...
MQTT Transmission for Ignition 7.9.x has two different types of Transmitters. There is the 'default' Transmitter and also 'custom' Transmitters. Transmitters define where in the tag tree MQTT Transmission will look for tags that should be published via MQTT. They also optionally define the 'Sparkplug Identifiers' that will be used in the topic namespace.
Default Transmitter
In the original release of MQTT Transmission the Default Transmitter was the only mechanism that could be used to define which tags would be published over MQTT. When in use, it would look in the specified Tag Provider that is configured for a folder called 'Edge Nodes'. Each folder under the 'Edge Nodes' folder would be considered a Sparkplug 'Group ID'. Each folder under each 'Group ID' folder would be considered a 'Edge Node ID'. Finally, each folder under each 'Edge Node ID' folder would be considered a 'Device ID'.
Consider the following tag tree:
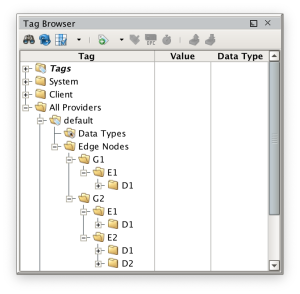 Image Added
Image Added
With the above tag tree while using MQTT Tranmission's Default Transmitter we end up with the following Sparkplug Edge Nodes.
- Edge Node with Group ID=G1 and Edge Node ID=E1 with one Device with Device ID=D1
- Edge Node with Group ID=G2 and Edge Node ID=E1 with one Device with Device ID=D1
- Edge Node with Group ID=G2 and Edge Node ID=E2 with two Devices with Device ID=D1 and Device ID=D2
Note each Edge Node also results in a single MQTT Client connection. So, the above configuration results in three Sparkplug MQTT clients publishing messages to an MQTT Server.
Custom Transmitters
Custom Transmitters were created later in the development of MQTT Transmission. This was done to provide more flexibility in how tags could be picked up and published over MQTT
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
