MQTT Engine provides a configuration section to the Ignition Gateway. These can be seen in the Configure section of the Ignition Gateway web UI in the left-hand navigation panelpane - Configure → MQTT Engine → Settings. Once in the configuration section there are three tabs: Servers, Advanced, and Namespaces. Each of these tabs is described in detail in the following sections.
...
- Enabled
- Whether or not the MQTT Engine module is enabled and connecting to configured MQTT Servers.
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to use for 'state' checks. These checks are used to ensure that the primary backend MQTT Engine client remains connected. If the primary host ID is set, MQTT Engine will publish it's connection state on a topic that contains the Primary Host ID. In the event that MQTT Engine becomes disconnected from the server, a death certificate will be published on the same topic, setting the state to 'offline'. Any connecting client that subscribes on the state topic will then be notified of the MQTT Engine state and walk to the next server is MQTT Engine is offline.
- This must contain only letters, numbers, and the following special characters: . $ % @ ! - _ ^ *
- Group ID Filters
- A comma separated list of group IDs to subscribe to.
...
Enable Tag Latching
- Whether or not to enable Tag latching to synchronize MQTT Tag updates with events in Ignition.
Latch Timeout
- The amount of time to wait for a Tag latch to be released before timing out.
Latch Tags
- A list of Trigger Tag and Latch Tag pairs.
Enable Primary Host Subscriptions
- Whether or not to enable MQTT Engine subscriptions on STATE/# and State/# topics even when a PrimaryHostID is not configured within MQTT Engine. This setting is for debugging purposes only.
Enable BD Sequence Validation
- Whether or not to enable BIRTH/DEATH sequence number validation (required by Sparkplug specification).
- Custom Properties
- Custom configuration properties that are fed into MQTT Engine. Custom properties should only be used at the direction of CIrrus Link and the specific properties will be provided.
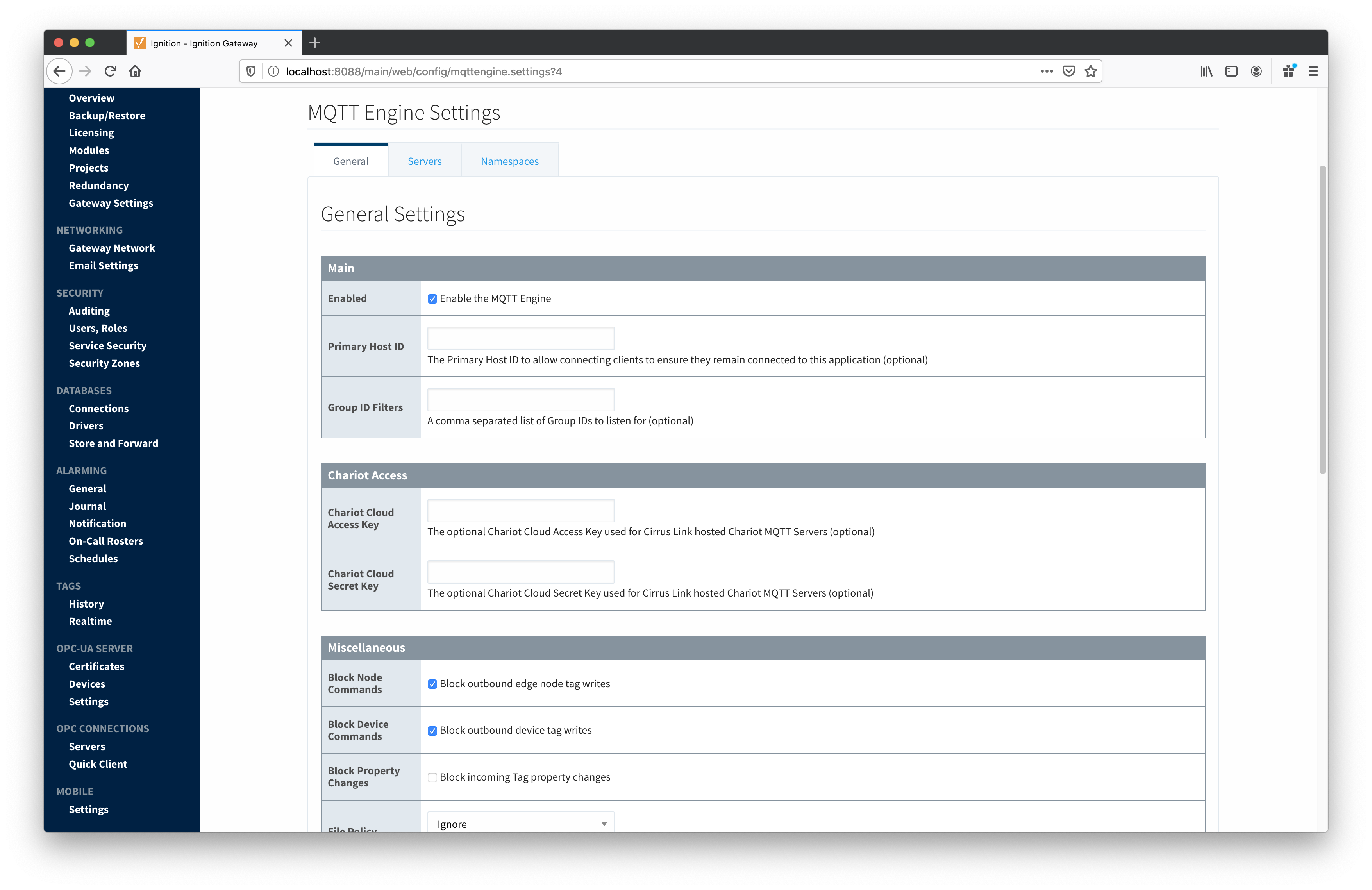 Image Modified
Image Modified
Servers
The second tab is a list of MQTT Servers that MQTT Engine should connect to. By default, MQTT Engine is configured to connect to the local MQTT Distributor based MQTT Server. It is set up to connect to localhost, port 1883, using the default username/password pair of admin/changeme. Out of the box MQTT Engine will work with MQTT Distributor and its default configuration. The connection status of each server can be seen in the 'Status' column. Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server' link will bring up the following form for adding a new MQTT Server setting.
...
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the MQTT Server used to easily identify it.
- Enabled
- Whether or not connections to this MQTT Server are enabled.
- URL
- This is the URL of the MQTT server. Its format is as follows: [protocol]://[location]:[port]. Each of these are shown below.
- protocol - Either tcp or ssl
- location - The server location. e.g. localhost, myserver.chariot.io, mydomain.com, etc
- port - The port the MQTT Server is listening on. Generally this is 1883 if using TCP or 8883 if using SSL
- Server Type
- This is the type of MQTT Server to connect to.
- Chariot - If connecting to a Cirrus Link Chariot on-premise or Chariot cloud based MQTT Server
- MQTT Distributor - If connecting to a Ignition MQTT Distributor server
- Third Party - If connecting to a third party 3.1.1 compliant MQTT Server
- Username
- Optional MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Password
- Optional MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
TLS Settings
- Certificates
- The server certificates to use if required. These are generally only required when connecting using TLS and the MQTT server does not have a genuine certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority.
- CA certificate must always end in 'ca.pem'
- If using client side certificates (i.e. a public/private keypair and CA cert), make sure the following naming conventions are followed.
- Edge/Device certificate must end in 'cert.pem'
- Edge/Device private key must end in 'private.key'
- Password
- A password associated with the certificate's private key.
- The configuration for TLS changed between MQTT Engine v3.4.6 and v3.4.7. See this document for TLS configuration: Configuring Secure MQTT Communication
Advanced Settings
- Client ID
- Optional MQTT client ID to use. If specified this will be used in the MQTT Engine connect packet when connecting to the server. If left blank, a random client ID will be create of the form 'IgnitionTarget-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx'. Caution: MQTT Clients IDs must be unique and if two clients attempt to connect with the same client ID, one will be forcefully disconnected from the server to allow the other client to connect.
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT client keep alive time (in seconds).
- Filtered Namespaces
- A comma separated list of namespaces that will be filtered/disabled for connections to this MQTT Server.
...
Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server...' link will bring up the following form to add a new Server.
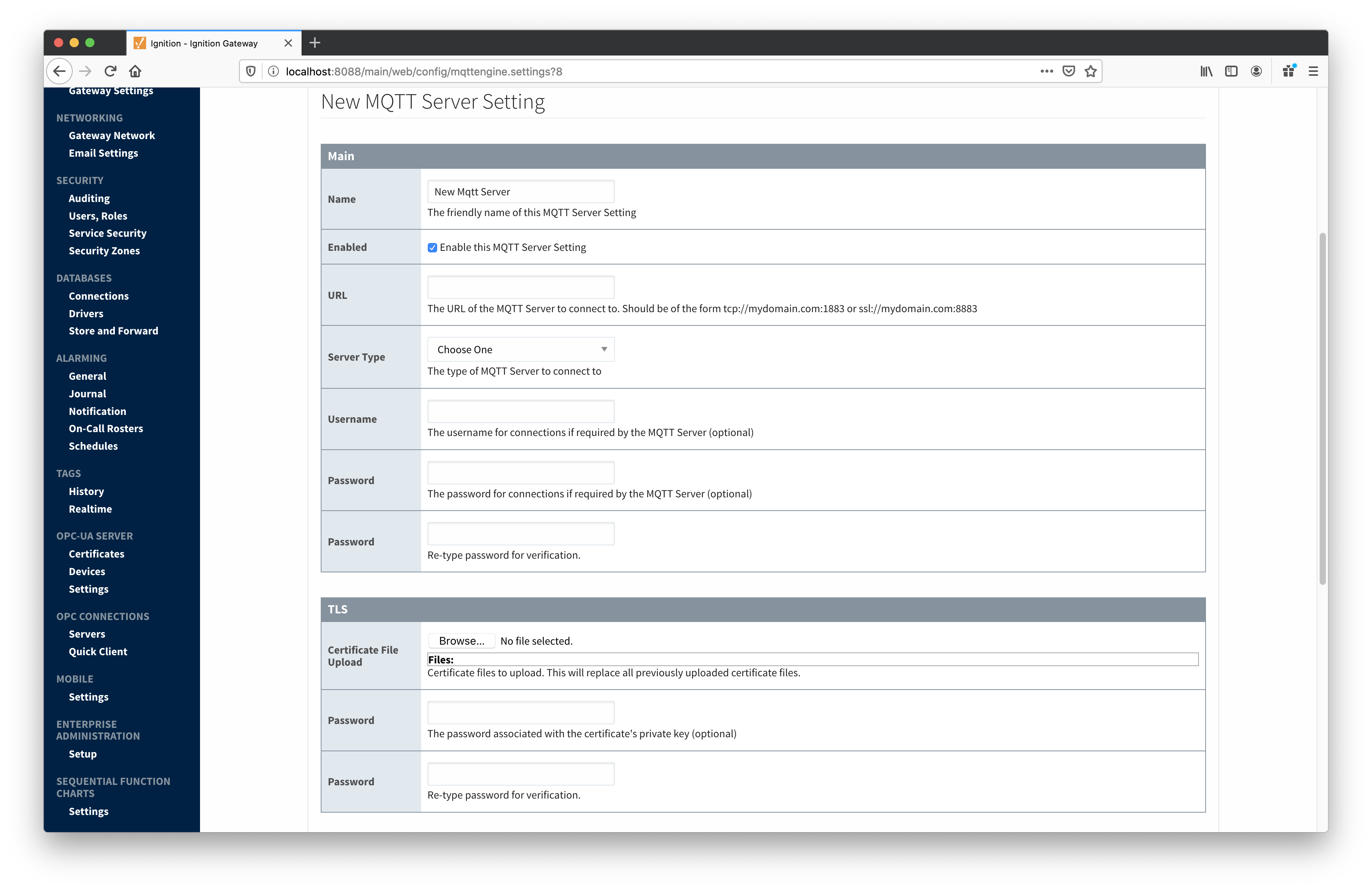 Image Modified
Image Modified
Namespaces
The third tab is used for configuring namespaces. Each namespace configuration represents a family of devices and/or data that MQTT Engine will support. A namespace defines the topics that each MQTT Engine client will subscribe on as well as indicates how the payload will be handled. There are two types of namespaces: Default and Custom.
...
- Root Tag Folder
- A name of a folder where all tags will be stored. If configured, this folder will be the base folder where all tag paths will start.
- Tag Name
- A tag name to be used for all tags. If not configured, the last token in the topic will represent the tag.
- JSON Payload
- A flag to indicate that the content of the string based payload is a JSON object.
Advanced
- Writable Tags
- Enables writes on tags created by the Custom Namespace. Note: This will only make the tags writable; it will not result in outgoing MQTT messages.
Note: if a Tag Name is not specified, care must be taken so that published messages do not end up overwriting previous tags.
Clicking on the 'Create new Custom Namespace...' link will bring up the following form to add a new Custom Namespace.
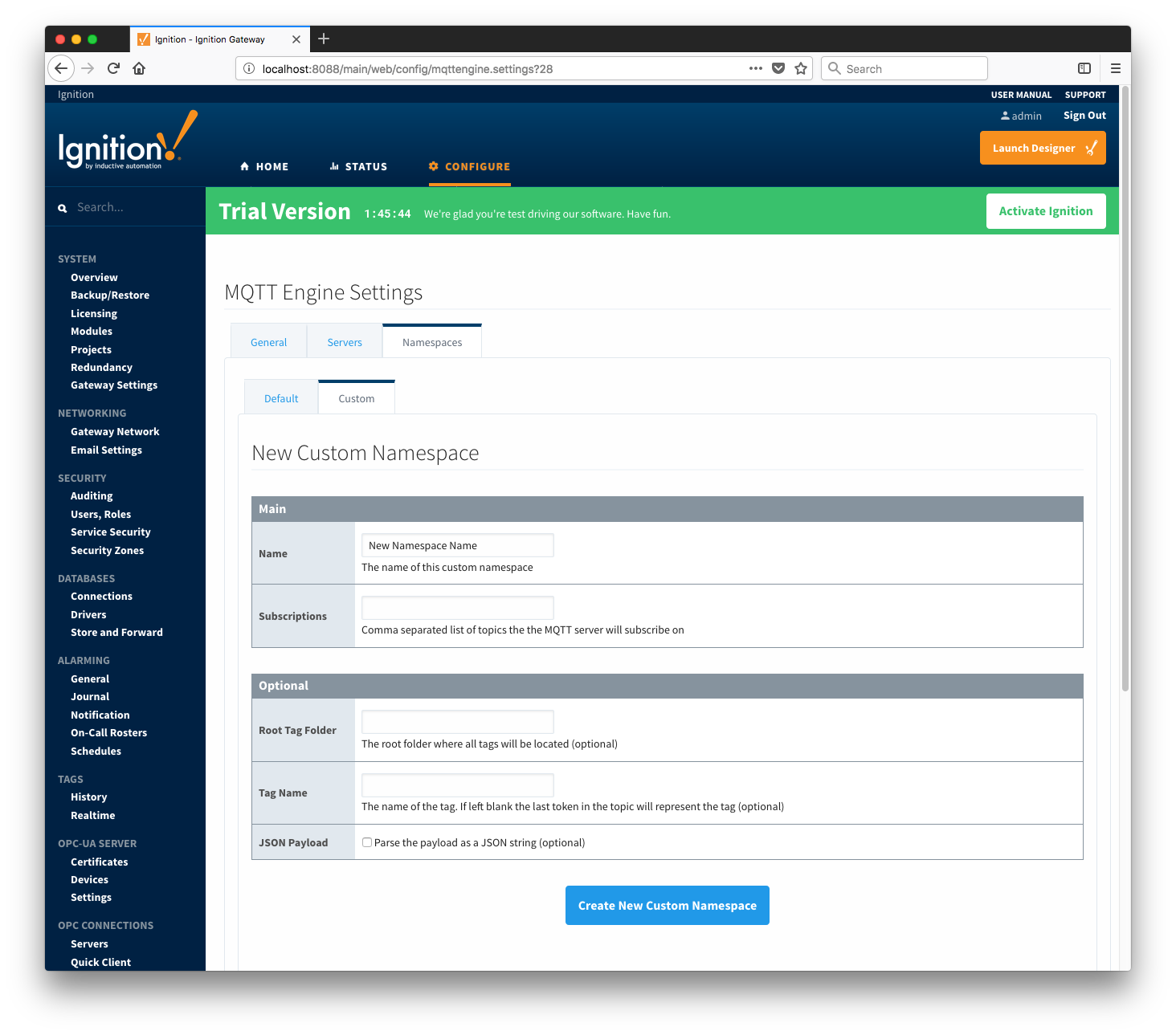 Image Removed
Image Removed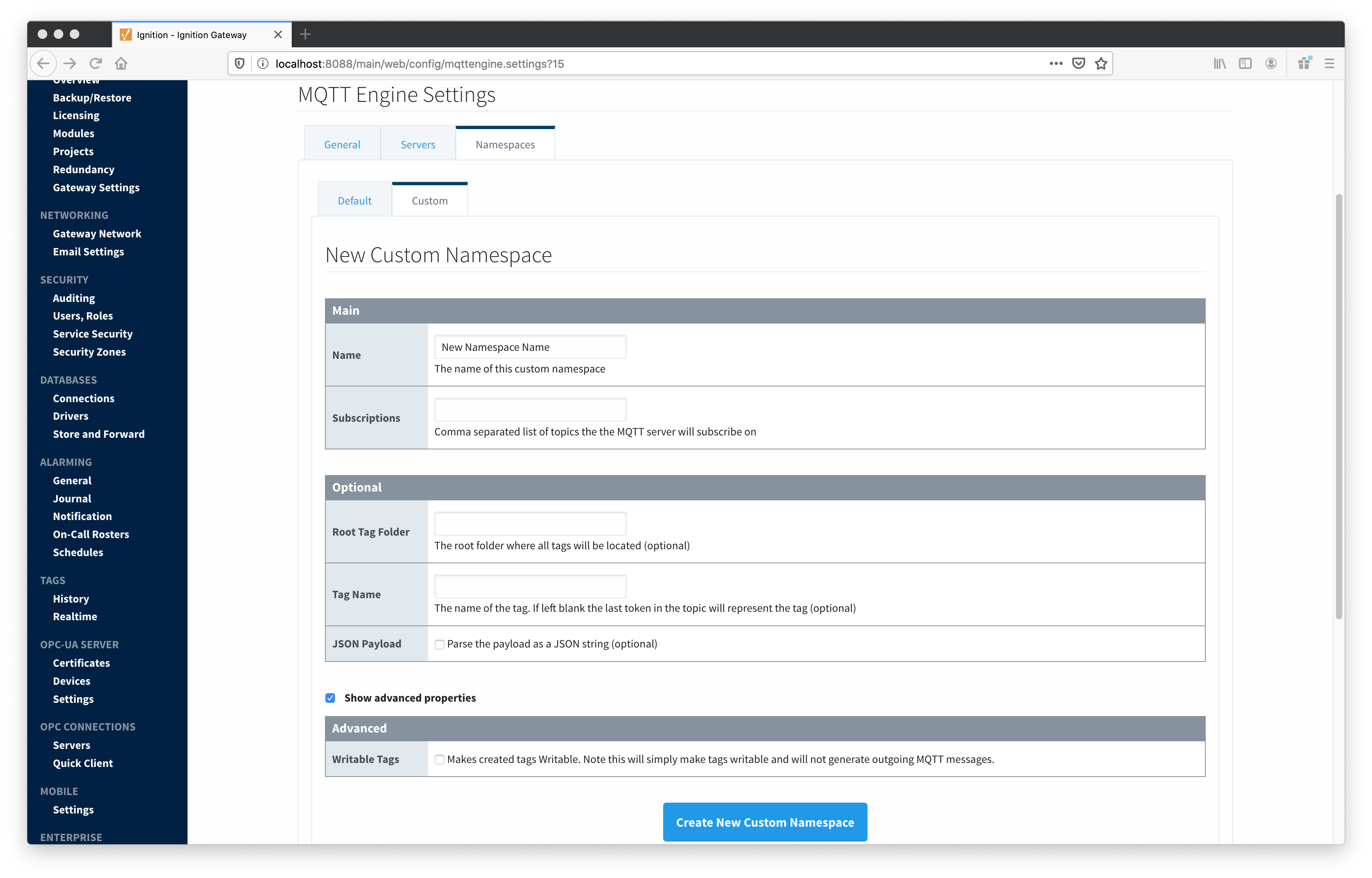 Image Added
Image Added
Custom Namespace Example
...
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



