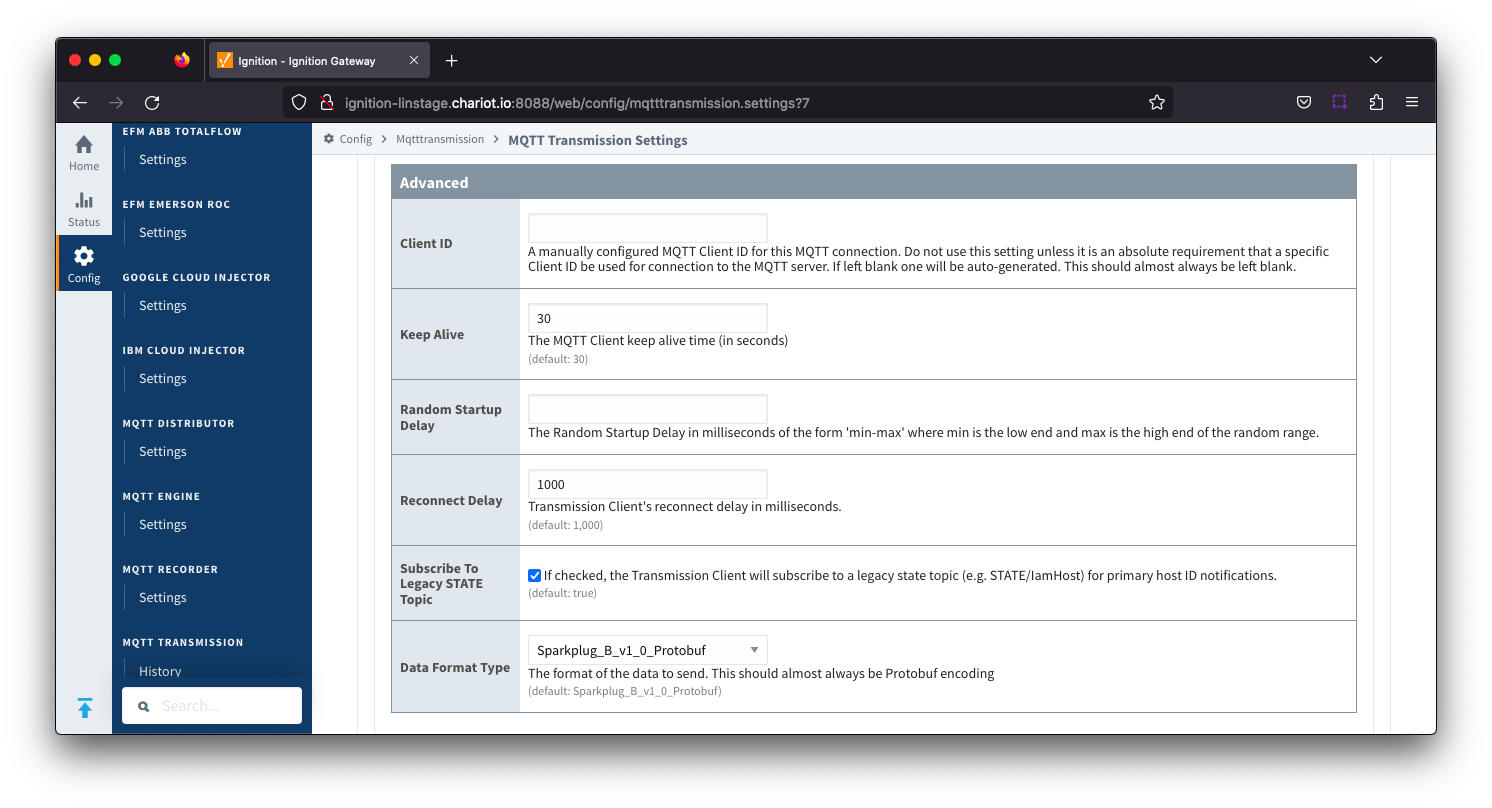
The configuration sections available are Tag Settings, File Settings, Sparkplug Settings and Advanced Settings.
- Tag Provider
- The name of the tag provider (i.e. default)
- Tag Folder Path
- The path to the tag folder under specified tag provider
Files - File Settings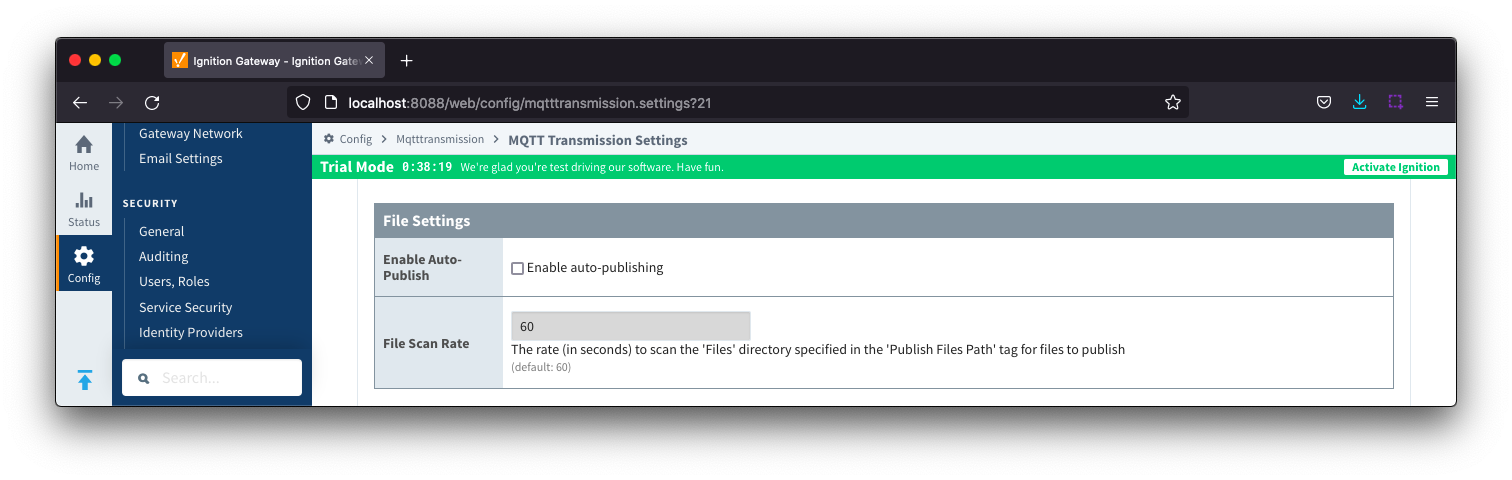
- Enable Auto-Publish
- Checkbox to enable/disable auto publish of files. Not selected by default.
- File Scan Rate
- The rate, in seconds, to scan the files directory specified in the 'Publish Files Path' tag for files to publish. Default is 60 seconds.
Files - Sparkplug Settings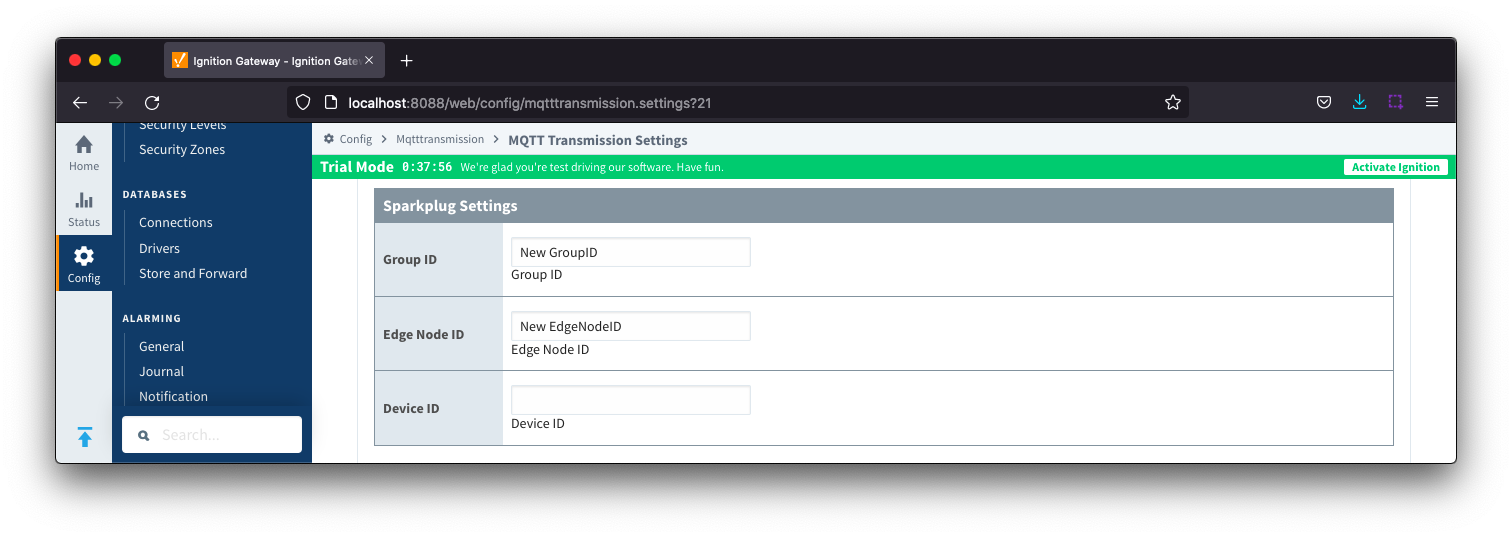
- Group ID
- An ID representing a logical grouping of MQTT Edge of Network (EoN) Nodes and Devices into the infrastructure.
- Edge Node ID
- An ID that uniquely identifies the MQTT Edge of Network (EoN) Node within the infrastructure.
- Device ID
- An Optional ID that uniquely identifies a Device within the infrastructure.
Files - Advanced Settings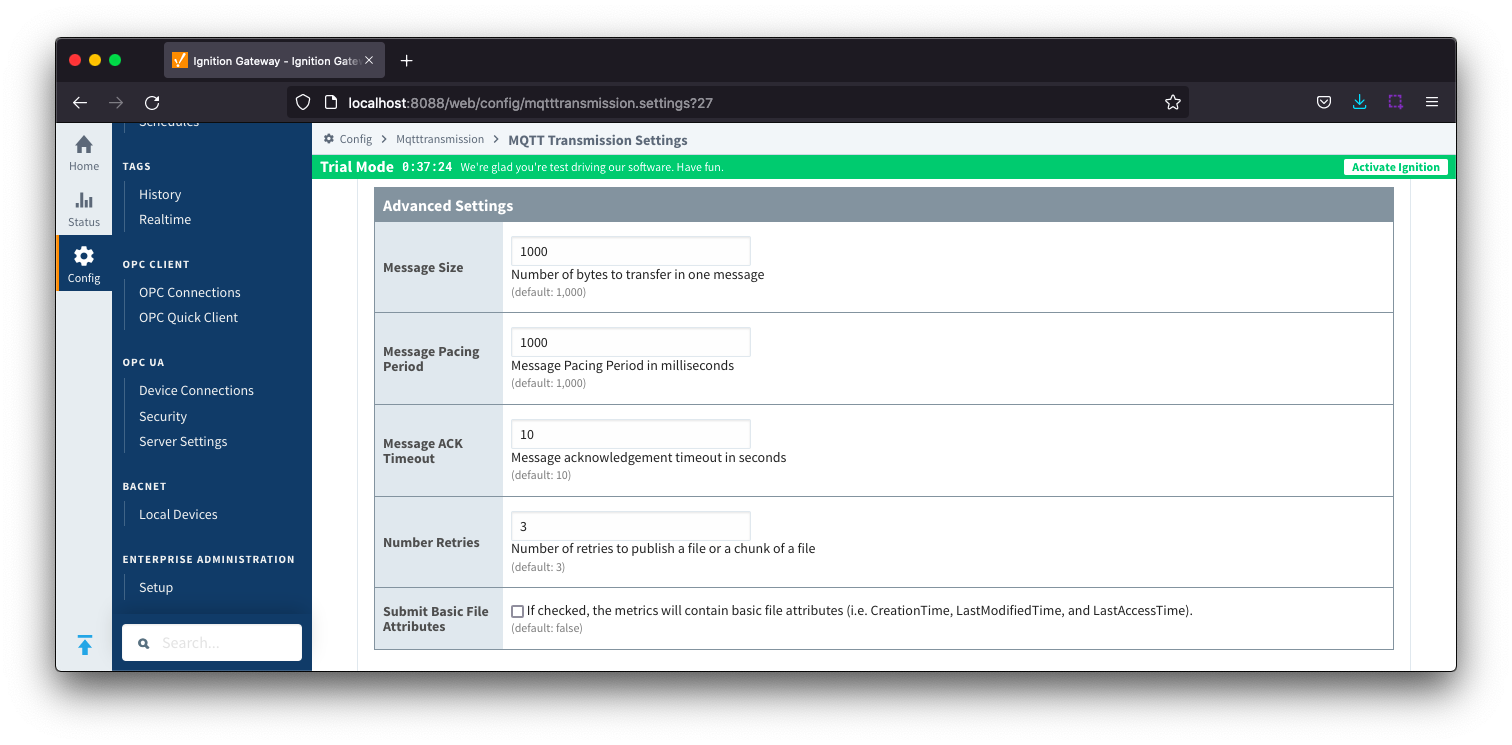
- Message Size
- Number of bytes to transfer in one message, Default 1000 bytes.
- Message Pacing Period
- Message Pacing Period is milliseconds. Default 1000 milliseconds.
- Message ACK Timeout
- Message acknowledgement timeout in seconds. Default 10 seconds.
- Number Retries
- Number of retries to publish a file or chunk or a file
- Submit Basic File Attributes
- Checkbox to enable/disable the basic file attributes to be included in the metrics. Not selected by default.
History
The "History" page allows for the configuration of MQTT Transmission History Stores. In the event that a Transmitter loses its connection with the MQTT Server and is unable to reconnect, a History Store (if enabled) will store all messages corresponding to change events on the monitored tags. Once a connection with an MQTT server is reestablished the History Store will publish the stored messages with a flag set to indicate that the messages are "historical" to prevent confusion with live data values.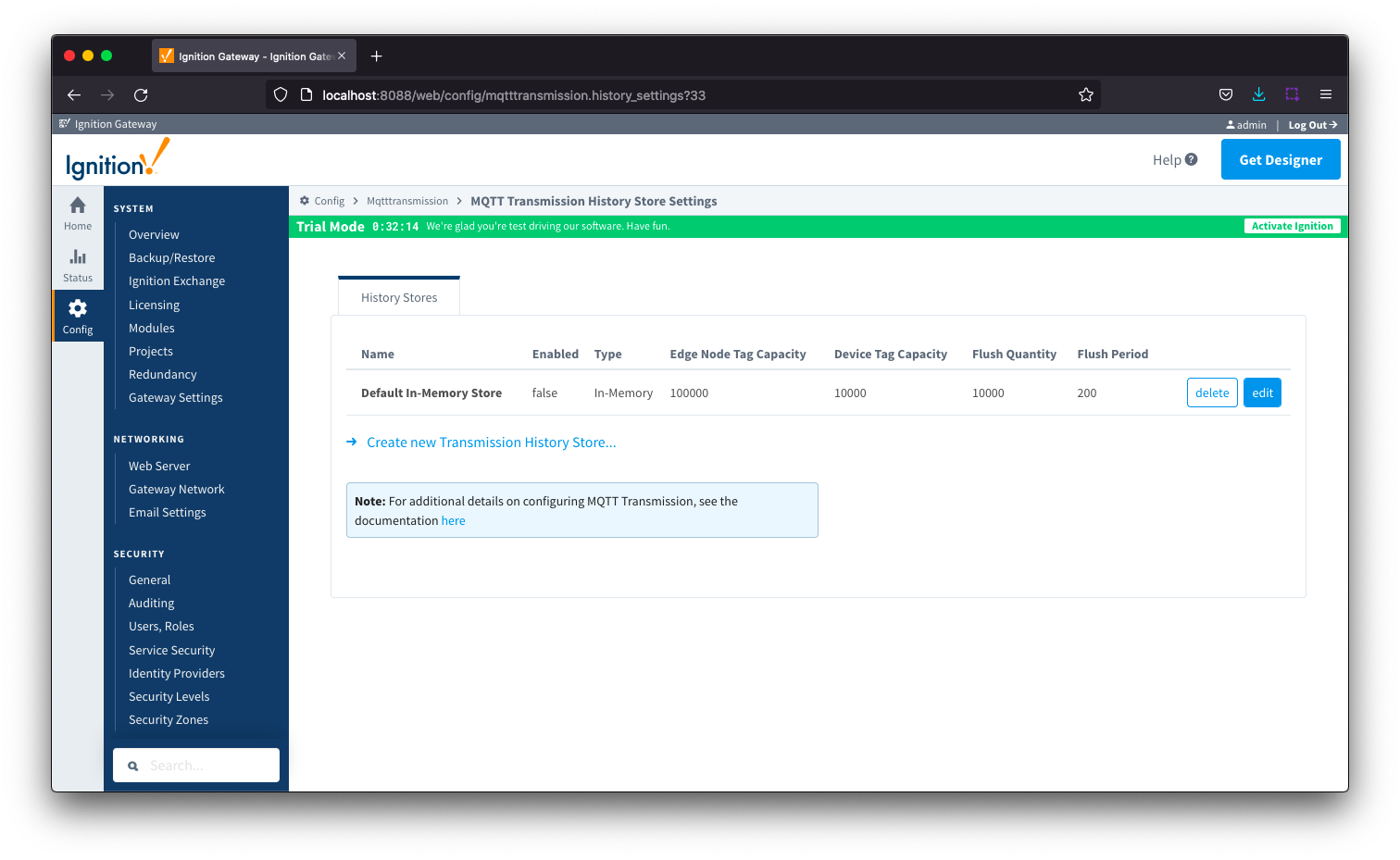
The History tab contains a single Main section.
History - Main

- Name
- The name of the History Store.
- Enabled
- Checkbox to enable/disable the History Store. Not selected by default.
- Type
- The type of History Store.
- Edge Node Tag Capacity
- The maximum number of tag change events to store, for each edge node folder, before dropping the oldest stored tag change event.
- A tag change event is triggered by either a change in value or quality and results in the tag's Qualified Value (which has three attributes of value, quality and timestamp) being stored.
- The Edge Node Tag Capacity is independent from, and in addition to, the Device Tag Capacity
- Device Tag Capacity
- The maximum number of tag change events to store, for each device folder, before dropping the oldest stored tag change event.
- A tag change event is triggered by either a change in value or quality and results in the tag's Qualified Value (which has three attributes of value, quality and timestamp) being stored.
- Flush Quantity
- The maximum number of tags to publish in a single message upon reestablishing communication.
- Flush Period
- The period to wait in milliseconds between publishes when flushing messages upon reestablishing communication.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()