MQTT Engine provides a configuration section to the Ignition Gateway . These and this can be seen in the Configure section left side bar of the Ignition Gateway web UI in the left panel.
 Image Removed
Image Removed
Once in the configuration section there are three tabs: Servers, Advanced, and Namespaces. Each of these tabs is described in detail in the following sections.
General
The first tab contains general settings which allows one to enable/disable the module, configure Application ID Filters, and Cirrus Link Chariot Access Settings. The Chariot access settings settings are used in conjunction with a Cirrus Link Chariot deployment and will be provided when purchasing Chariot Cloud services.
Main
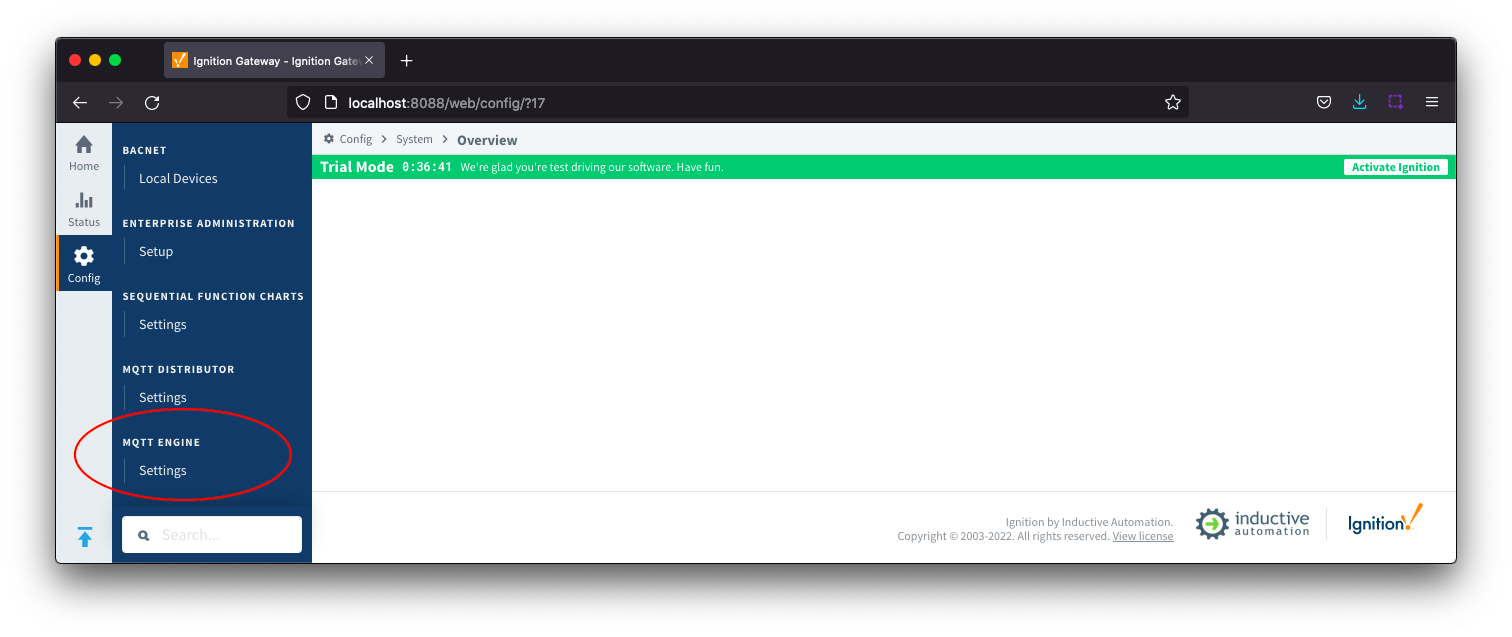 Image Added
Image Added
The configuration options for each of the three tabs - General, Servers, and Namespaces - are detailed below.
GeneralThe configuration sections available are Main, Command Settings, Miscellaneous and Advanced.
General - Main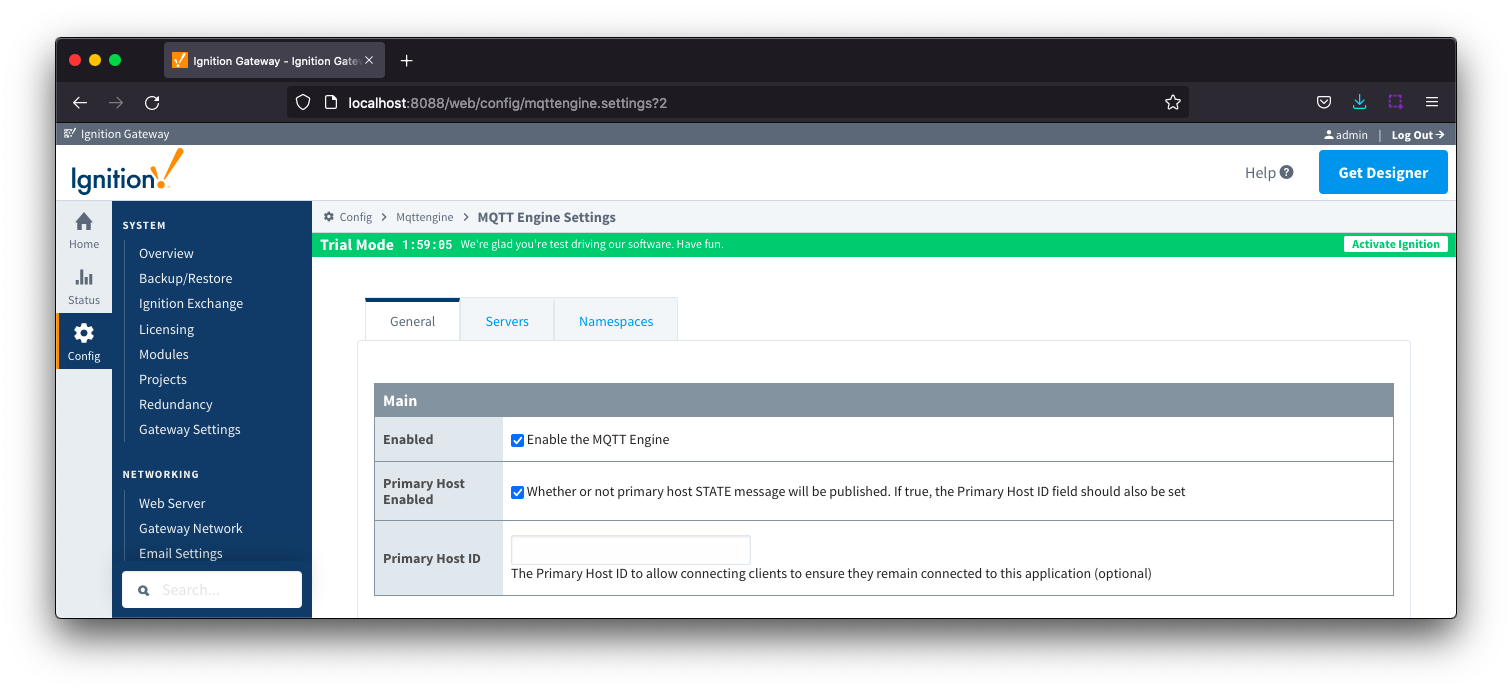 Image Added
Image Added
Enabled
- Whether or not the MQTT Engine module is enabled and connecting to configured MQTT Servers.
| Anchor |
|---|
| PrimaryHostEnabled |
|---|
| PrimaryHostEnabled |
|---|
|
Primary Host IDEnabled- Whether or not primary host STATE message will be published. If true, the Primary Host ID must also be set.
- When enabled, the The primary host ID to use for 'state' checks. These checks are used to ensure that the primary backend MQTT Engine client remains connected. If the primary host ID is set, MQTT Engine will publish it's connection state on a topic that contains the Primary Host ID. In the event that MQTT Engine becomes disconnected from the server, a death certificate will be published on the same topic, setting the state to 'offline'. Any connecting client that subscribes on the state topic will then be notified of the MQTT Engine state and walk to the next server is MQTT Engine is offline.
- Group ID Filters
- A comma separated list of group IDs to subscribe to.
Chariot Access
- Chariot Cloud Access Key
- If using Cirrus Link's Chariot platform, this is the provided Access Key
- Chariot Cloud Secret Key
- If using Cirrus Link's Chariot platform, this is the provided Secret Key
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to allow connecting clients to ensure they remain connected.
- This must contain only letters, numbers, or any of the following special characters: . $ % @ ! - _ ^ *
| Anchor |
|---|
| GeneralCommandSettings |
|---|
| GeneralCommandSettings |
|---|
|
General - Command Settings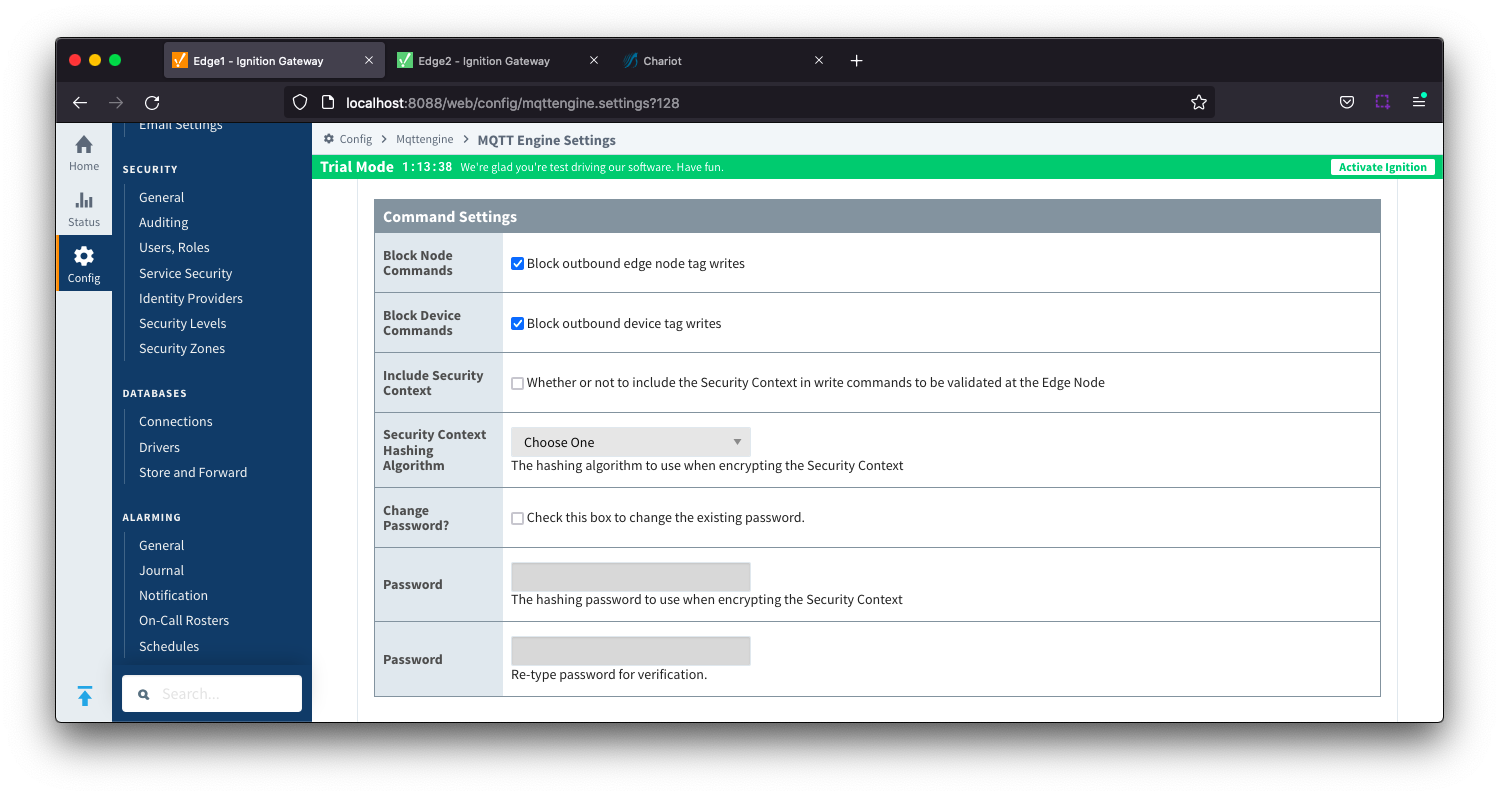 Image Added
Image Added
...
- Block Node Commands
- Whether or not to block outgoing commands from MQTT Engine to Edge Nodes. This is true by default and provides a security mechanism for preventing accidental outgoing commands from MQTT Engine.
- Block Device Commands
- Whether or not to block outgoing commands from MQTT Engine to Devices. This is true by default and provides a security mechanism for preventing accidental outgoing commands from MQTT Engine.
- File Policy
- The policy for handling Files contained within a Sparkplug payload.
- Ignore: The default policy. The file will be ignored.
- Store: The file will be stored to the local file system in the directory specified by the File Location field. A Tag will be created with a String value representing the file URI.
- Include Security Context
- Whether or not to include the Security Context in write command to be validated at the Edge Node. This is deselected by default.
- Reference the Ignition MQTT Security Context HowTo for additional details on how to use this configuration.
- Security Context Hashing Algorithm
- Hashing algorithm to use when encrypting the Security Context. Options include SHA_1, SHA_224, SHA_256, SHA_384 and SHA_512
- Change Password?
- Checkbox to allow existing password to be changed
- Password
- Password to be used when encrypting the Security Context
| Anchor |
|---|
| GeneralMiscellaneous |
|---|
| GeneralMiscellaneous |
|---|
|
General - Miscellaneous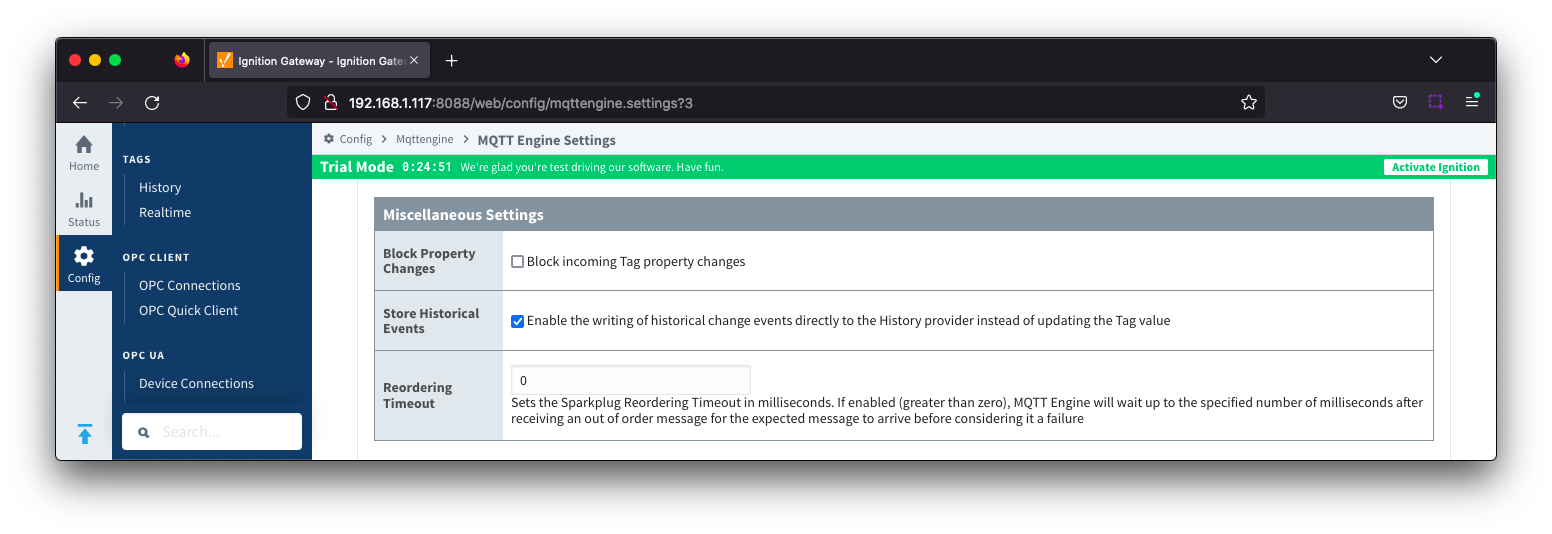 Image Added
Image Added
- Block Property Changes
- Whether or not to block incoming properties from modifying MQTT Engine tag properties. This is false by default so property changes will be applied if not included in the Filtered Property list under 'Advanced'
File Location
- The directory to store the files when using the Store policy described above.
- Store Historical Events
- Whether or not to write historical change events directly to the Historian (if history is enabled on a Tag) instead of updating the live Tag value.
- Note: Store and Forward does not guarantee all data is stored and forwarded. There are some edge cases that are not currently handled with regard to data loss in the event of connection failures related to MQTT keep alive timeouts. This window of potential missed data can be reduced by decreasing MQTT Transmission and MQTT Engine configurable keep alive timeouts.
- Reordering Timeout
...
General - Advanced| Warning |
|---|
| These are advanced settings/features and they should be left with default values in almost all cases. Please be careful when changing these settings from their default values. |
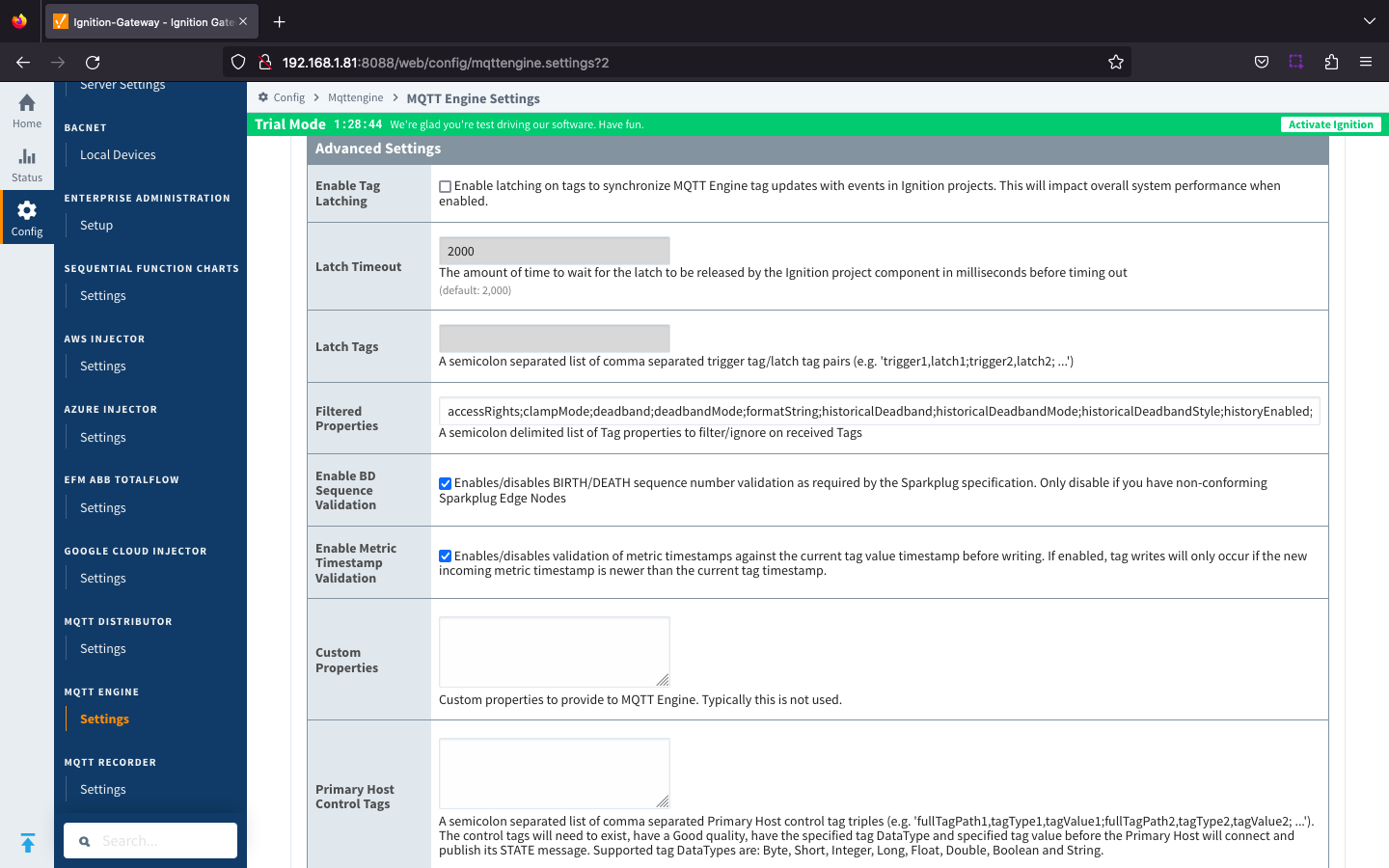 Image Added
Image Added
- Enable Tag Latching
- Whether or not to enable Tag latching to synchronize MQTT Tag updates with events in Ignition.
Latch Timeout
- The amount of time to wait for a Tag latch to be released before timing out.
Latch Tags
- A semicolon separated list comma separated list of Trigger Tag and Latch Tag pairs.
- Filtered Properties
- A semicolon delimited list of Tag properties to filter/ignore on received Tags.
- By default the filtered properties list contains: accessRights;clampMode;deadband;deadbandMode;formatString;historicalDeadband;historicalDeadbandMode;historicalDeadbandStyle;historyEnabled;historyMaxAge;historyMaxAgeUnits;historyProvider;historySampleRate;historySampleRateUnits;historyTagGroup;historyTimeDeadband;historyTimeDeadbandUnits;opcItemPath;opcServer;permissionModel;rawHigh;rawLow;sampleMode;scaleFactor;scaleMode;scaledHigh;scaledLow;tagGroup;valueSource;expression;expressionType;ConfiguredTagPath;eventScripts;readPermissions;writePermissions;eventScripts;parentEnabled;sourceTagPath
- Tag properties are only published from Transmission if different from the default Ignition tag property settings and are only published in BIRTH messages.
Enable BD Sequence Validation
- Whether or not to enable BIRTH/DEATH sequence number validation (required by Sparkplug specification).
- Enable
...
- Whether or not to enable MQTT Engine subscriptions on STATE/# and State/# topics even when a PrimaryHostID is not configured within MQTT Engine. This setting is for debugging purposes only.
- Metric Timestamp Validation
- Enables/disables validation of metric timestamps against the current tag value timestamp before writing. If enabled, tag writes will only occur if the new incoming metric timestamp is newer than the current tag timestamp.
- Custom Properties
- Do not use unless instructed to by Cirrus Link personnel.
- Primary Host Control Tags
- A semicolon separated list of comma separated Primary Host Control tags triples (e.g., tagPath1,tagDataType1,tagValue1;tagPath2,tagDataType2,tagValue2). Review MQTT Engine Primary Host Control for additional information.
- Supported tag DataTypes are: Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Float, Double, Boolean and String
ServersThe Servers tab has two parts - Settings and Certificates
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServerSettings |
|---|
| ServerSettings |
|---|
|
Servers - SettingsThis tab provides a list of the
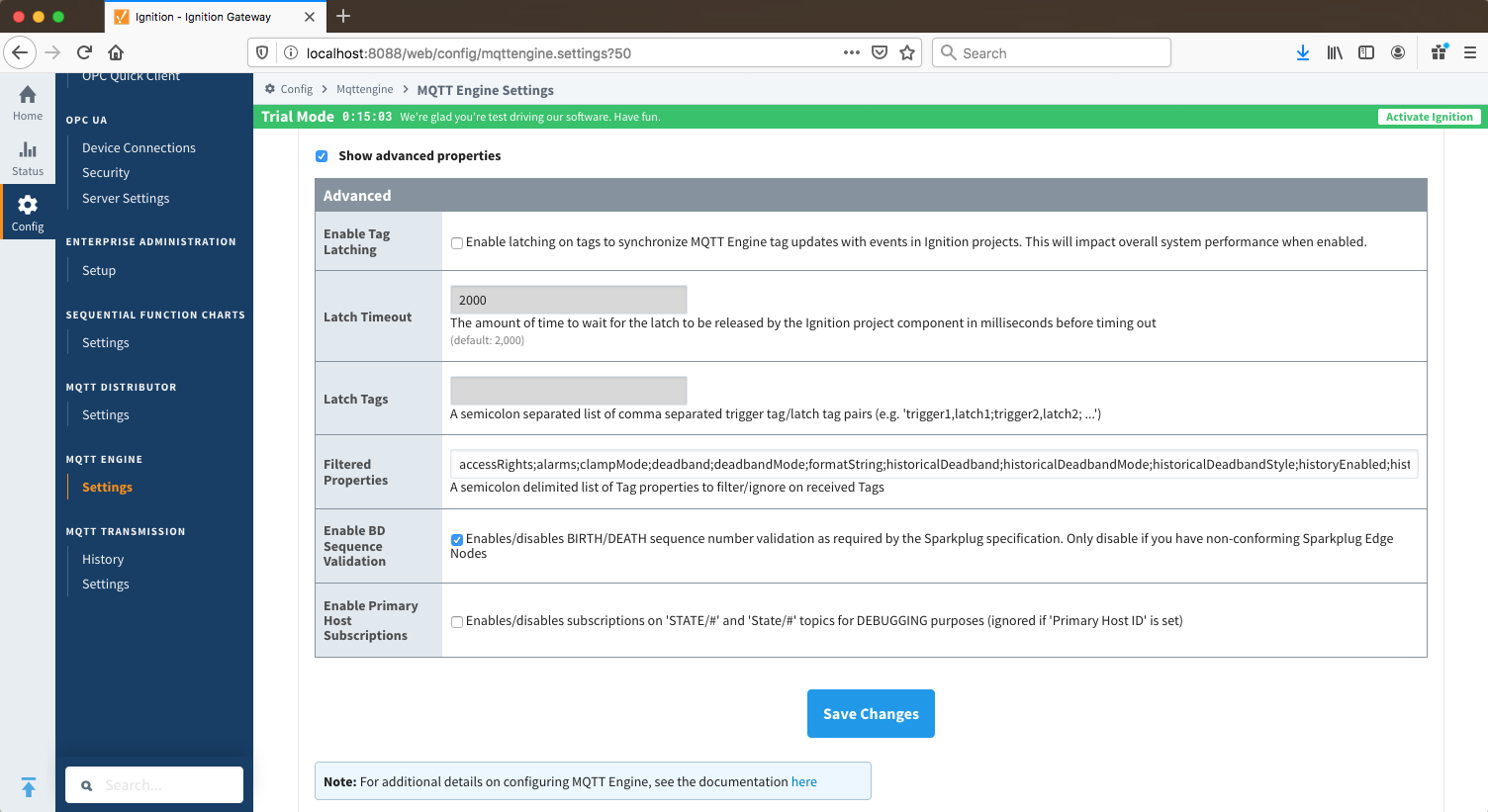 Image Removed
Image Removed
Servers
The second tab is a list of MQTT Servers that MQTT Engine should connect to. By default, MQTT Engine is configured to connect to the local MQTT Distributor based MQTT Server . It and is set up to connect to localhost, port 1883, using the default username/password pair of admin/changeme. Out of the box MQTT Engine will work with MQTT Distributor and its default configuration. The connection status of each server can be seen in the 'Status' column. .
Additional or alternative MQTT Servers can be configured in MQTT Engine - often times more than one will be configured to handle fail-over in redundant or geographically distributed systems. Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server' link will bring up the following a form for adding a new MQTT Server setting.
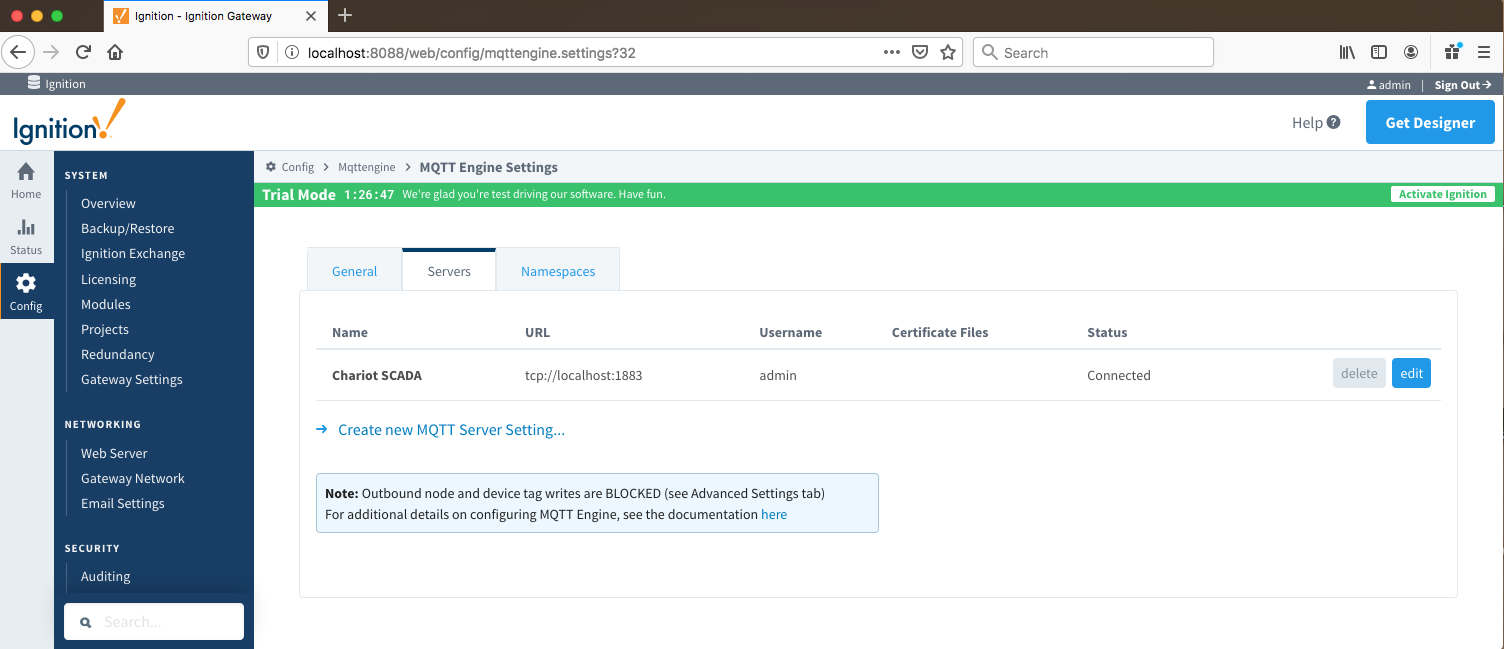 Image Removed
Image Removed
Additional or alternative MQTT Servers The connection status of each server can be configured in MQTT Engine. Often times more than one will be configured to handle fail-over in redundant or geographically distributed systems. The configuration options for servers are listed below.
...
seen in the 'Status' column.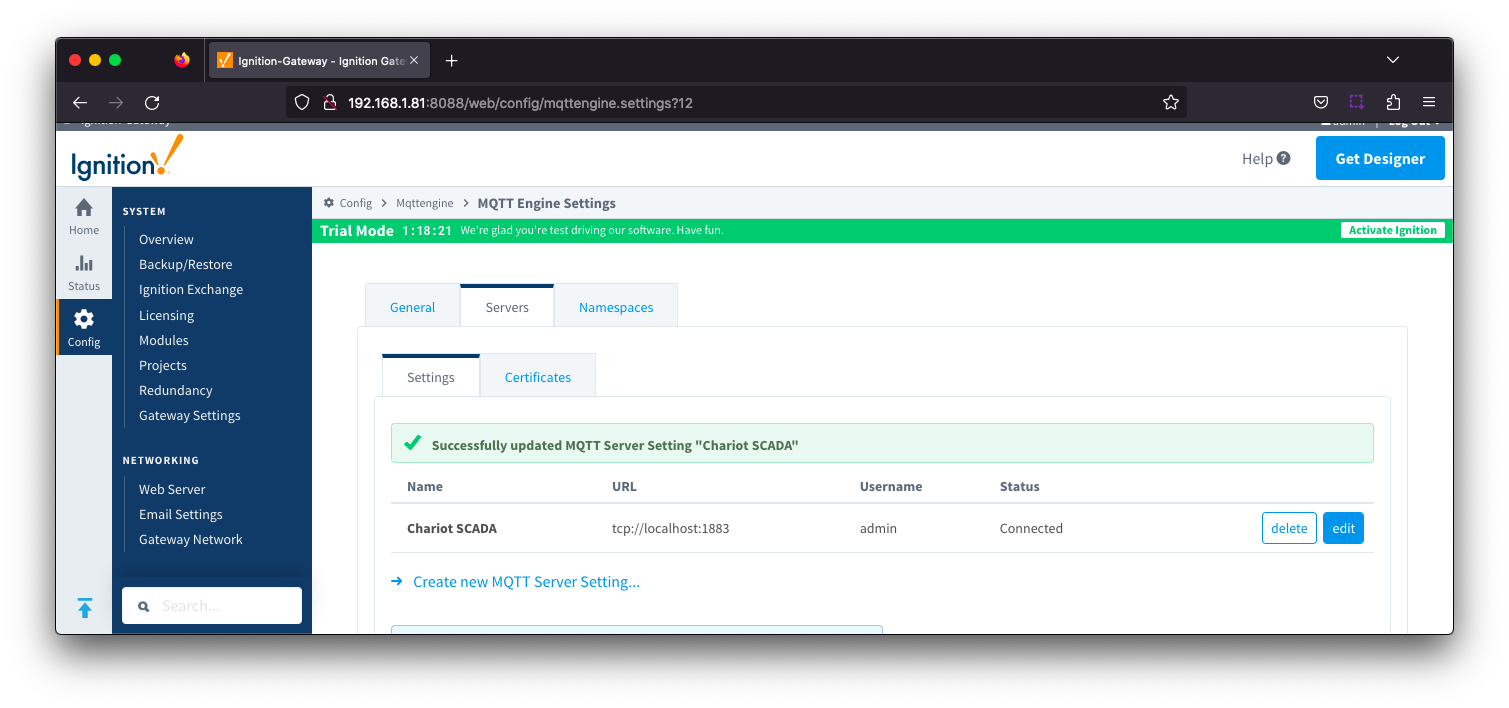 Image Added
Image Added
The configuration sections available are Main, TLS, Advanced and Advanced Legacy State
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServerSettingsMain |
|---|
| ServerSettingsMain |
|---|
|
Server Settings - Main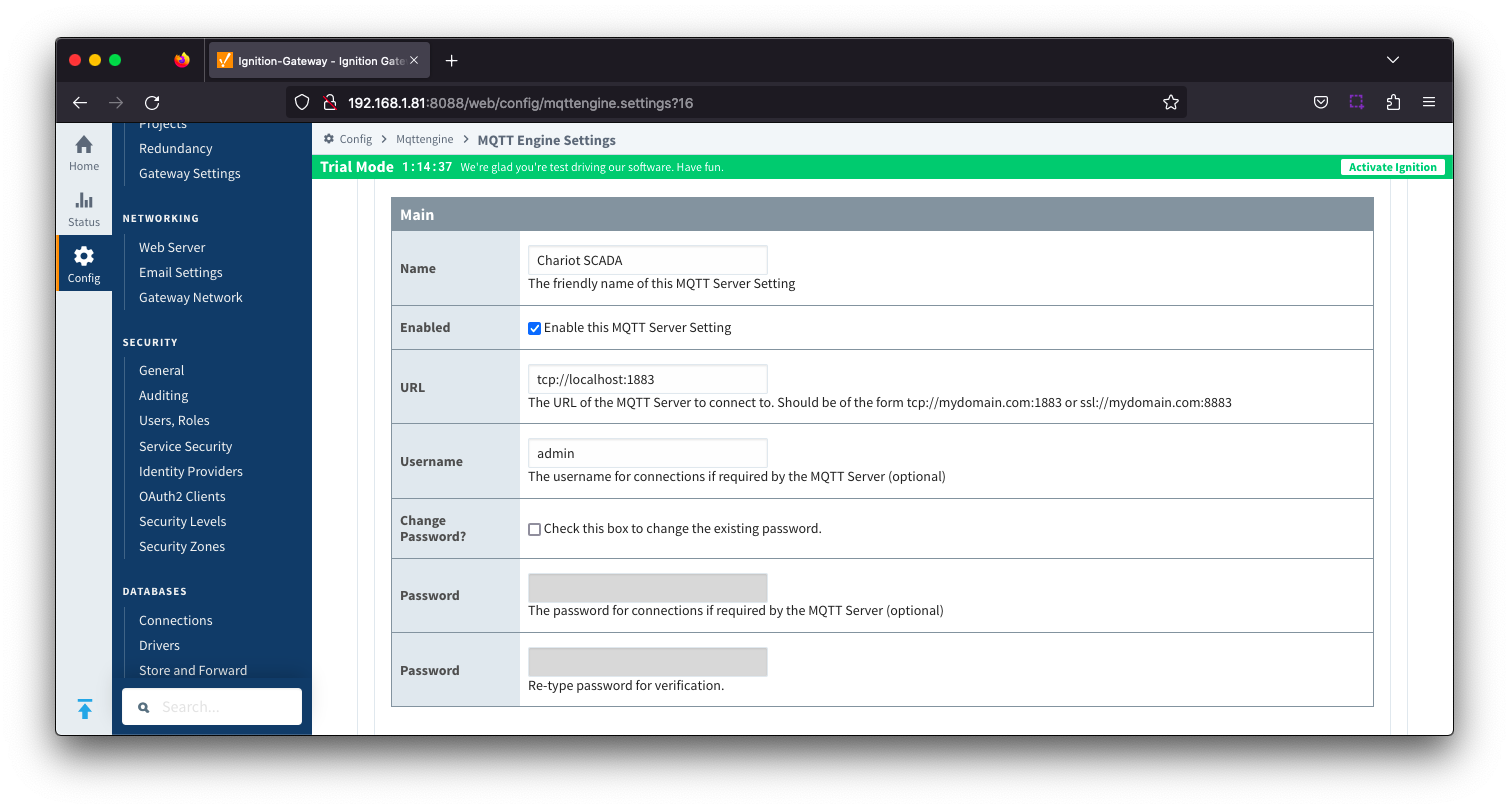 Image Added
Image Added- Name
- This is the friendly name of the MQTT Server used to easily identify it.
- Enabled
- Whether or not connections to this MQTT Server are enabled.
- URL
- This is the URL of the MQTT server. Its format is as follows: [protocol]://[location]:[port]. Each of these are shown below.
- protocol - Either tcp or ssl
- location - The server location. e.g. localhost, myserver.chariot.io, mydomain.com, etc
- port - The port the MQTT Server is listening on. Generally this is 1883 if using TCP or 8883 if using SSL
Server Type- This is the type of MQTT Server to connect to.
- Chariot - If connecting to a Cirrus Link Chariot on-premise or Chariot cloud based MQTT Server
- MQTT Distributor - If connecting to a Ignition MQTT Distributor server
- Third Party - If connecting to a third party 3.1.1 compliant MQTT Server
- Username
- Optional MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Password
- Optional MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServerSettingsTLS |
|---|
| ServerSettingsTLS |
|---|
|
Server Settings - TLS...
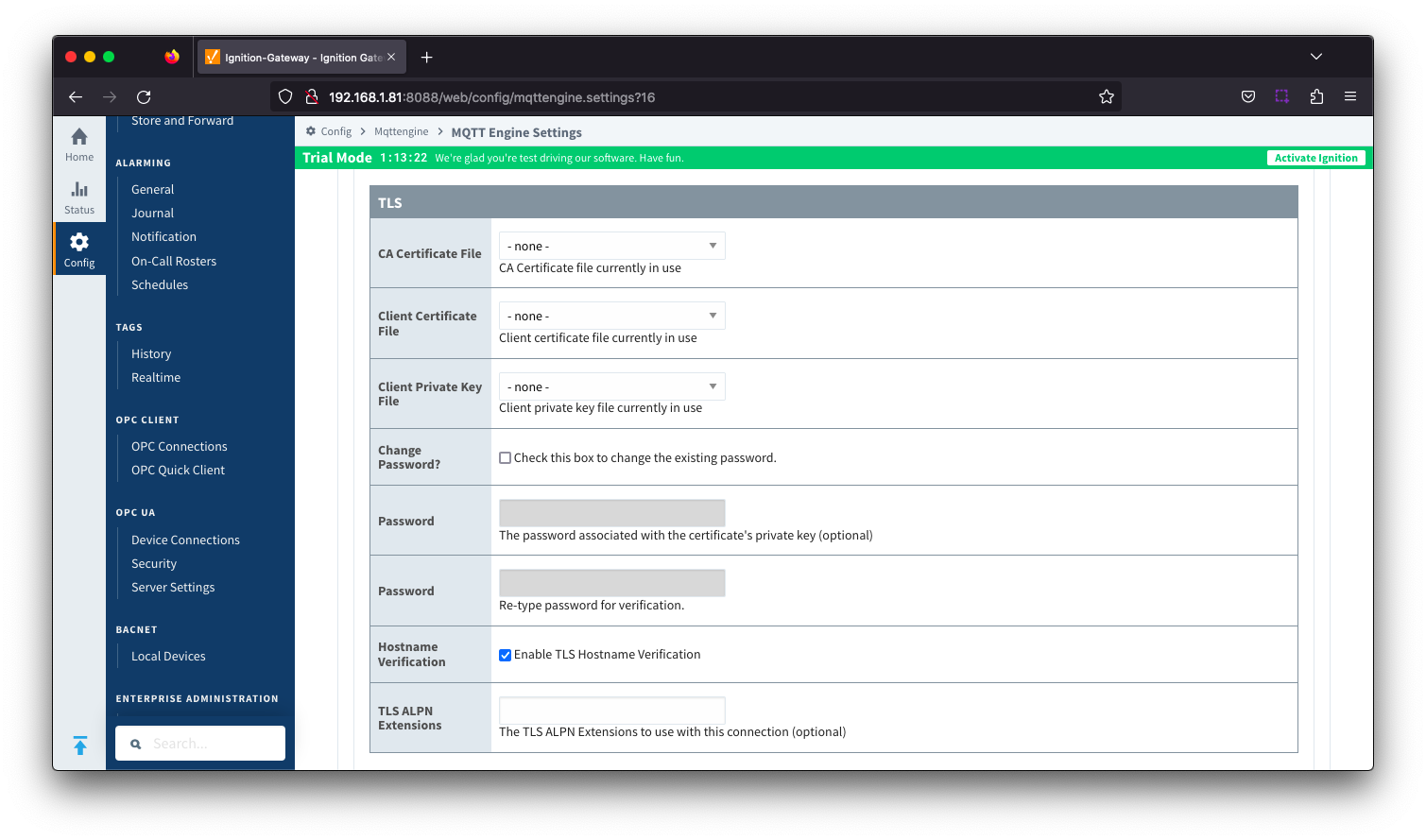 Image Added
Image Added
| Tip |
|---|
| See this document for TLS configuration: Secure MQTT Communications using SSL or TLS |
- CA Certification File
- CA Certification file currently in use.
- Client Certification File
- Client Certification file currently in use.
- Client Private Key File
- Client Private Key file currently in use
- Password
- Certificates
- The server certificates to use if required. These are generally only required when connecting using TLS and the MQTT server does not have a genuine certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority.
- CA certificate must always end in 'ca.pem'
- If using client side certificates (i.e. a public/private keypair and CA cert), make sure the following naming conventions are followed.
- Edge/Device certificate must end in 'cert.pem'
- Edge/Device private key must end in 'private.key'
- Password
- A password associated with the certificate's private key.
- Hostname Verification
- Enable TLS Hostname Verification. This is true by default.
- TLS ALPN Extensions
- Optional TLS ALPN Extensions, such as http/1.1, to use with this connection if supported by the MQTT Server.
...
| ServerSettingsAdvanced |
|---|
| ServerSettingsAdvanced |
|---|
|
Server Settings - Advanced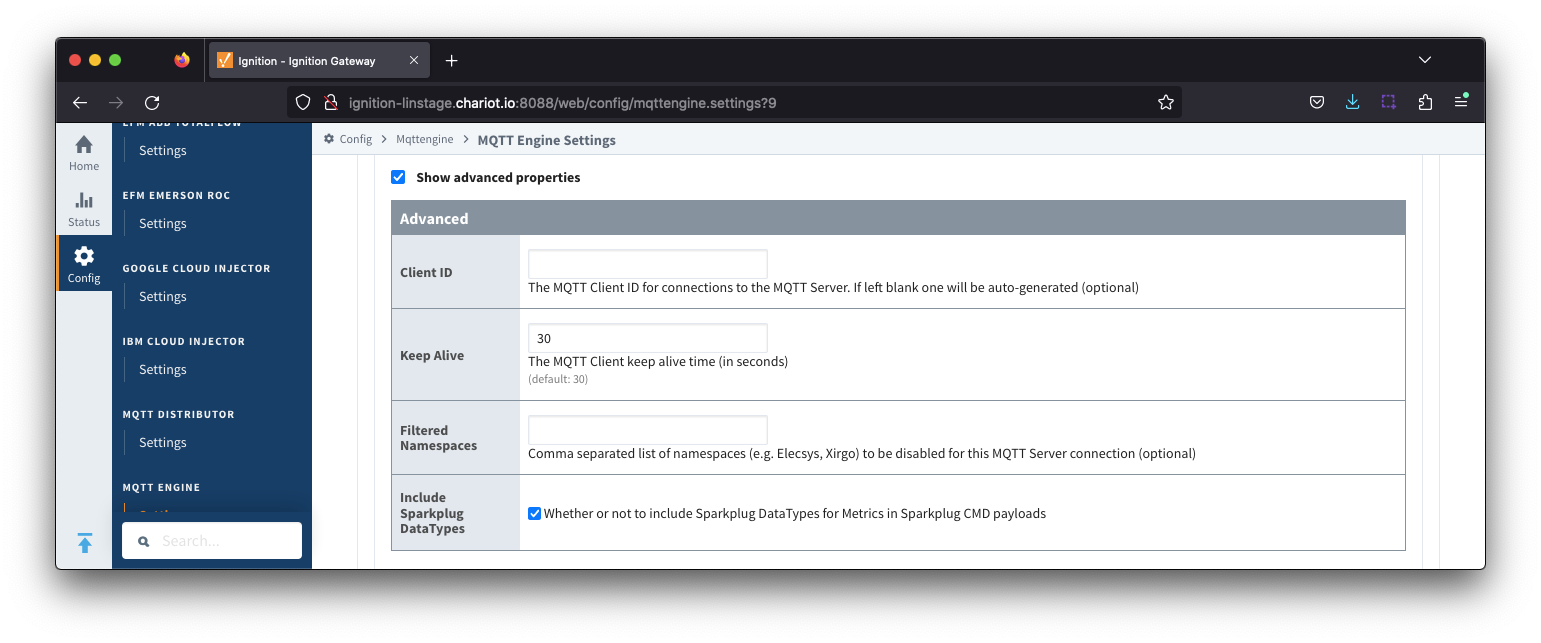 Image Added
Image Added- Client ID
- Optional MQTT client ID to use. If specified this will be used in the MQTT Engine connect packet when connecting to the server. If left blank, a random client ID will be create created of the form 'IgnitionTargetME-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx'.
| Warning |
|---|
| Caution: MQTT Clients IDs must be unique and if two clients attempt to connect with the same client ID, one will be forcefully disconnected from the server to allow the other client to connect. |
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT client keep alive time (maximum interval in seconds (5-65,535) between any two MQTT protocol control packets sent by the client to the server.
- Minimum Keep Alive for MQTT Engine is 5.
- If the client is idle and has no control packets to send, it will send PINGREQ protocol packet and the server is required to respond with a PINGRESP packet. If no response is received from the server within 1.5 times the Keep Alive, the client will close the connection.
If the server does not receive, at minimum, a PINGREQ message from a client within 1.5 times the Keep Alive, it will terminate the connection and send the client's LWT message if defined.
For MQTT Engine with Primary Host enabled, this is a message of format spBv1.0/STATE/primary_host_id with a payload {"online" : false, "timestamp" : 1668114759262}
- For MQTT Engine with Legacy Primary Host enabled, this is a message of format STATE/primary_host_id with a payload of OFFLINE
- Filtered Namespaces
- A comma separated list of namespaces that will be filtered/disabled for connections to this MQTT Server.
Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server...' link will bring up the following form to add a new Server.
- The default namespaces are Elecsys, Xirgo, Sparkplug A and Sparkplug B.
- Include Sparkplug DataTypes
- Whether or not to include Sparkplug DataTypes for Metrics in Sparkplug CMD payloads
- Enabled by default
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServerSettingsAdvancedLegacy |
|---|
| ServerSettingsAdvancedLegacy |
|---|
|
Server Settings - Advanced Legacy StateFrom release 4.0.14 MQTT Engine will support the new STATE message format and be in compliance with MQTT Sparkplug™ B specification v3.0.0.
However as there will still be many existing clients which are only compatible with the MQTT Sparkplug™ B specification v2.2, we have made changes to MQTT Engine to establish a MQTT client whose only function is to publish the STATE message in its legacy format.
If you are updating from a previous version of MQTT Engine to v4.0.14, the configuration of the Legacy State template will be completed as part of the upgrade process and the Legacy Client enabled.
| Note |
|---|
| Note: For some MQTT servers, the Username/Password for each client connection must be unique and so these parameters for the second legacy client will need to be edited |
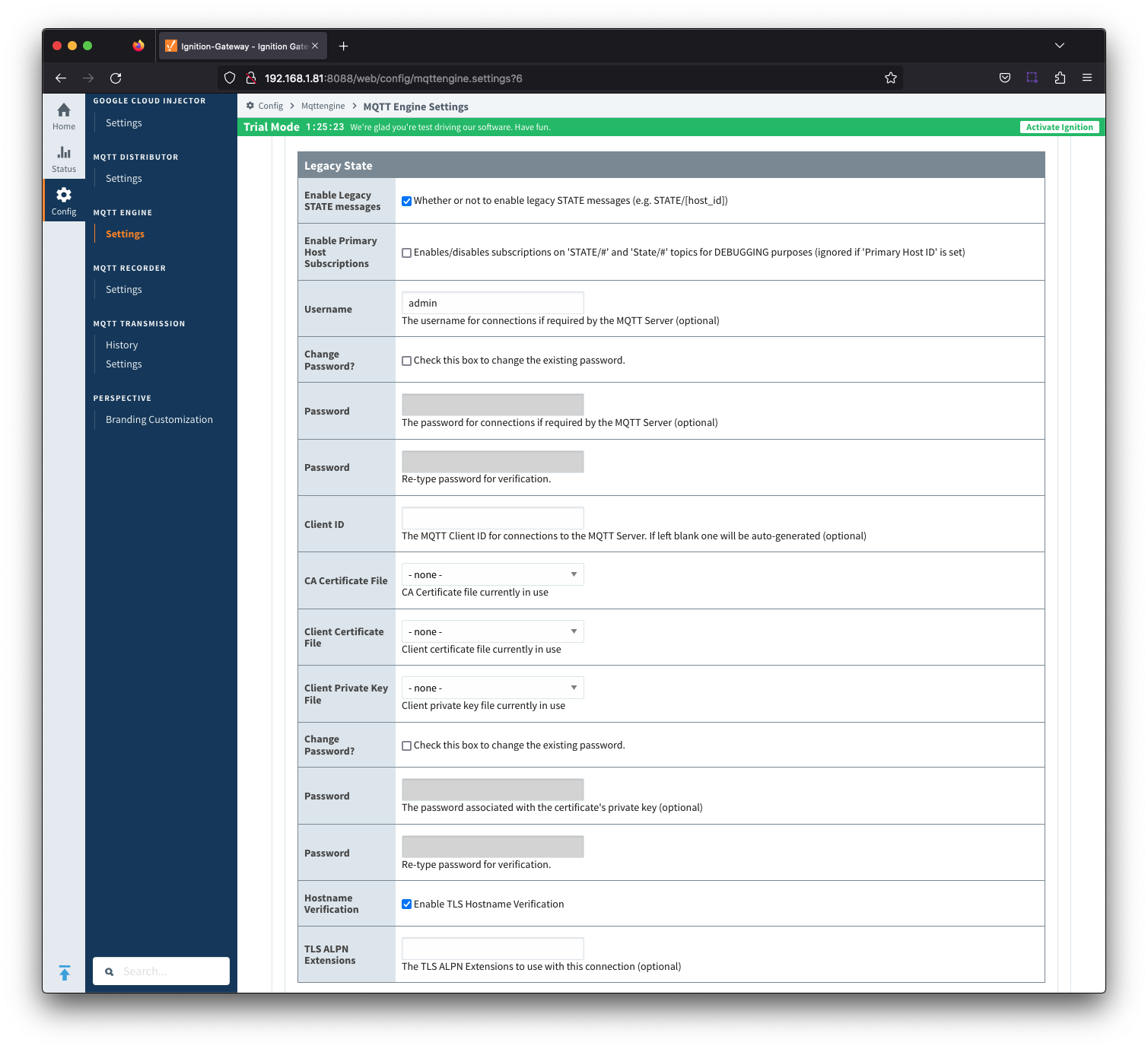 Image Added
Image Added
- Enable Legacy STATE messages
- Whether or not connections to enable legacy STATE messages (e.g. STATE/[host_id]). This is false by default unless upgrading from a previous module version.
Enable Primary Host Subscriptions
- Whether or not to enable MQTT Engine subscriptions on legacy STATE/# and State/# topics.
- Requires that Enable Legacy STATE messages is TRUE and Primary Host Enabled is FALSE and/or Primary Host ID is null.
- This setting is for debugging purposes only.
- Username
- Optional MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Password
- Optional MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Client ID
- The MQTT Client ID for connections to the MQTT Server. If left blank one will be auto-generated of the form ME-LS-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx
- CA Certification File
- CA Certification file currently in use.
- Client Certification File
- Client Certification file currently in use.
- Client Private Key File
- Client Private Key file currently in use
- Password
- Optional password associated with the certificate's private key.
- Hostname Verification
- Enable TLS Hostname Verification. This is true by default.
- TLS ALPN Extensions
- Optional TLS ALPN Extensions to use with this connection
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServersCertificates |
|---|
| ServersCertificates |
|---|
|
Servers - CertificatesThis tab provides a list of the certificate or private key files if loaded and available for TLS configuration.
| Note |
|---|
All certificate or private keys must be in PEM format. If using modules pre 4.0.9, any private key file must also be in RSA PKCS1 format. If using modules 4.0.9 or greater, any private key must also be in either RSA PKCS1 or PKCS8 format. |
 Image Added
Image Added
The Certificates tab contains a single Main section.
| Anchor |
|---|
| ServersCertificatesMain |
|---|
| ServersCertificatesMain |
|---|
|
Servers Certificates - Main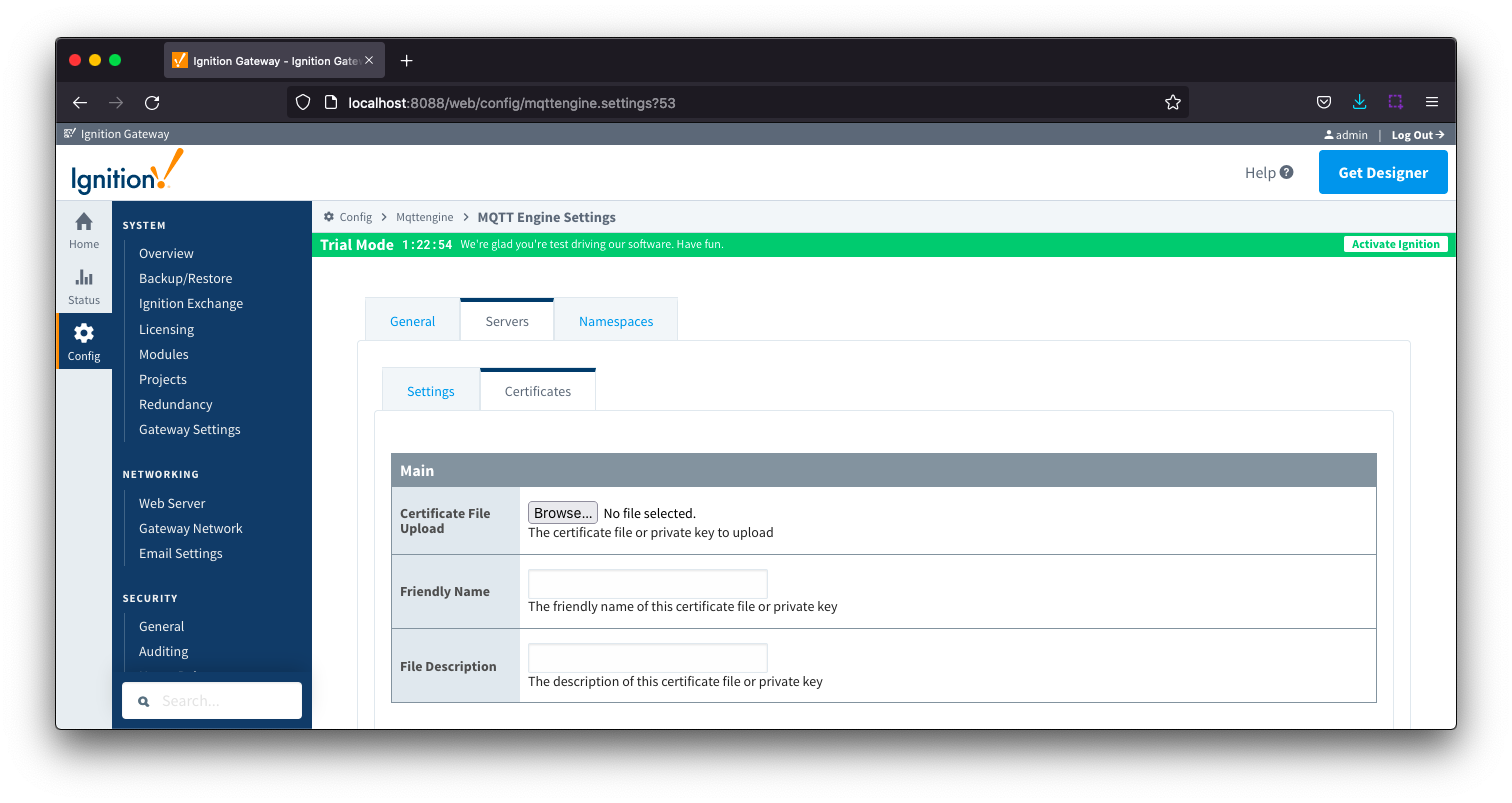 Image Added
Image Added- Certificate File Upload
- Browse to the certificate file or private key to upload.
- Friendly Name
- The friendly name of the certificate file or private key.
- File Description
- The description of the certificate file or private key.
...
NamespacesThe third tab is used for configuring namespaces. Each namespace configuration represents a family of devices and/or data that MQTT Engine will support. A namespace defines the topics that each MQTT Engine client will subscribe on as well as indicates how the payload will be handled. There are two types of namespaces:
 Image Added
Image Added
The Namespace tab has two parts - Default and Custom.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesDefault |
|---|
| NamespacesDefault |
|---|
|
Namespaces Default...
Default namespaces are provided out of the box and can simply be enabled or disabled. When MQTT Engine is first installed, all non Sparkplug B default namespaces are enabled. Each default namespace has the following properties:disabled.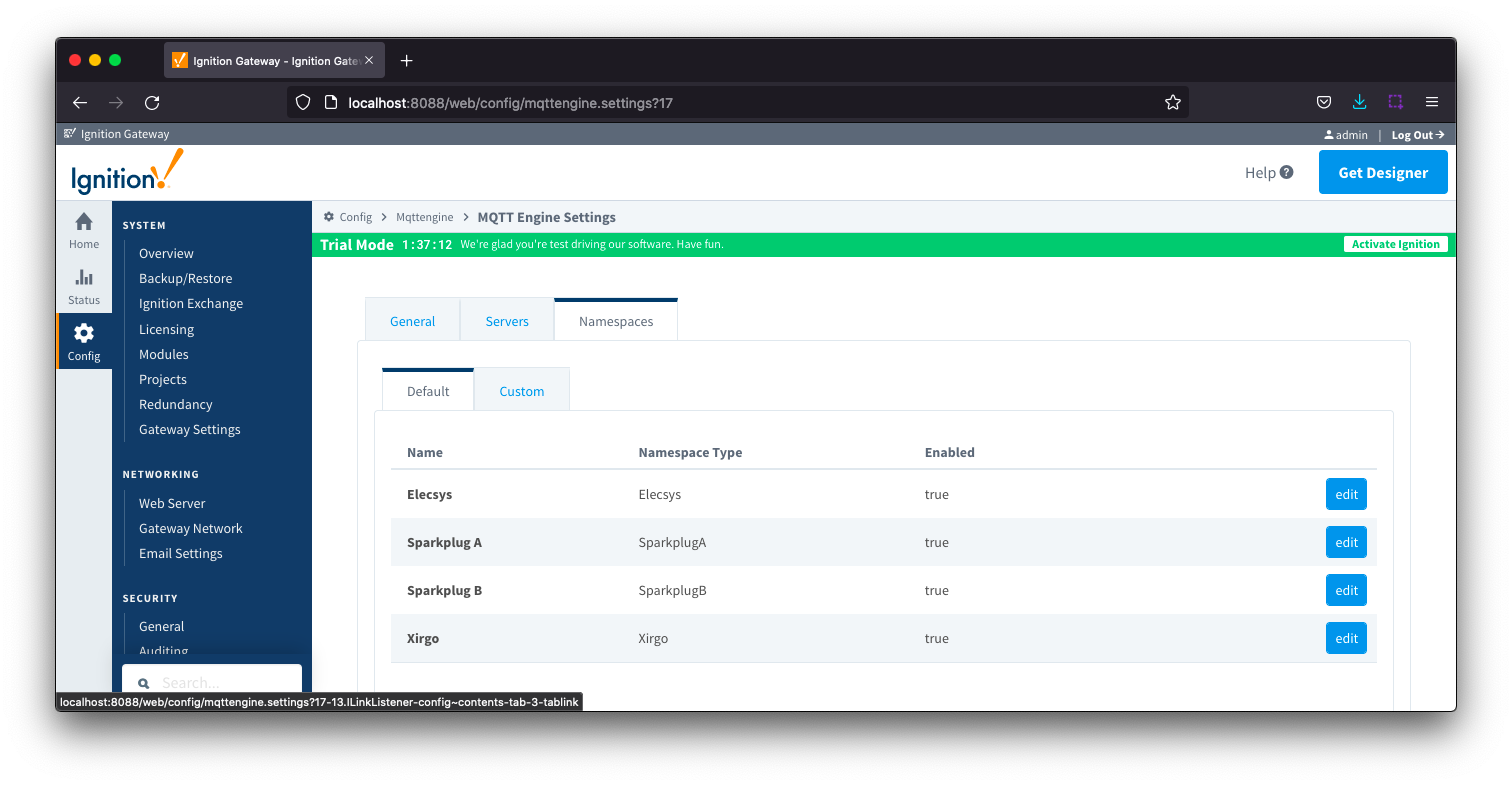 Image Added
Image Added
The Default tab has four parts - General, Filters, Files and String Conversions
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultGeneral |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultGeneral |
|---|
|
Namespaces Default - General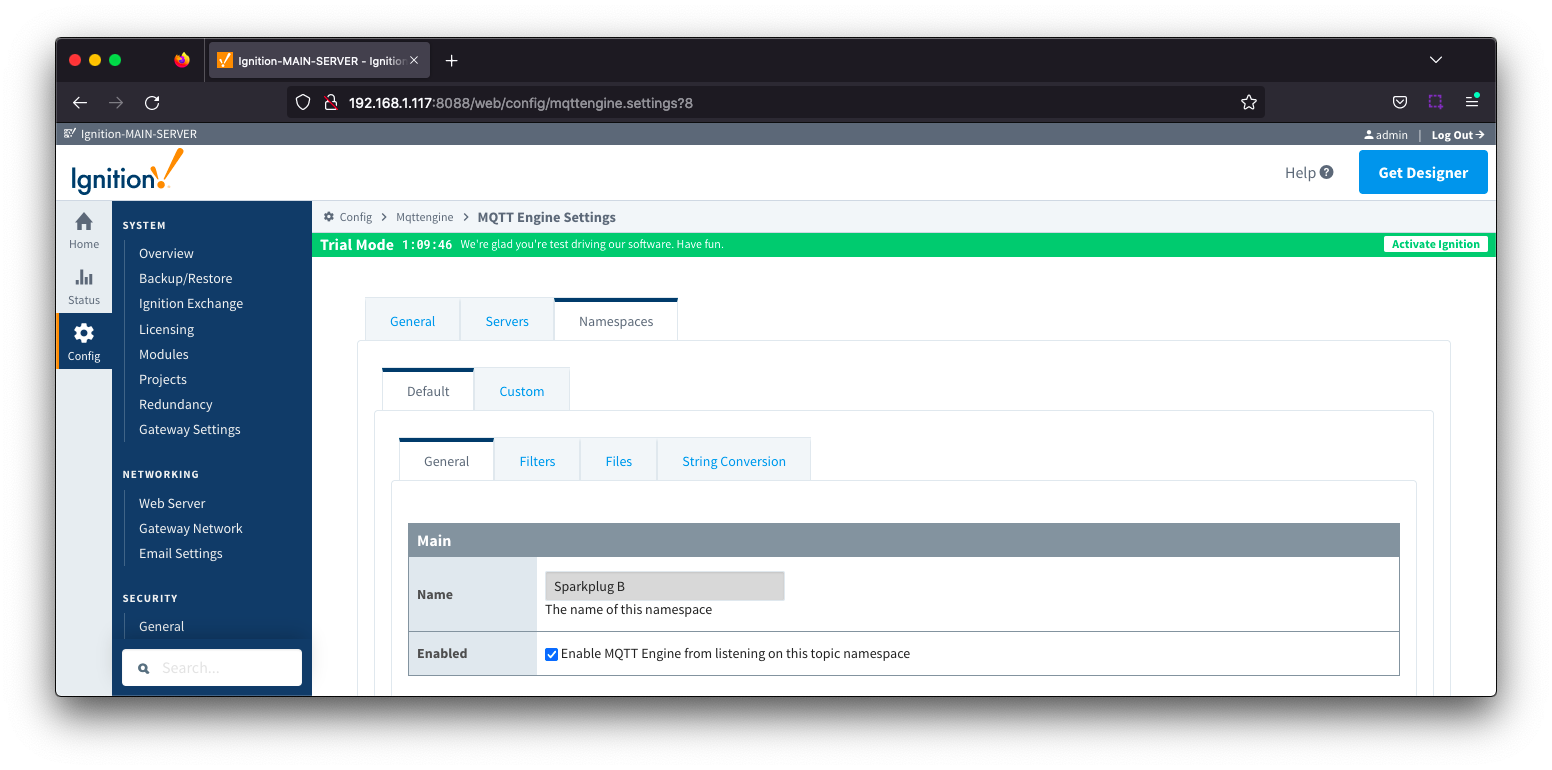 Image Added
Image Added
- Name
- A friendly name of the namespace to easily identify it.
- Namespace Type
- Enabled
- Whether or not the namespace is enabled.
- If
...
- enabled, MQTT Engine will subscribe to the topics necessary to provide support for devices and data associated with that namespace. If
...
- disabled, MQTT Engine will unsubscribe from those topics and no longer support the devices and data associated with that namespace.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultFilters |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultFilters |
|---|
|
Namespaces Default - FiltersNamespace filters allows you to specify Group or Group/EdgeNode combinations which will be included in the MQTT Engine subscriptions for this specific namespace.
From MQTT Engine 4.0.16 and newer, it also allows for the filters to be applied to specific MQTT Servers.
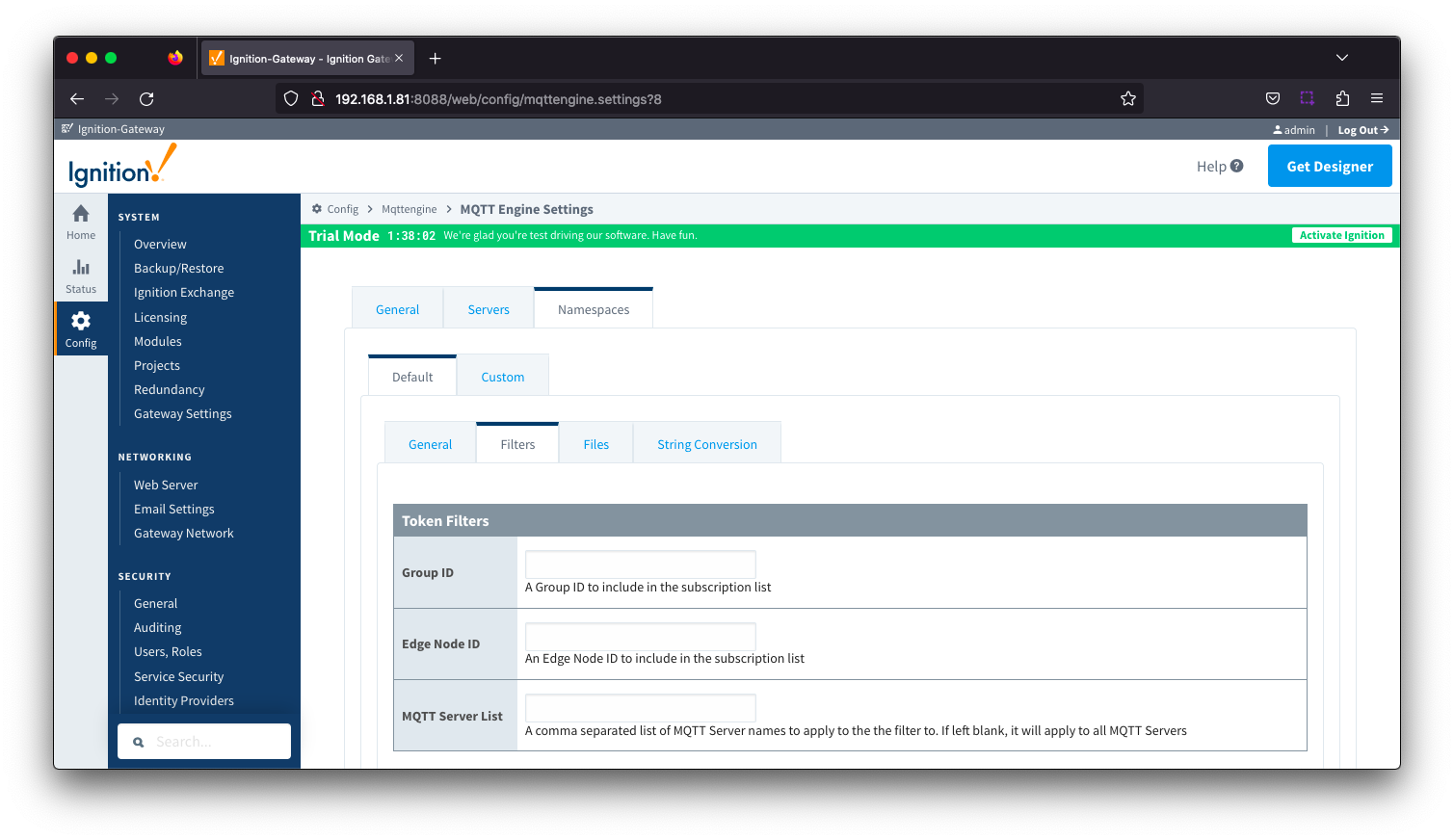 Image Added
Image Added
- Group ID
- The Group ID to be included in the MQTT Engine subscriptions for this specific namespace.
- Edge Node ID
- Edge Node ID to be included in the MQTT Engine subscriptions for this specific namespace.
- MQTT Server List
- A comma separated list of MQTT Server names to apply the filter to. If left blank, it will apply to all MQTT Servers
Additional detail on the default namespaces is available here.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultFiles |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultFiles |
|---|
|
Namespaces Default - Files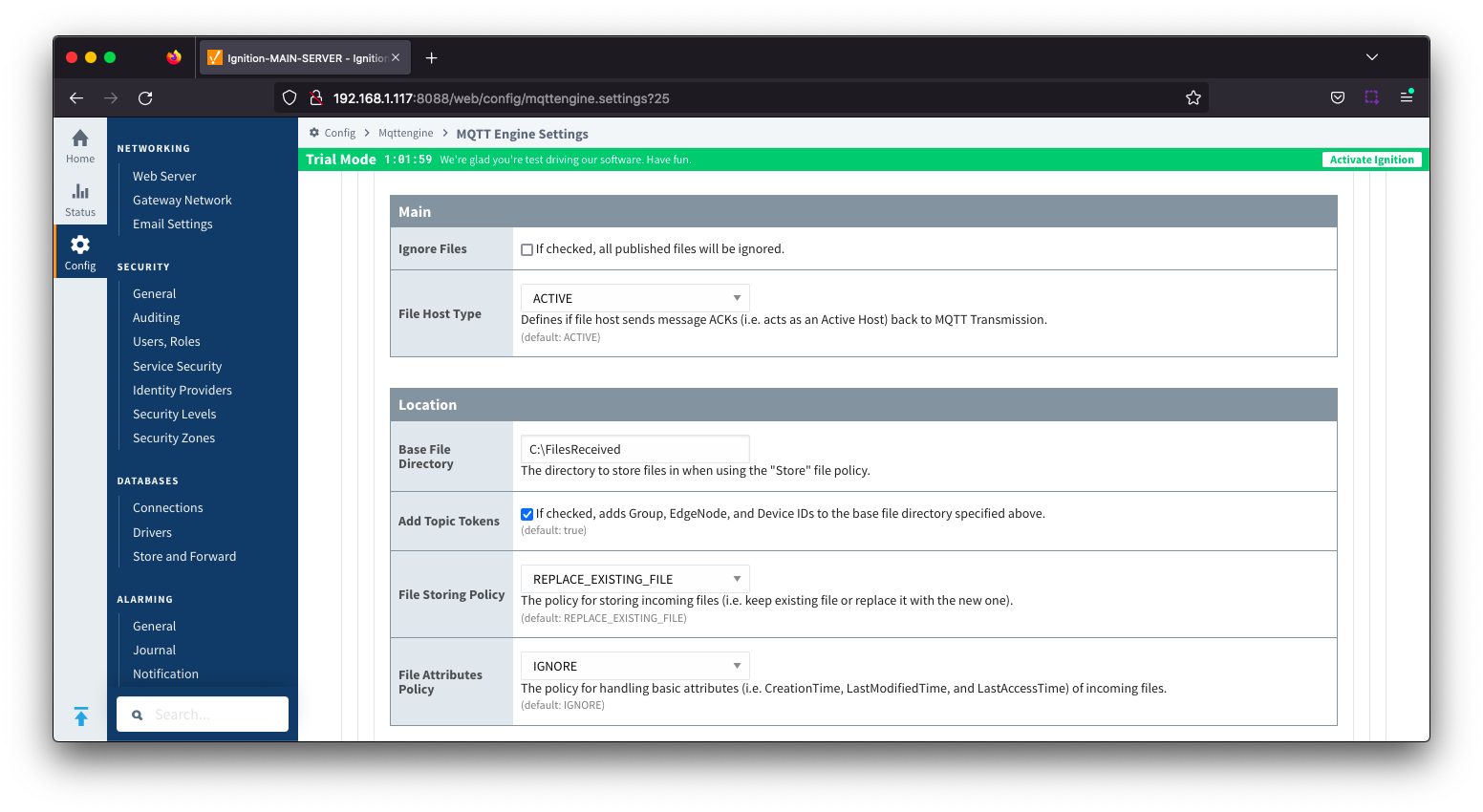 Image Added
Image Added
- Main
- Ignore Files
- Default: Unchecked.
- If checked, all published files will be ignored
- File Host Type
...
- Host will send message ACKs back to MQTT Transmission acting as an Active Host
- Options are ACTIVE and PASSIVE
- Location
- Base File Directory
- The directory to store files when 'Ignore Files' is unchecked
- Add Topic Tokens
- Default: Checked. If selected, appends the Group ID, Edge Node Id and device ID to the Base File Directory when storing files
- File Storing Policy
- The file policy for storing incoming files. Options are REPLACE_EXISTING_FILE and KEEP_EXISTING_FILE
- Default: REPLACE_EXISTING_FILE
- File Attributes Policy
- The policy for handling basic file attributes such as CreationTime, LastModifiedTime and LastAccessTime of incoming files. Options are IGNORE, APPEND_TO_FILENAME, UPDATE_FILE_ATTRIBUTES and APPEND_AND_UPDATE
- Default is IGNORE
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultStringConversion |
|---|
| NamespacesDefaultStringConversion |
|---|
|
Namespaces Default - String Conversion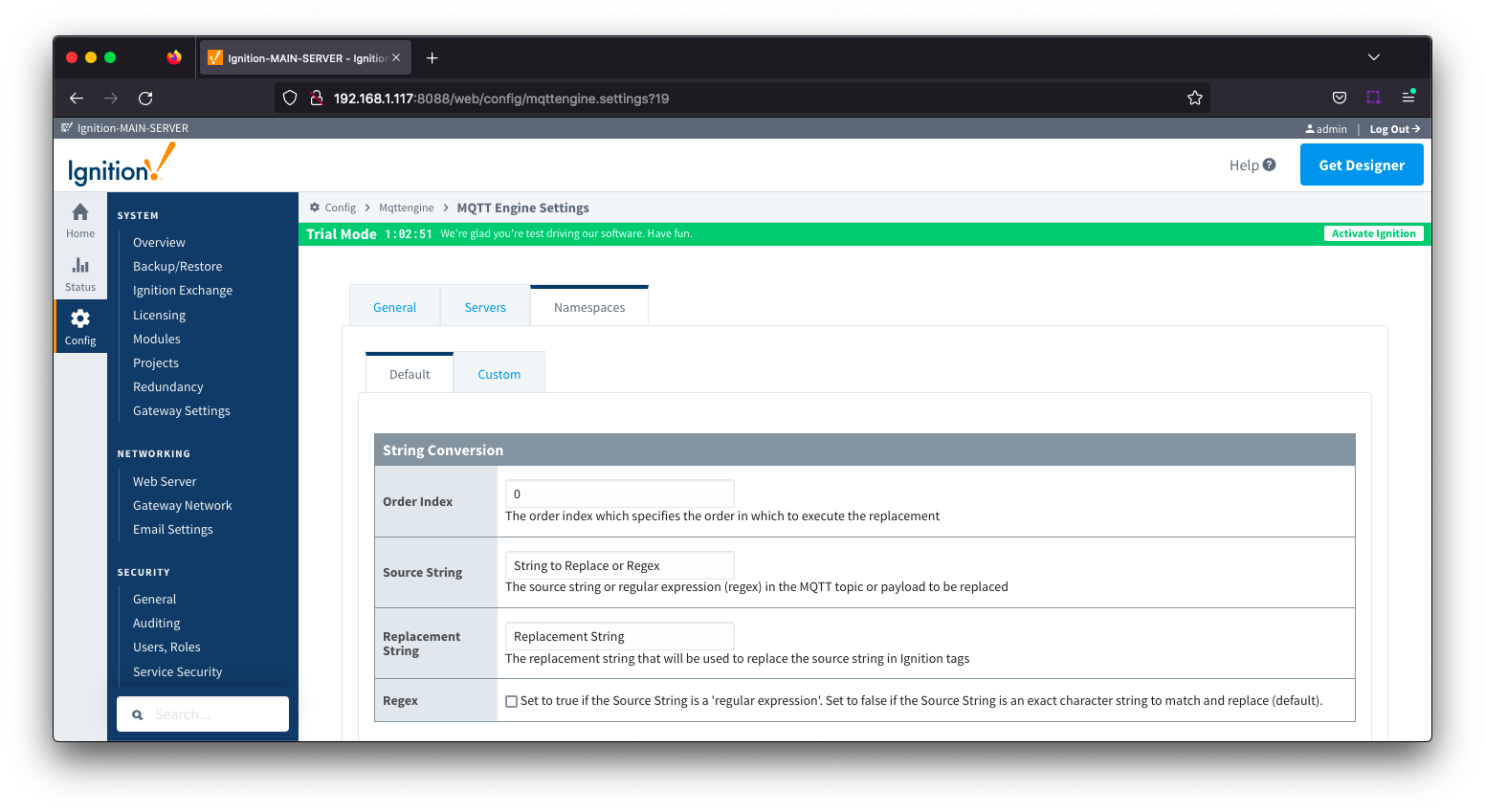 Image Added
Image Added
- Order Index
- The order index which specifies the order in which to execute the replacement
- Source String
- Free form field for the source string or regular expression (regex) in the MQTT Topic or payload to be replaced
- Replacement String
- Free form field for the replacement string that will be used to replace the source string in Ignition tags
- Regex
- If checked, the source string will be treated as a 'regular expression'
- If unchecked, the source string is an exact character string to match and replace
- Default: unchecked
Reference the MQTT Engine String Replacement HowTo tutorial for additional details
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustom |
|---|
| NamespacesCustom |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom
Custom Namespaces
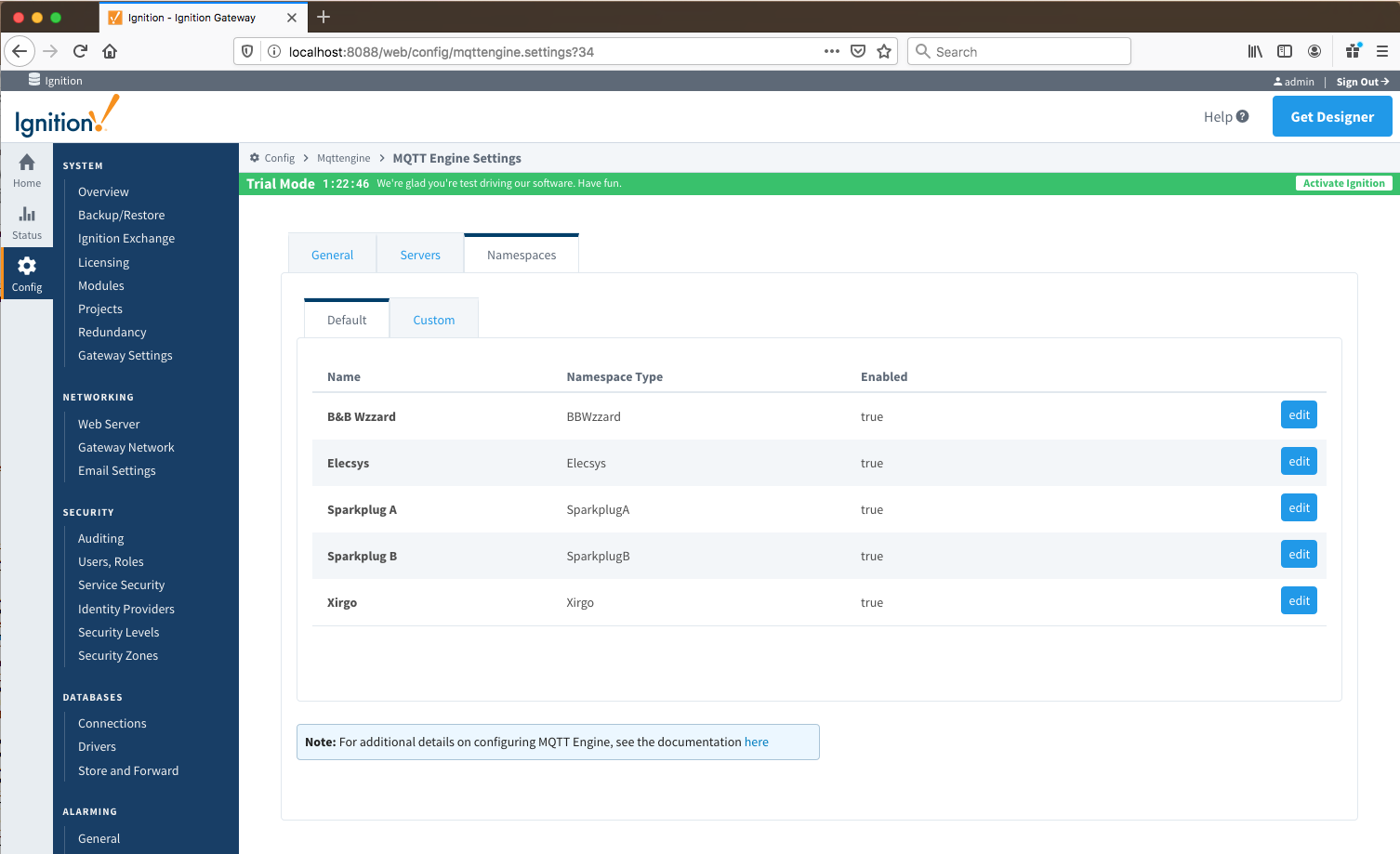 Image Removed
Image Removed
Custom Namespaces
Custom namespaces are used to provide support for generic, non Sparkplug compliant MQTT messages with string based payloads. If If a custom namespace is configured MQTT Engine will convert all messages received to tags . The where the topic of each message will translate directly translate into to the tag's path . The payload of the message and the payload will be that the tag's value. .
| Note |
|---|
| We recommend disabling the Sparkplug B default namespace if defining a custom namespace. |
MQTT Engine supports MQTT Engine String Replacement for both MQTT Topics and Payloads for character sequences that will become part of an Ignition tag path.
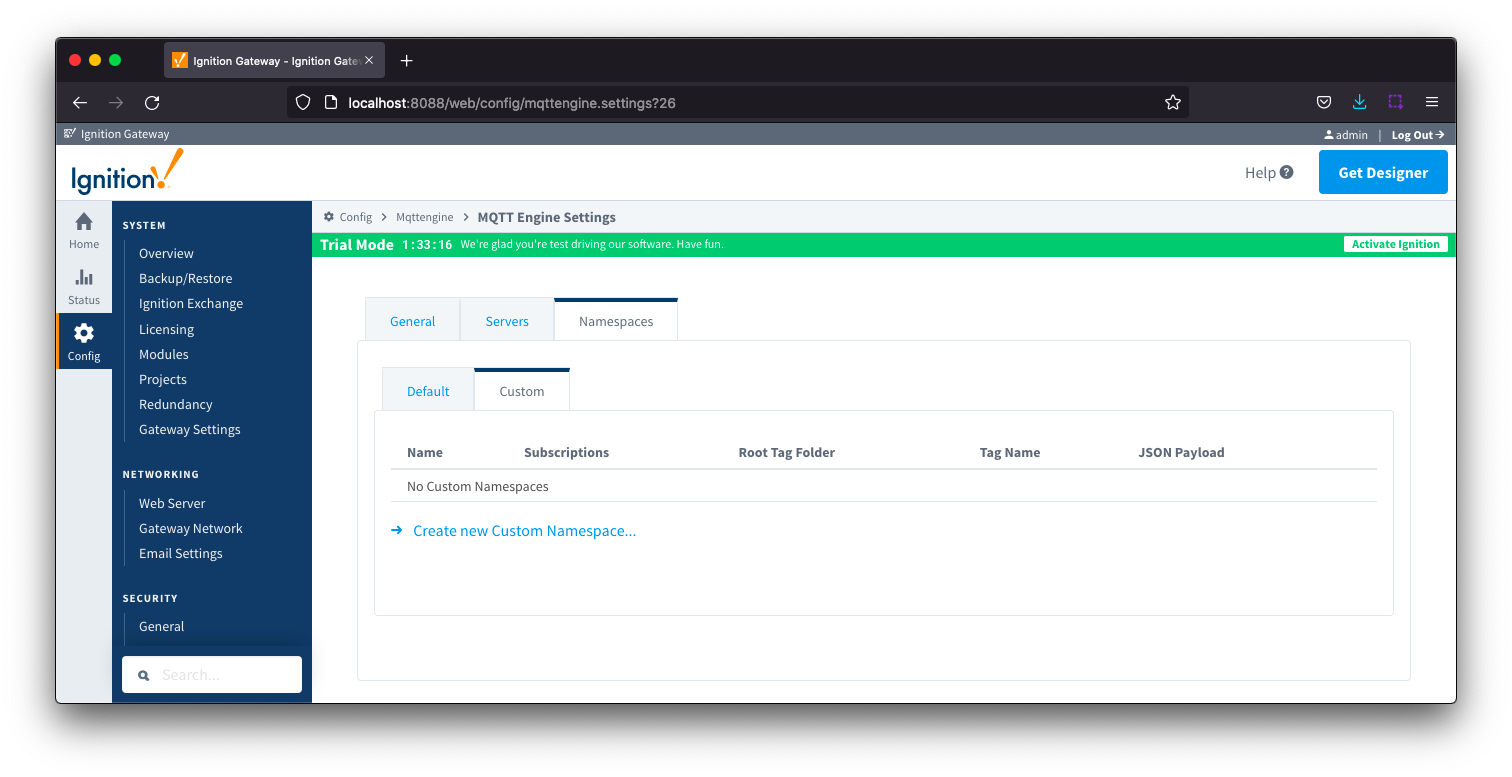 Image Added
Image Added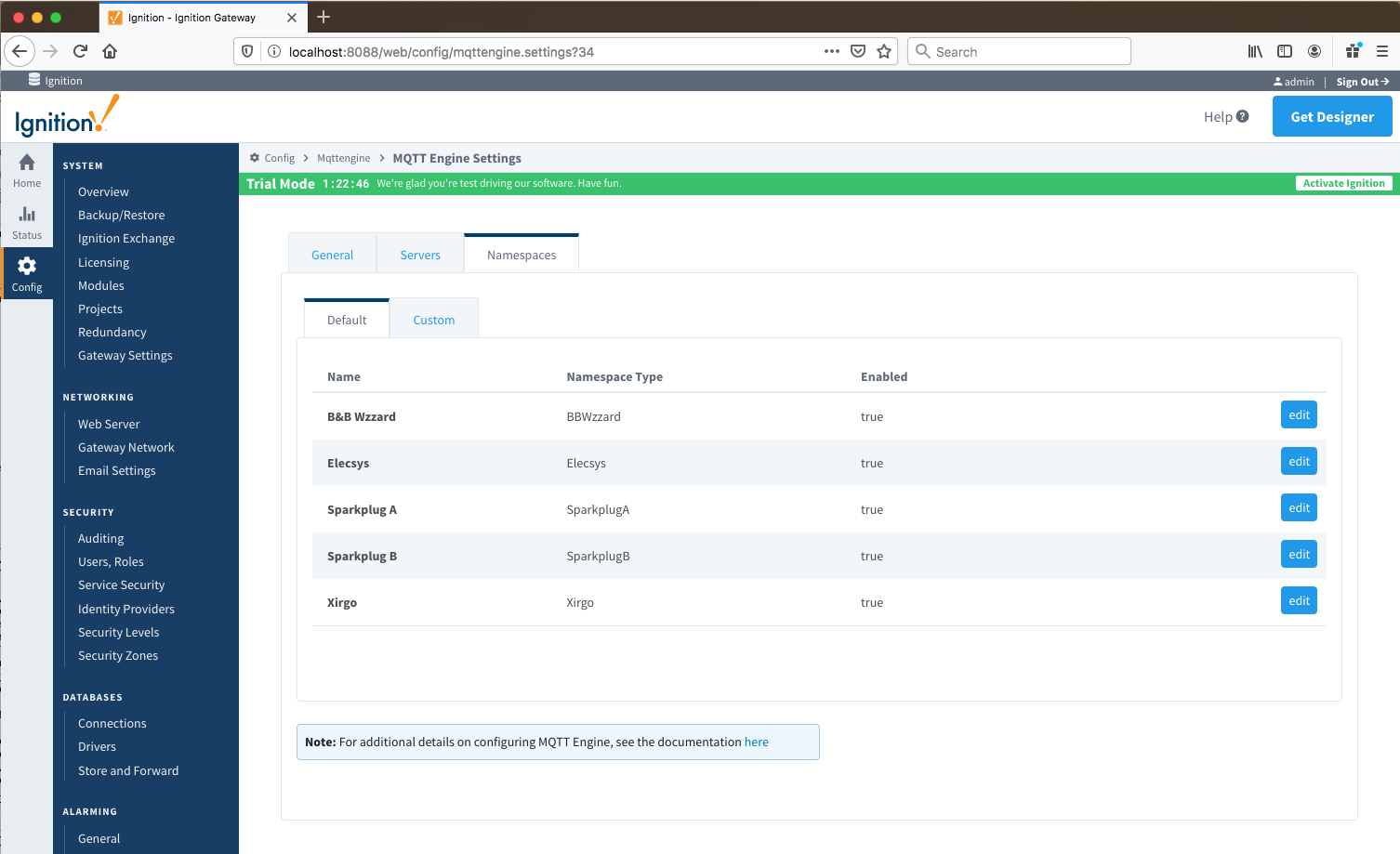 Image Removed
Image Removed
Each custom namespace has the following properties:
Main
configuration has two parts - General andString Conversion.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneral |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneral |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom GeneralThe configuration sections available are Main, Optional and Advanced.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralMain |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralMain |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom - General Main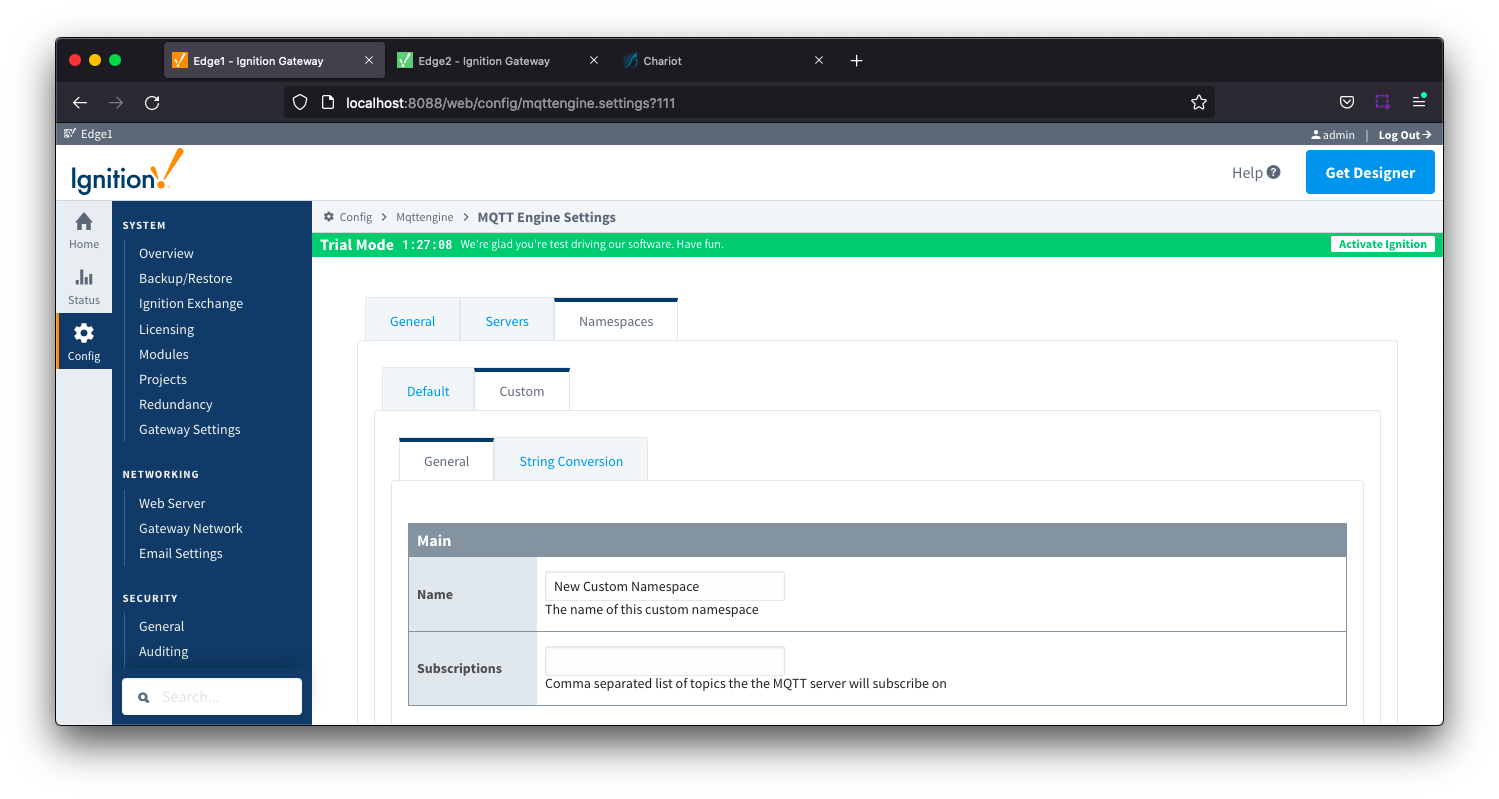 Image Added
Image Added
- Name
- A friendly name of the namespace to easily identify it.
- Subscriptions
- A comma separated list of subscriptions and supports both the multi-level (#) and single level (+) wild card characters.
(+) is a a single level wildcard that matches any name for a specific topic level. This can be used instead of specifying a name for any topic level in the topic filter.
(#) is a multi level wildcard that can only be used at the end of the topic filter as the last level and matches any topic whose first levels are the same as the topic levels specified at the left-hand side of the # symbol.
| Warning |
|---|
Check your MQTT Topic subscriptions to verify if they contain valid Ignition tag path or tag name characters. View the Ignition Understand Tag Naming document for details on the tag name rules. While MQTT and Sparkplug both support characters such as . & % =, Ignition does not support these as valid characters in a tag path or tag name and as a result, it may be necessary to tell MQTT Engine to replace certain characters or strings of characters with something else so the tag path and tag names can be properly created in Ignition. Reference the MQTT Engine String Replacement HowTo for additional details on how to use this configuration. |
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralOptional |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralOptional |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom - General Optional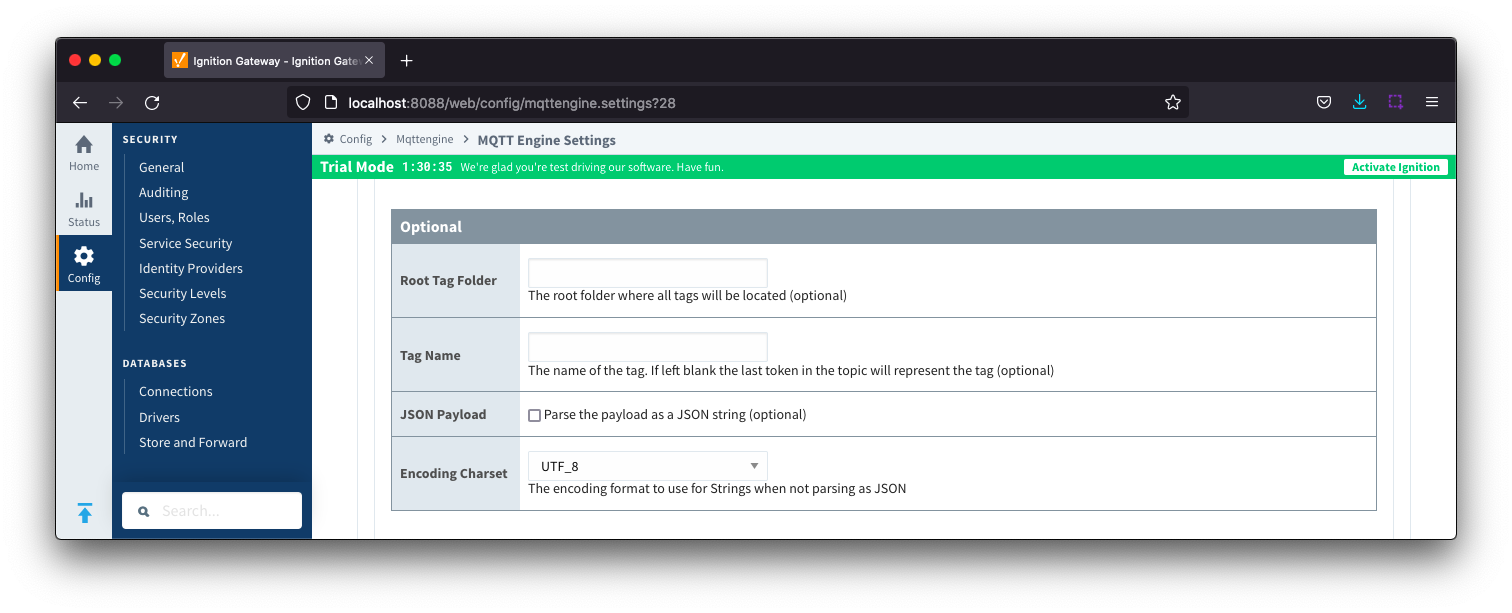 Image Added
Image Added
- Root Tag Folder
- A name of a folder where all tags will be stored. If configured, this folder will be the base folder where all tag paths will start.
- Tag Name
- A tag name to be used for all tags. If not configured, the last token in the topic will represent the tag.
- JSON Payload
- A Optional flag to indicate that the content of the string based payload is a JSON object.
- Encoding Charset
- The encoding format to use when not parsing as JSON.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralAdvanced |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomGeneralAdvanced |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom - General Advanced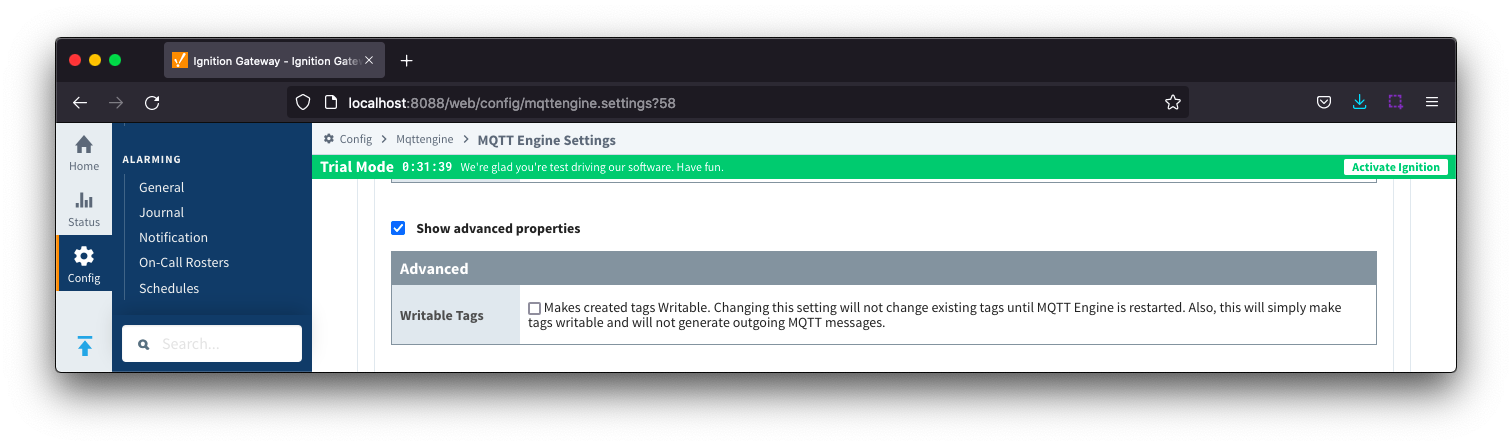 Image Added
Image Added- Writable Tags
- Enables writes on tags created by the Custom Namespace. Note: This will only make the tags writable; it will not result in outgoing MQTT messages.
Note: if a Tag Name is not specified, care must be taken so that published messages do not end up overwriting previous tags.
Clicking on the 'Create new Custom Namespace...' link will bring up the following form to add a new Custom Namespace.
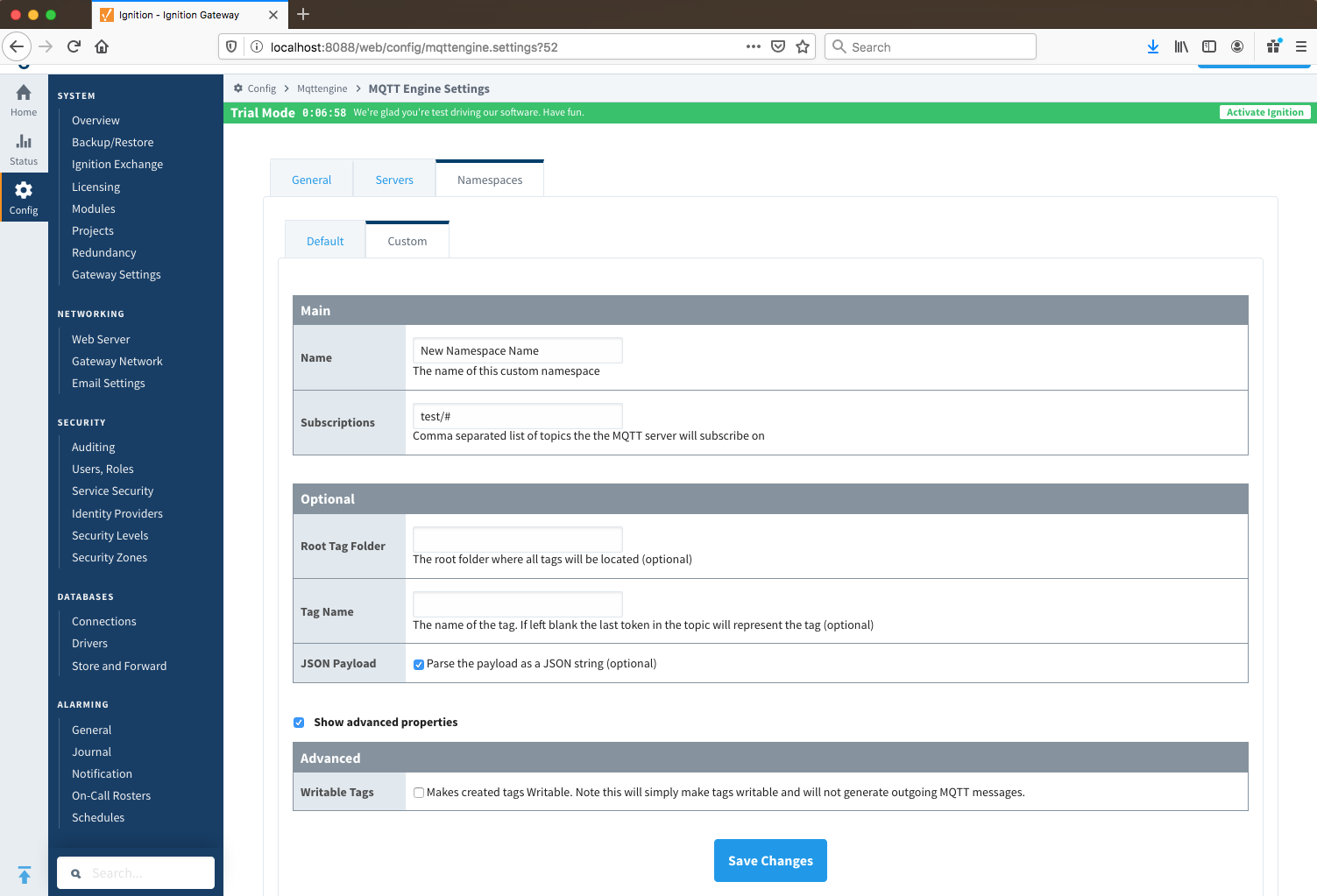 Image Removed
Image Removed
Custom Namespace Example
Let say we have a publish received on the topic "test/data/point" with value "12345". If no Tag Value is configured, and a message is received, MQTT Engine will create a two folders "test" and "data" and a tag "point" with the value of "12345".
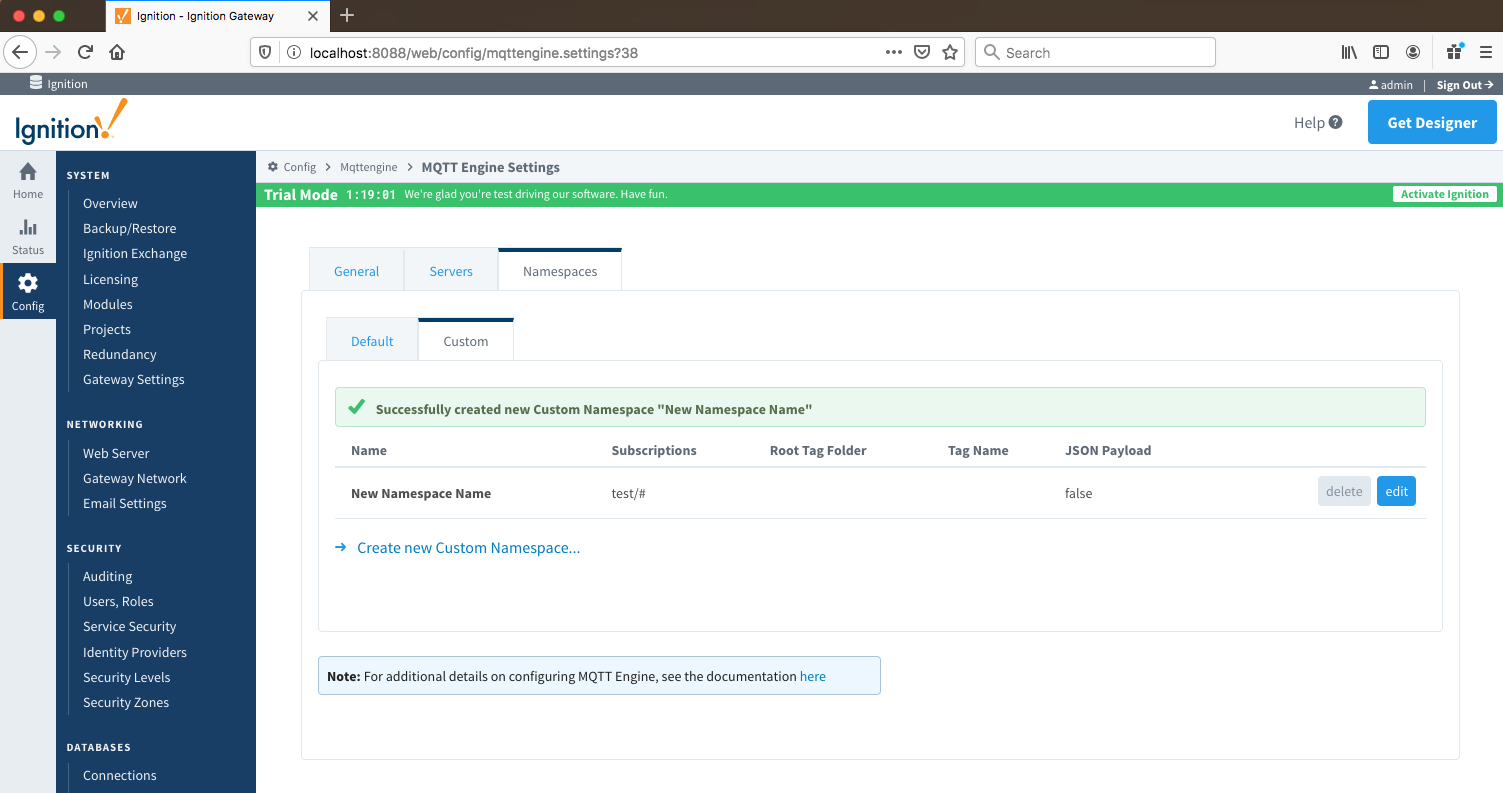 Image Removed
Image Removed
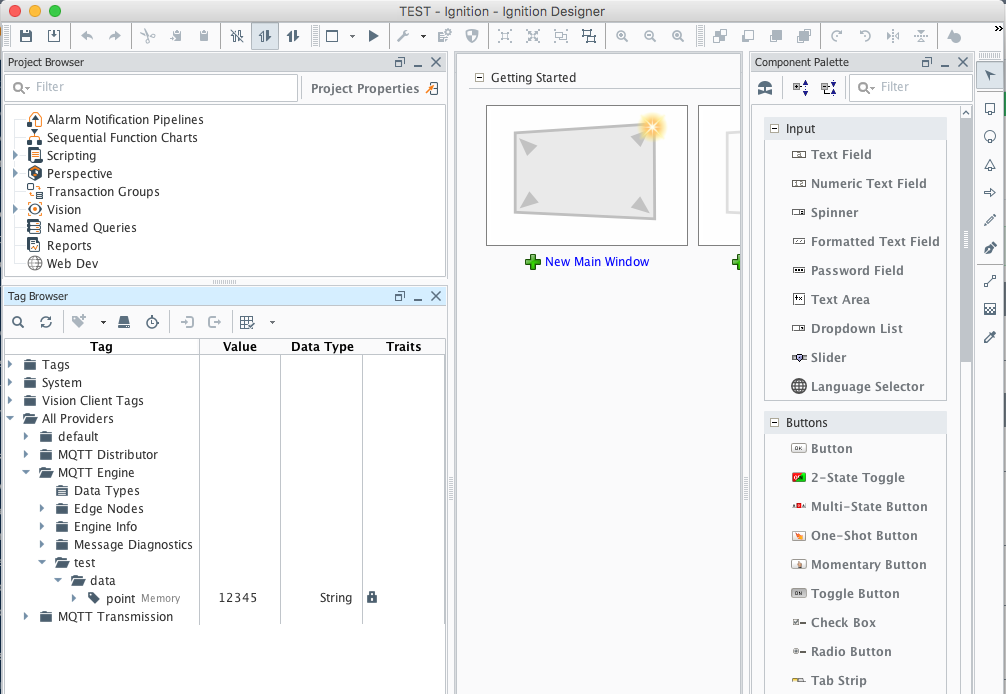 Image Removed
Image Removed
Alternatively if a Tag Name is configured, lets call it "payload", then MQTT Engine will convert each token in the topic to a folder and create a tag called "payload" with the value "12345"
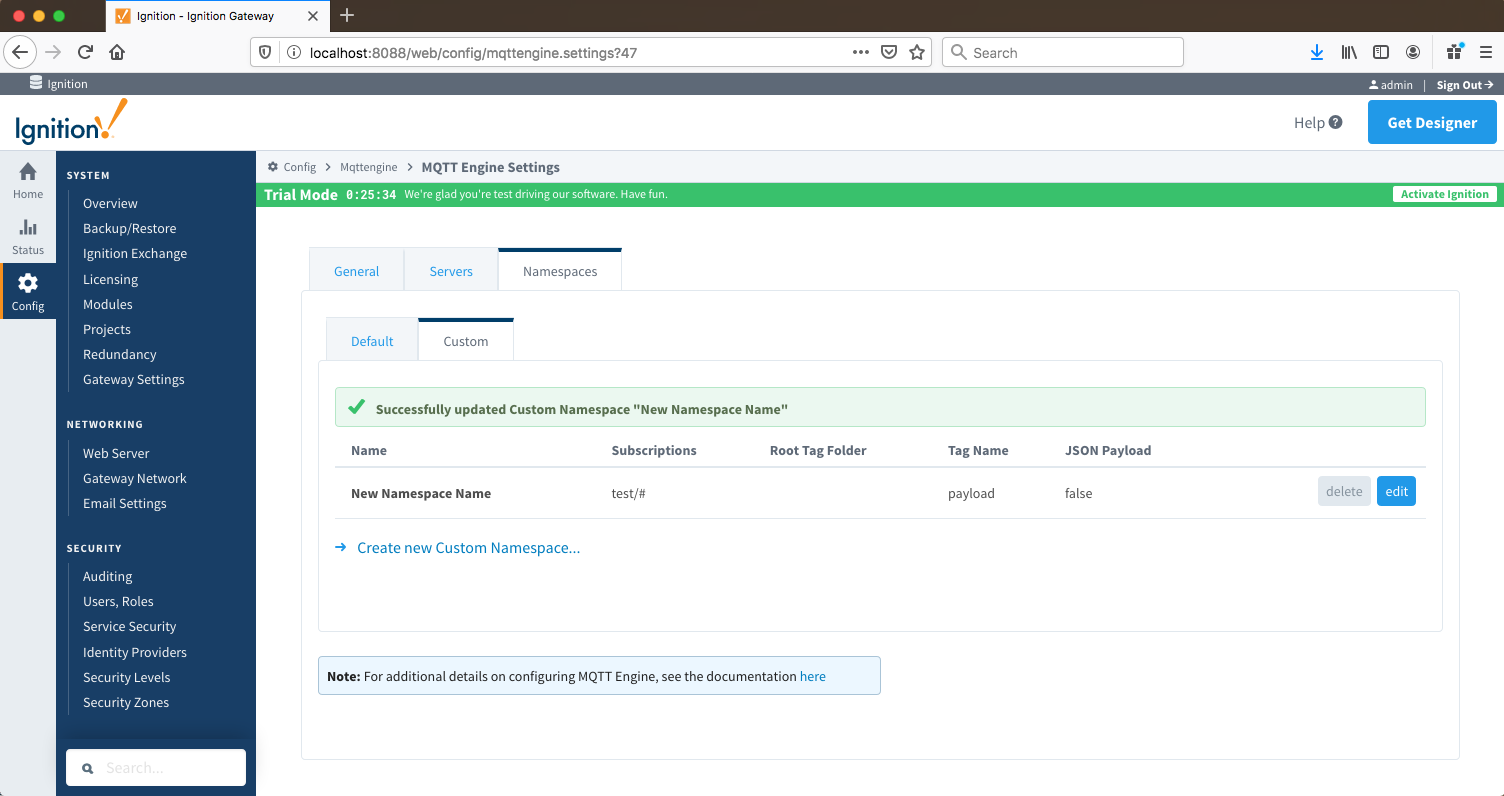 Image Removed
Image Removed
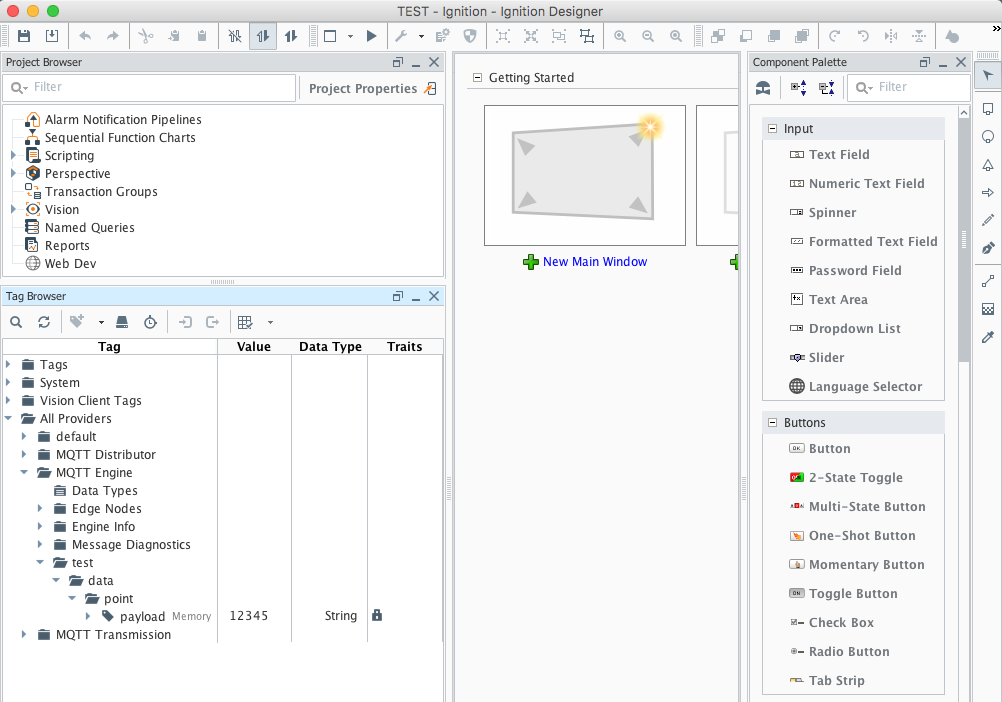 Image Removed
Image Removed
In most cases it is useful to specify a Tag Name in order to prevent cases when a publish on a topic can overwrite a previously created tag, changing it into a folder. Consider the case where you have the following two publishes:
1st publish on topic "one/two" will create a tag named "two" in the folder "one"
2nd publish on topic "one/two/three" will create a tag named "three" in the folder "one/two"
When the 2nd publish is received it will overwrite the first tag because "two" is now a folder instead of a tag. This folder/tag name collision can be avoided by specifying the Tag Name to always use for tags.
Custom Namespace JSON Example
Let say we have a publish received on the topic "test/data/json" with value '{ "stringTag" : "12345", "folderTag" : { "intTag" : 1, "boolTag" : true } }'. MQTT Engine will create a three folders "test", "data" and "point" followed by a tag/folder structure representing the JSON value of the payload.
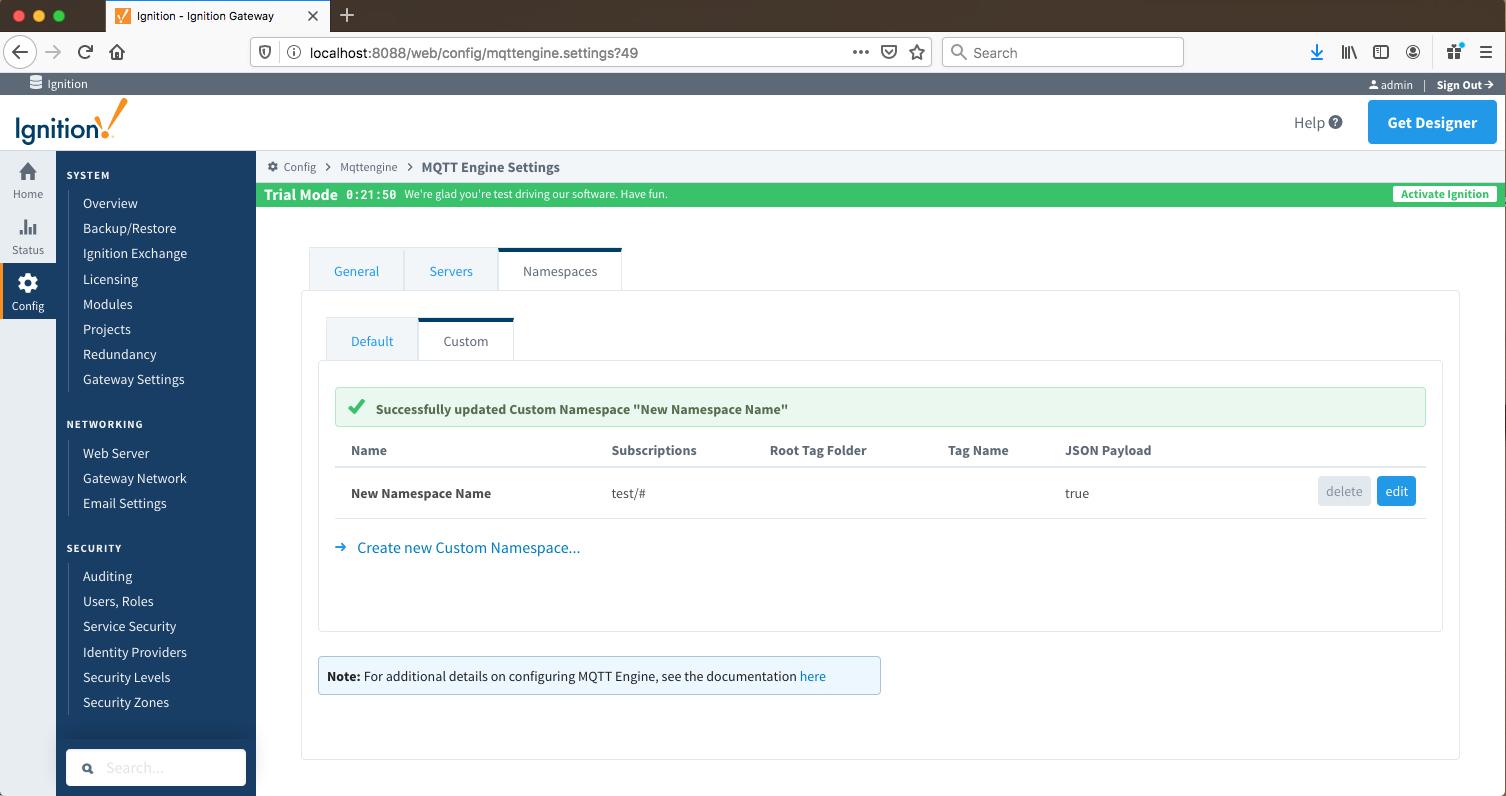 Image Removed
Image Removed
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomStringConversion |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomStringConversion |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom - String ConversionThere is one configuration section available Main Settings
Reference the MQTT Engine String Replacement HowTo for additional details on how to use this configuration.
| Anchor |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomstringConversionMain |
|---|
| NamespacesCustomstringConversionMain |
|---|
|
Namespaces Custom - String Conversion Main Settings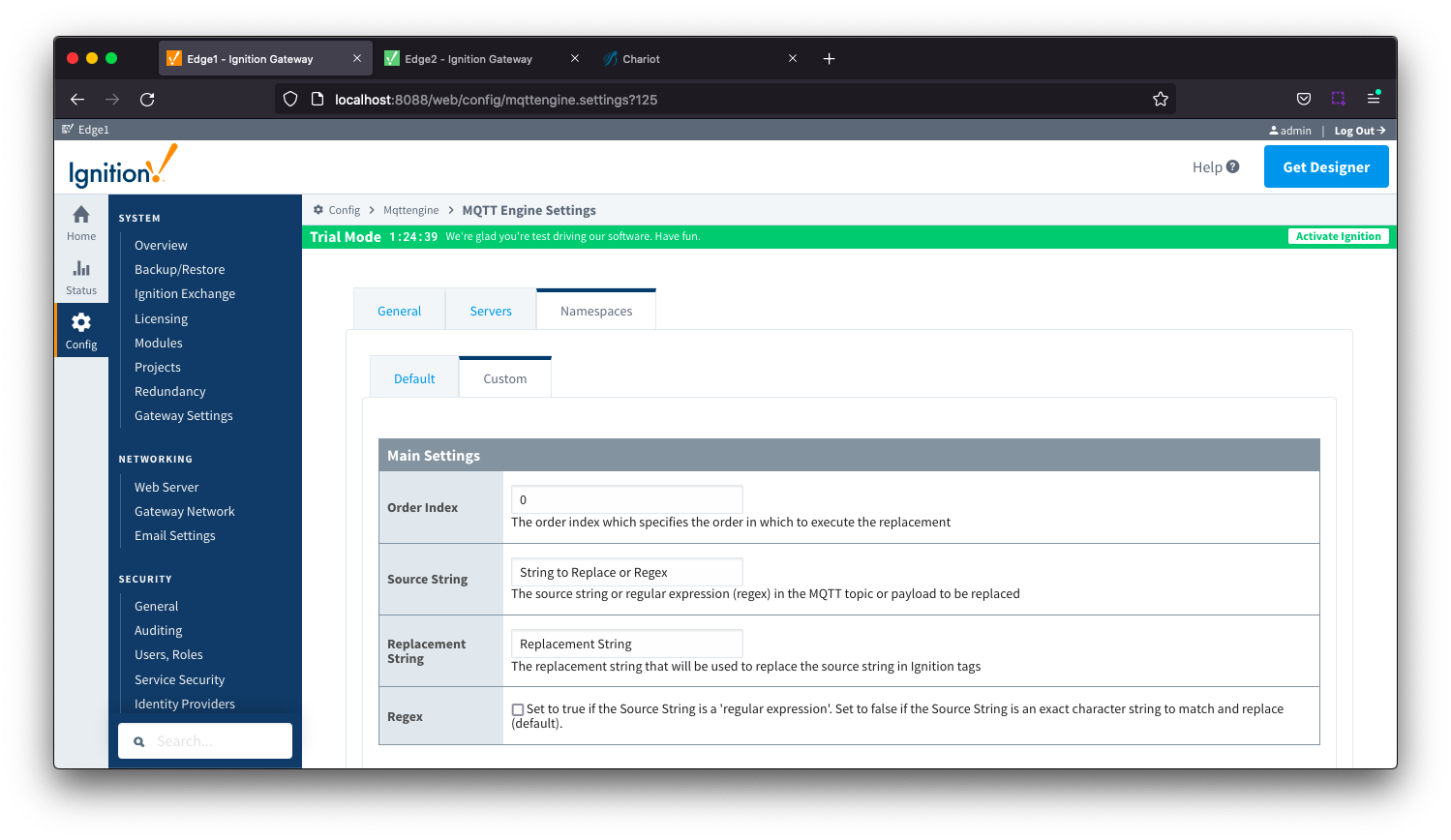 Image Added
Image Added
- Order Index
- The order index which specifies the order in which to execute the replacement
- Source String
- The source string or regular expression (regex) in the MQTT topic or payload to be replaced
- Replacement String
- The replacement string that will be used to replace the source string in the Ignition tags
- Regex
- Checkbox to determine the source string format. If selected, source string is a 'regular expression'. If deselected, source string is an exact character string to match and replace.
...
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()