...
Once you have Ignition installed and running, and the Google Cloud Injector module downloaded, browse to the Ignition Gateway console (e.g. http://localhost:8088). Login using the default credentials of admin/password. Click on Configuration tab and then click on the Modules tab on the left side of the page. Scroll to the bottom of the Modules section and click on the Download/Upgrade modules button. When prompted, select the Google Cloud Injector module from the file browser and install it. When complete, the Ignition Gateway Web UI module section should look similar to what is shown below:
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Select the "Google Cloud Injector" → "Settings" link on the lower left of the page to navigate to the Google Cloud Injector Module's configuration page. A detailed explanation of each configuration tab can be found here. For this tutorial, we will only be adding a new Cloud IoT Core Setting.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Click on the "Create new Cloud IoT Core Setting..." link to bring up the following configuration form:
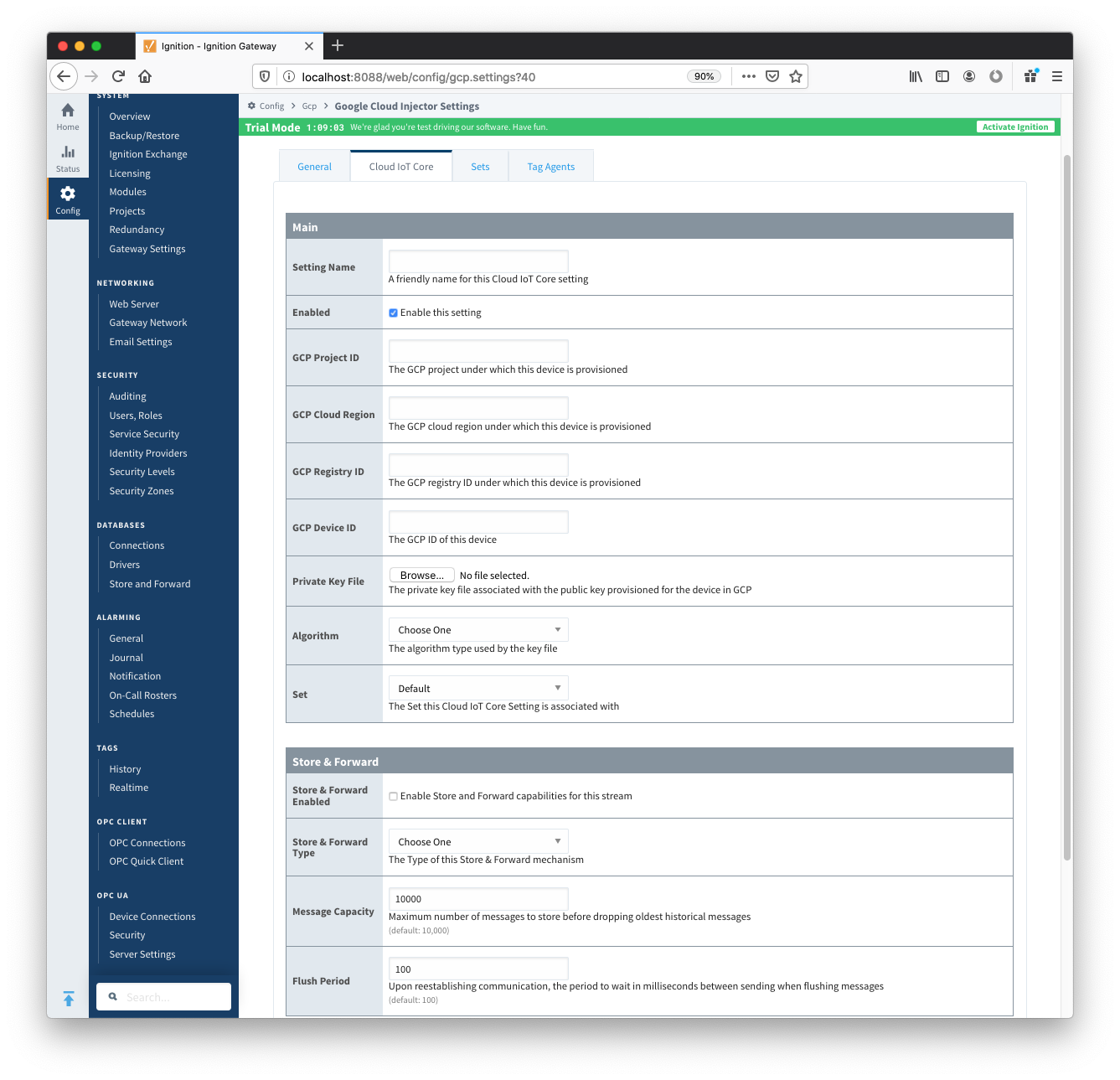 Image Added
Image Added
 Image RemovedFor the Setting Name you can enter any unique identifier, we will use "TestSetting". For For the GCP Project ID you will need to ID of the project that was created with the Google Cloud Platform account. The GCP Cloud Region, Registry ID, and Device ID should all be obtained from the Cloud IoT Core that was created.
Image RemovedFor the Setting Name you can enter any unique identifier, we will use "TestSetting". For For the GCP Project ID you will need to ID of the project that was created with the Google Cloud Platform account. The GCP Cloud Region, Registry ID, and Device ID should all be obtained from the Cloud IoT Core that was created. Image Removed
Image Removed
Now the Google Cloud Injector module is connected to the Cloud IoT Core and ready to push Tag data.
If you click on the "Tag Agents" tab you will see that out-of-the-box the Google Cloud Injector module will have one default Tag Agent defined. For this tutorial we will not need to make any configuration changes to the Tag Agents.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
The Default Tag Agent will monitor tags that are in the "Edge Nodes" folder of the "default" Tag Provider. In the next step we go into more detail about the tags in this folder.
...
 After Designer opens, you will see the default Designer screen as shown below.
After Designer opens, you will see the default Designer screen as shown below.
 Image Added
Image Added
 Image RemovedWith the Google Cloud Injector module installed in Ignition, a new folder is created under the "All Providers" folder and is called “Google Cloud Injector”. This folder will contain both information tags about the module's version and state, as well as control tags for refreshing the module and Tag Agents.
Image RemovedWith the Google Cloud Injector module installed in Ignition, a new folder is created under the "All Providers" folder and is called “Google Cloud Injector”. This folder will contain both information tags about the module's version and state, as well as control tags for refreshing the module and Tag Agents.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Next, we need to create a folder structure where we will create a virtual Edge device and some tags to be published by the Google Cloud Injector module. When the Google Cloud Injector module is installed in Ignition, a folder is automatically created in the Ignition tag structure with the following path:
- All Providers/default/Edge Nodes
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Step 5: Use Ignition Designer to Create New Tags
...
With this folder structure in place, now we can create some memory tags of various data types to publish. Right click on the Tutorial Device folder and select ’New Tag’/’Memory Tag’. In the tag editor change the Name of the tag to “Boolean001”, and change the Data Type to Boolean. Follow this same procedure for new memory tags called “Integer001” of type Integer, “Float001” of type Float, and “String001” of type String. The resulting folder structure should look as follows.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Step 6: Use Ignition Designer to Publish Tag Data (Current Tag Values)
Now that we have a folder structure with some tags we can refresh the Google Cloud Injector module. Make sure that the Ignition Designer has read/write communications turned on by selecting Project/Comm Read/Write.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
To refresh the default Tag Agent with the folder structure we’ve created, open the folder "All Providers/Google Cloud Injector/Google Cloud Injector Control" and click on the Refresh Boolean. Note the Boolean tag will not change to true. This is really a one-shot and as a result, the tag will not change to true.
When this happens, the Tag Agent will scan the "Edge Nodes" folder and find the new Memory Tags that we have created, construct JSON payloads representing those tags with their current values and publish the payload to the Cloud IoT Core that we have configured.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image AddedThe Google Cloud Injector Tag Agent will publish two JSON payloads to the Cloud IoT Core. The format of these messages closely follows the Sparkplug B Specification's payload structure.
Image AddedThe Google Cloud Injector Tag Agent will publish two JSON payloads to the Cloud IoT Core. The format of these messages closely follows the Sparkplug B Specification's payload structure.
...
Click on the value of the "Boolean001" Memory Tag to change the value.
 Image RemovedThis will result in the following payload to be constructed to represent this Tag change event and pushed to the Cloud IoT Core:
Image RemovedThis will result in the following payload to be constructed to represent this Tag change event and pushed to the Cloud IoT Core:
...
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()






















