...
MQTT Transmission provides a configuration section to the Ignition Gateway. These can be seen in the Configure section of the Ignition Gateway web UI. There are two configuration pages "History" and "Settings".
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Settings
Once in the "Settings" configuration section there are five tabs: General, Servers, Sets, Transmitters, and Records. Each of these tabs is described in detail in the following sections.
...
- Enabled
- Whether or not to enable or disable MQTT Transmission from connecting to the configured MQTT Servers.
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to use for 'state' notifications. These notifications are used to notify MQTT Transmission if the primary backend application loses connection with the MQTT Server, meaning it has gone 'offline'. If MQTT Transmission is notified that the primary backend application has gone 'offline', it will close it's client connection with the MQTT server and walk to the next MQTT server defined in the set. If the primary host ID is not set, MQTT Transmission will not subscribe on the notification topics and not receive any 'state' notifications.
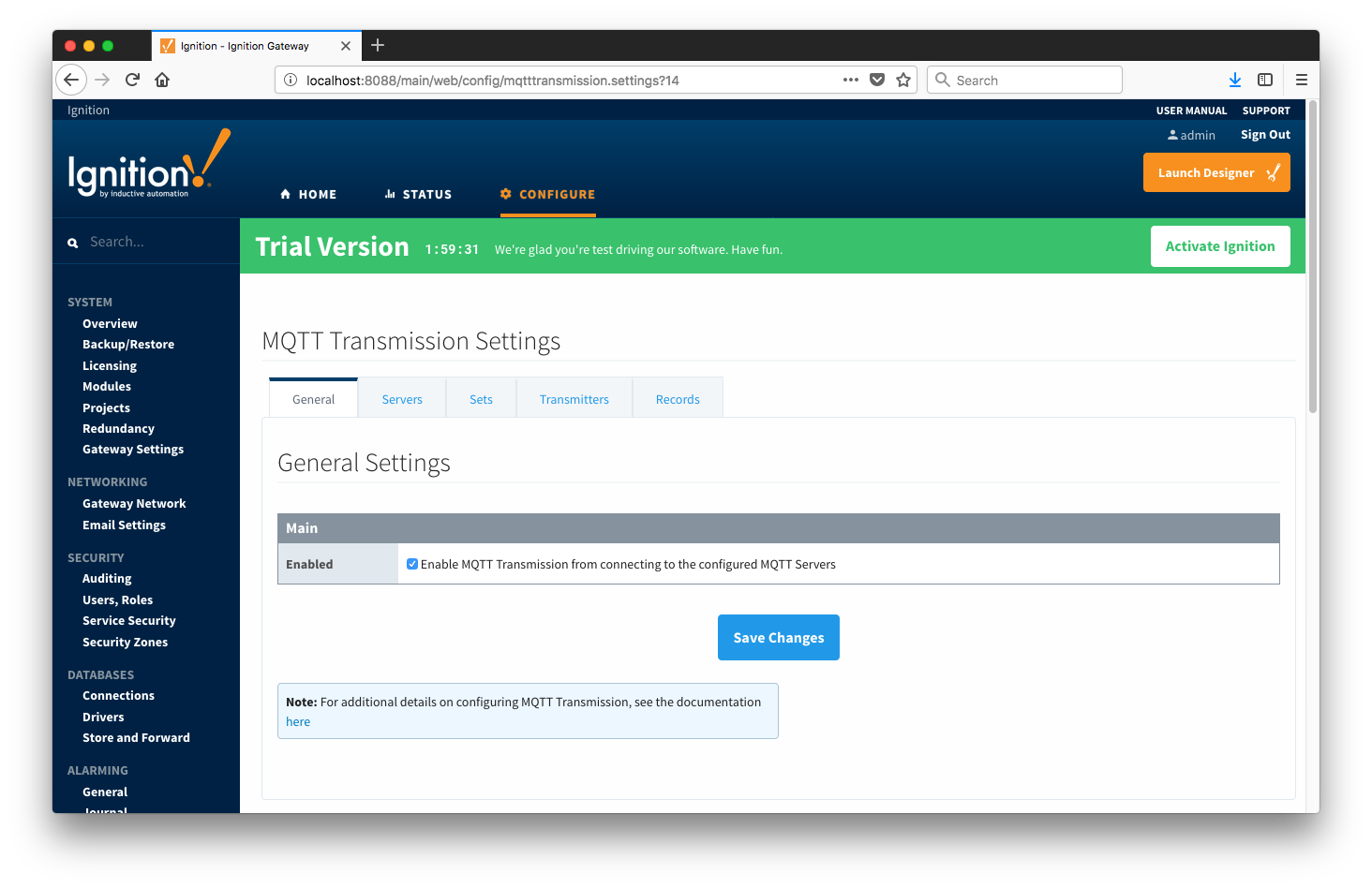 Image Removed
Image Removed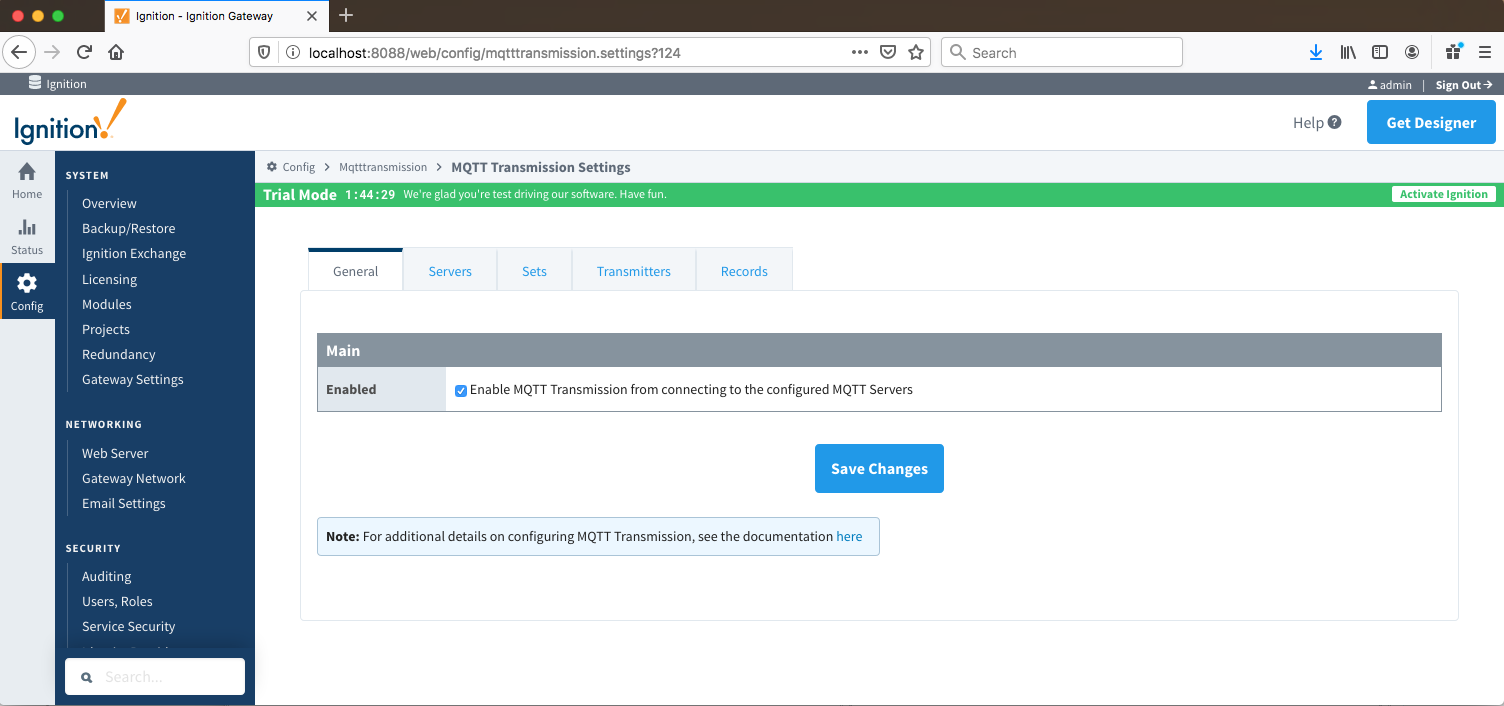 Image Added
Image Added
Servers
The first tab is a list of MQTT Servers that MQTT Transmission should connect to. By default, MQTT Transmission is configured to connect to a local MQTT Distributor based MQTT Server. It is set up to connect to localhost, port 1883, using the default username/password pair of admin/changeme. Out of the box MQTT Transmission will work with MQTT Distributor and its default configuration.
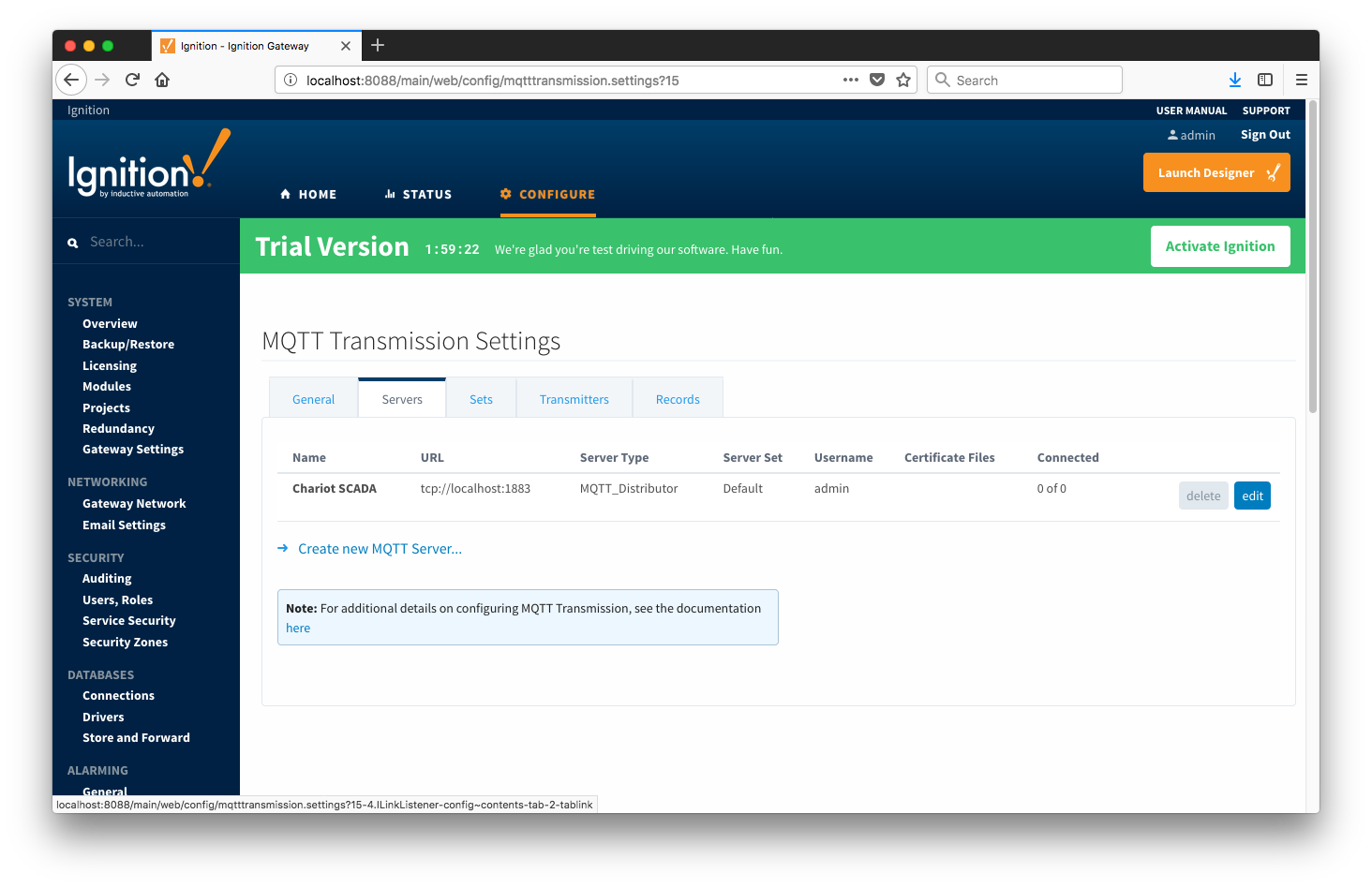 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Additional or alternative MQTT Servers can be configured in MQTT Transmission. Often times more than one will be configured to handle fail-over or in redundant or geographically distributed systems. The configuration options for servers are listed below.
...
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the MQTT Server used to easily identify it
- URL
- This is the URL of the MQTT server. Its format is as follows: [protocol]://[location]:[port]. Each of these are shown below
- protocol - Either tcp or ssl
- location - The server location. e.g. localhost, myserver.chariot.io, mydomain.com, etc
- port - The port the MQTT Server is listening on. Generally this is 1883 if using TCP or 8883 if using SSL
Server Type- This is the type of MQTT Server to connect to
- Chariot - If connecting to a Cirrus Link Chariot on-premise or Chariot cloud based MQTT Server
- MQTT_Distributor - If connecting to a Ignition MQTT Distributor server
- Third_Party - If connecting to a third party 3.1.1 compliant MQTT ServerAWS_Greengrass - If connectiong to an AWS Greengrass
- Server .
- Note: This server type should not be used whe using MQTT Transmission in conjunction with MQTT Engine.
Server Set- The Set that this server is a member of.
- Username
- The MQTT username to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
- Password
- The MQTT password to use in the MQTT connect packet. This is required if the MQTT Server to connect to requires it.
...
- Certificates
- The server certificates to use if required. These are generally only required when connecting using TLS and the MQTT server does not have a genuine certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority.
- CA certificate must always end in 'ca.pem'
- If using client side certificates (i.e. a public/private keypair and CA cert), make sure the following naming conventions are followed.
- Edge/Device certificate must end in 'cert.pem'
- Edge/Device private key must end in 'private.key'
- Password
- A password associated with the certificate's private key.
- Hostname Verification
- Enable TLS Hostname verification
Advanced Properties
- Client ID
- Optional MQTT client ID to use. If specified this will be used in the MQTT Engine connect packet when connecting to the server. If left blank, a random client ID will be create of the form 'IgnitionTarget-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx
- Keep Alive
- The MQTT client keep alive time (in seconds).
- Random Startup Delay
- The Random Startup Delay in milliseconds of the form 'min-max' where min is the low end and max is the high end of the random range. e.g. '10-1000'
- Data Format Type
- The format of the data to send. This should almost always be Protobuf encoding. The other options is JSON.
Clicking on the 'Create new MQTT Server...' link will bring up the following form to add a new Server.
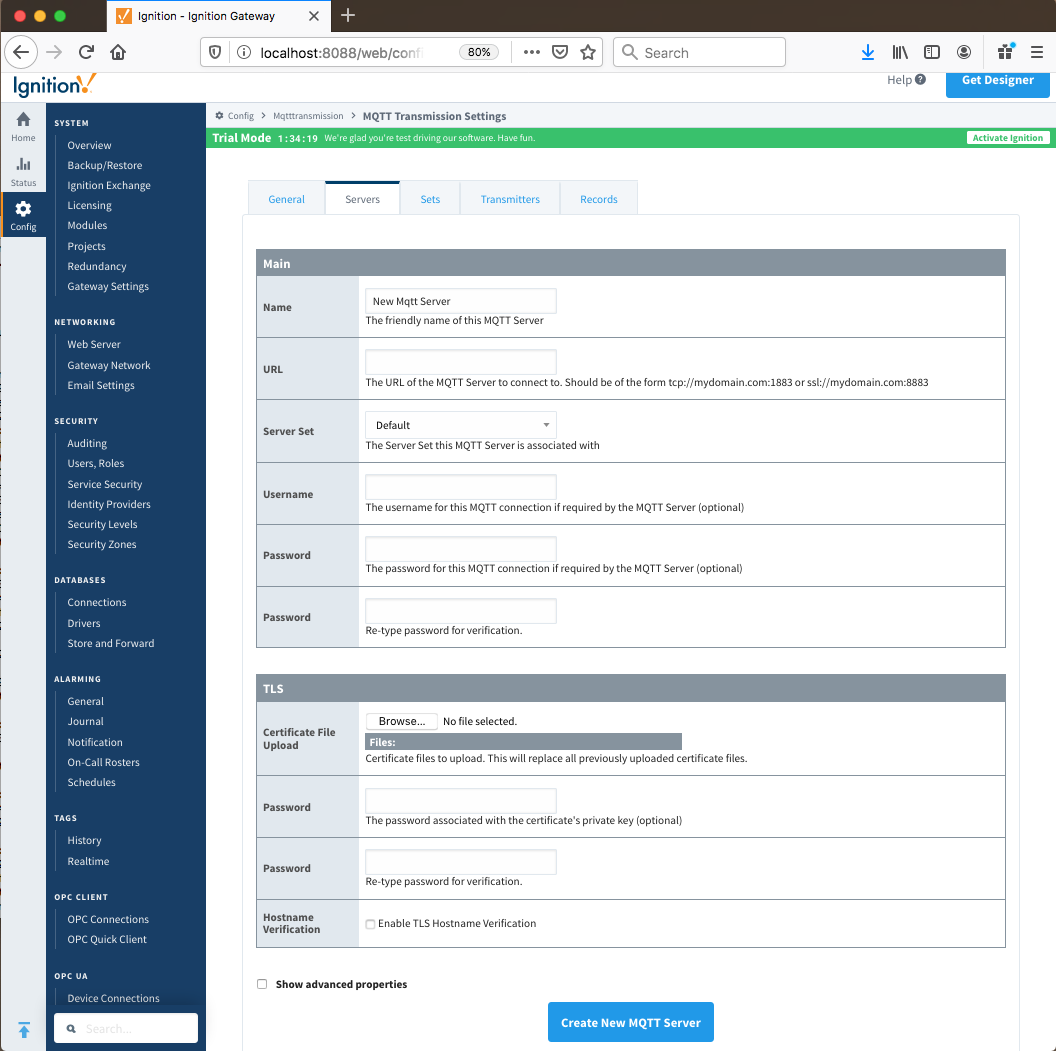 Image Added
Image Added
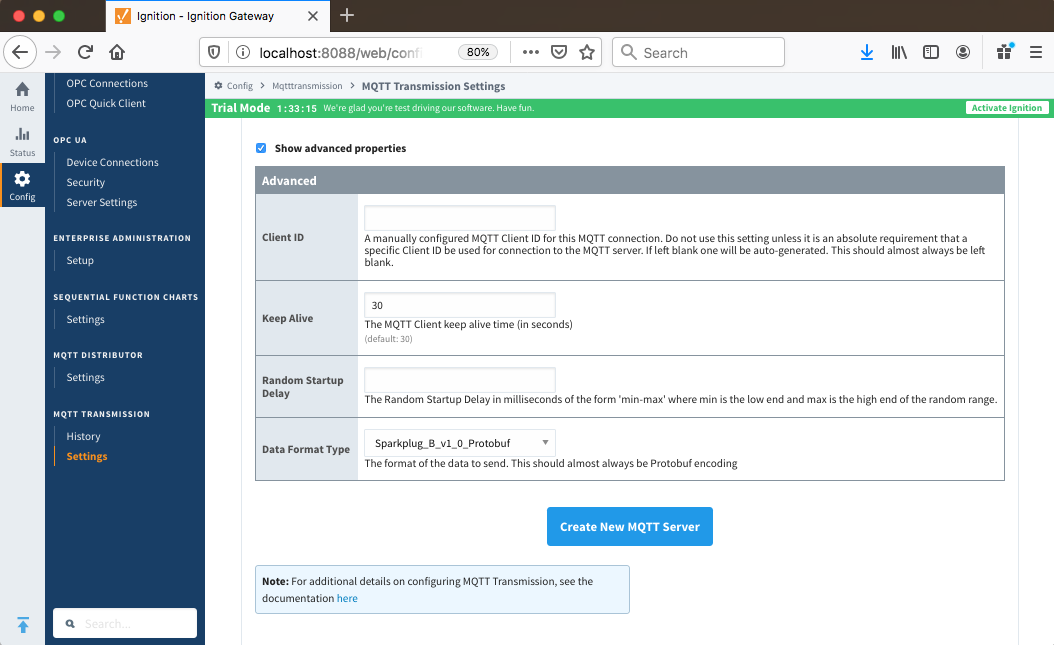 Image Added
Image Added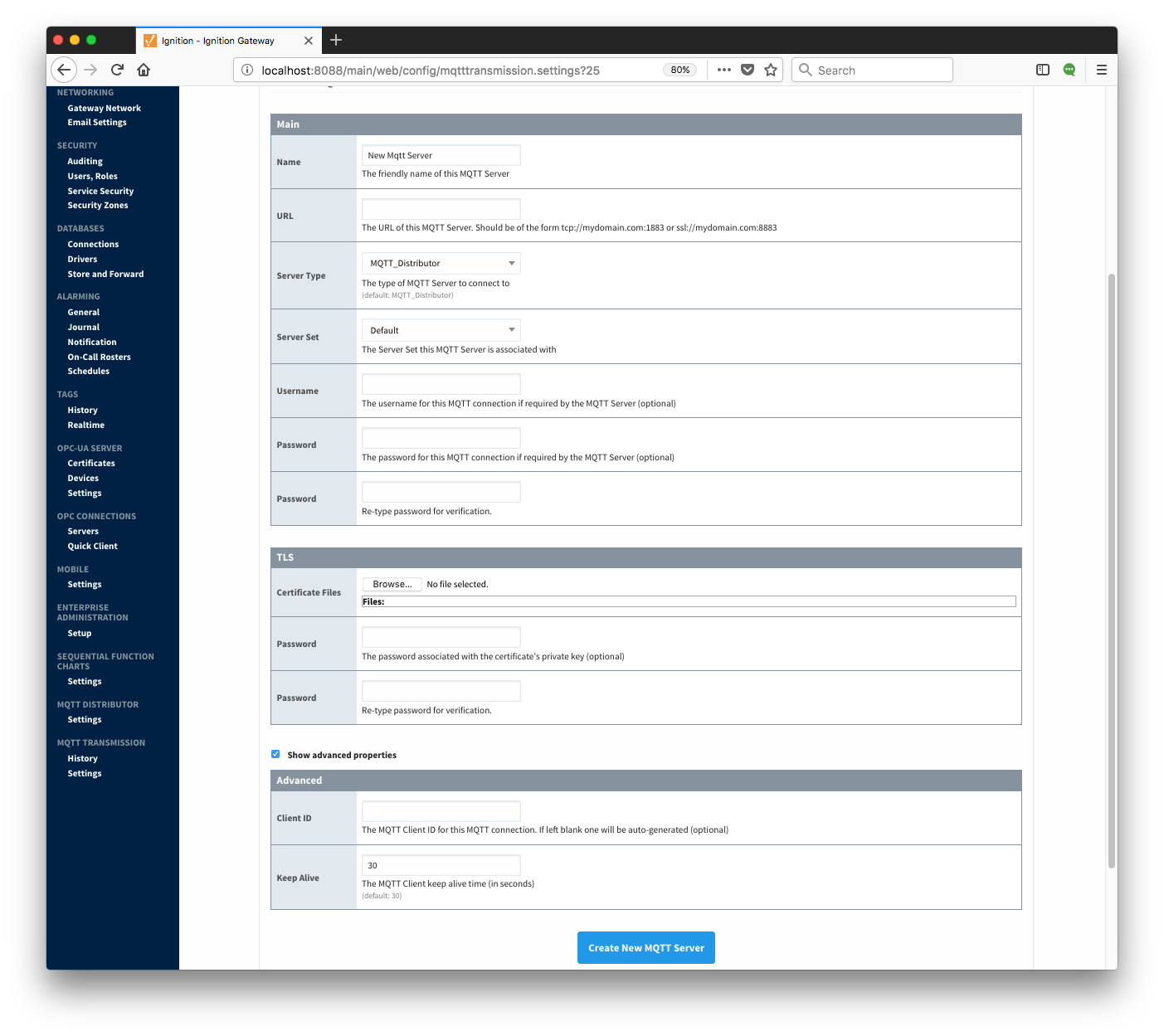 Image Removed
Image Removed
Sets
The Sets tab contains a list of server sets. Each set represents a logical grouping of MQTT servers. When a set is referenced by a Transmitter configuration a single connection to one of the servers in the set will be maintained. The other servers will act as failover in the case that a connection with the first is lost. Server sets are disjoint, meaning that a single MQTT server cannot be in more than one set.
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Additional sets can be configured in MQTT Transmission for situations where multiple Custom Settings will need to point to different sets (or groupings) of MQTT servers. The configuration options for sets are listed below.
- Name
- This is the friendly name of the set used to easily identify it.
- Description
- This is a friendly description of the set.
- Primary Host ID
- The primary host ID to use for 'state' notifications. These notifications are used to notify MQTT Transmission if the primary backend application loses connection with the MQTT Server, meaning it has gone 'offline'. If MQTT Transmission is notified that the primary backend application has gone 'offline', it will close it's client connection with the MQTT server and walk to the next MQTT server defined in the set. If the primary host ID is not set, MQTT Transmission will not subscribe on the notification topics and not receive any 'state' notifications.
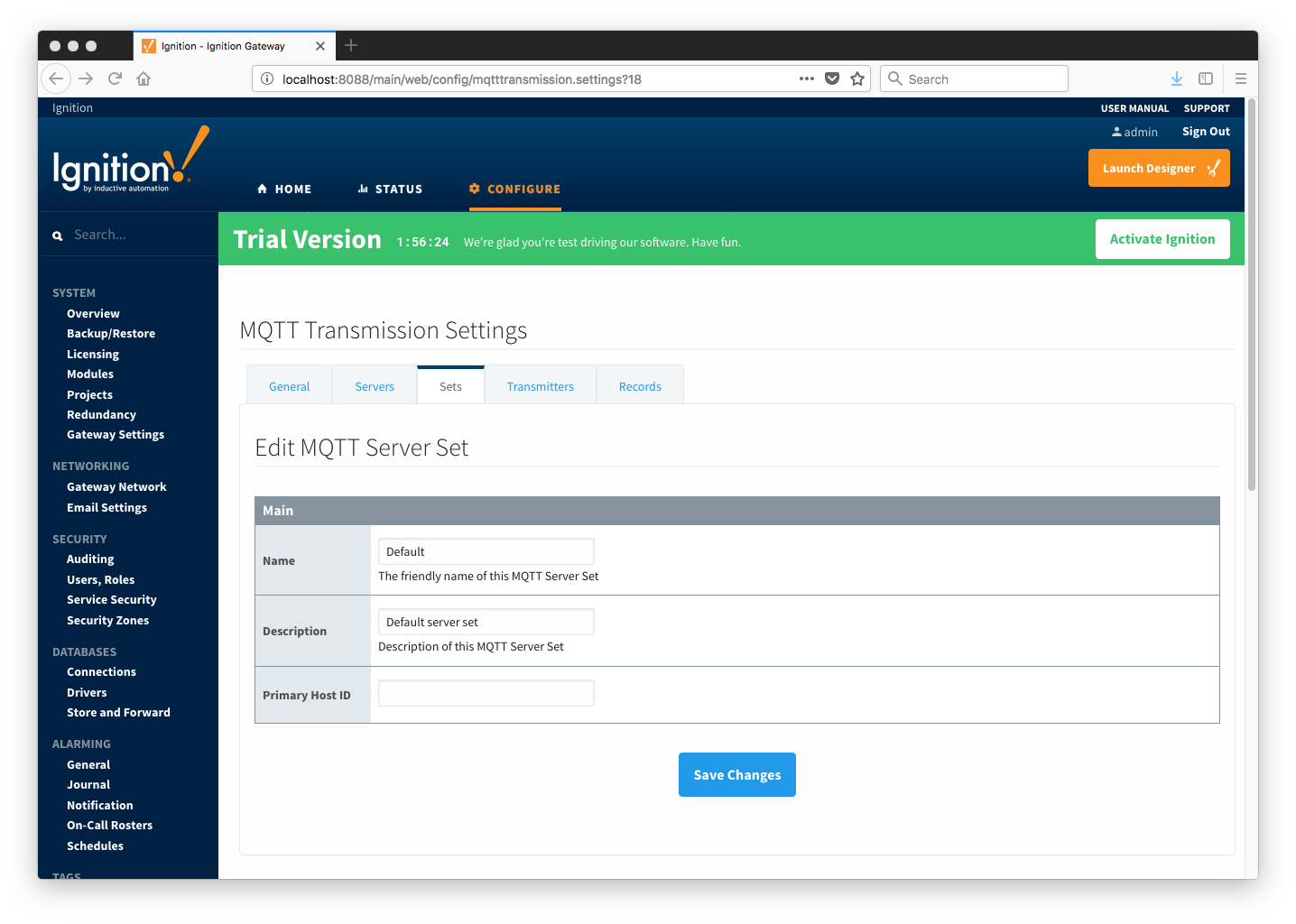 Image Removed
Image Removed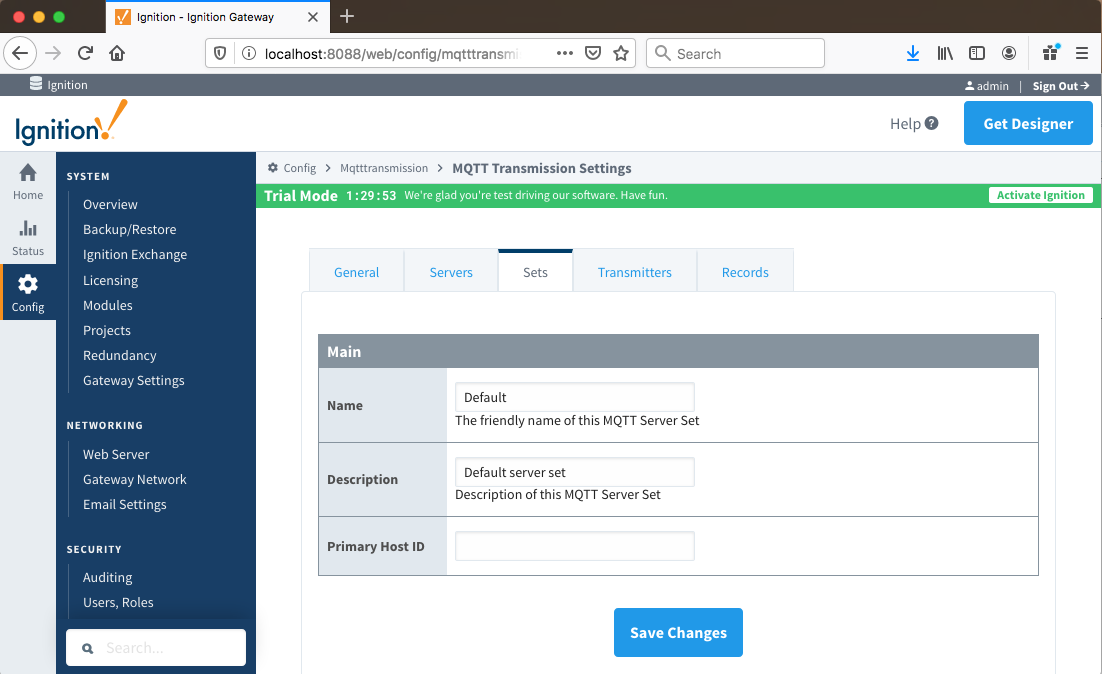 Image Added
Image Added
Transmitters
Transmitters are the agents within MQTT Transmission that monitor tags, convert them to Sparkplug Messages, and publish them to an MQTT Server. Each transmitter is configured with a server Set and will attempt to maintain an MQTT client connection with one server in that Set at all times.
...
The configuration options for the Default Transmitter are listed below.:
- Name
- Enabled
- Whether the Default Transmitter is enabled
- Tag Provider Name
- The name of the tag provider that Transmission will monitor. By default this is the Ignition 'default' provider.
- Tag Path
- A path to the root folder where the tag tree starts (optional)
- Tag Pacing Period
- The buffer period for outgoing Transmission messages in milliseconds. The default is 1000ms. This means when a tag change event is detected 1000ms will elapse before an MQTT message is sent. This allows additional tag change events to be buffered and put into the message and in turn reduce the number of generated MQTT messages.
- Set
- The Set that the default MQTT Transmission client will connect to.
- Discovery Delay
- An optional startup delay, in milliseconds, to wait before scanning for Tags to monitor. This is useful when Tags are dynamically created on initial startup, as is the case when using the MQTT Engine module.
- History Store
- The MQTT Transmission History Store to use with the Default Transmitter.
- Aliased Tags
- Whether to use aliases for tag names when published data messages as tag values change. This is used to optimize payload size when publishing data.
- Compression
- The algorithm to use to compress payloads before they are published to the MQTT Server. If 'NONE' is selected then compression is disabled.
- Block Commands
- Whether to block commands and tag writes received as messages from the MQTT server.
- Convert UDTs
- Whether to convert UDT members to normal Tags before publishing. If enabled the Tags representing the UDT member will retain their member path prefixed by the UDT Instance name.
...
- Publish UDT Definitions
- Whether to publish UDT Definitions in BIRTH
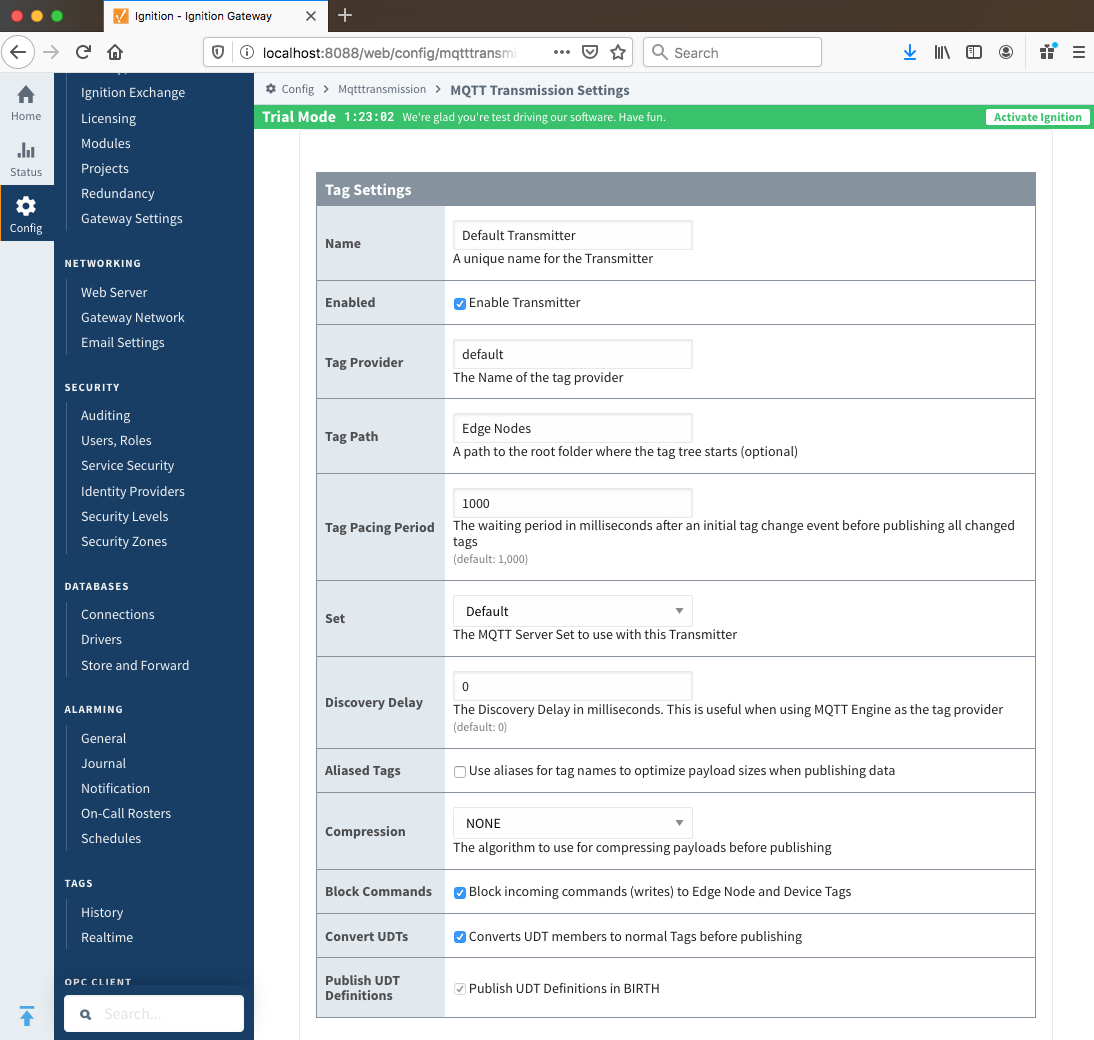 Image Added
Image Added
- History Store
- The MQTT Transmission History Store to use with the Default Transmitter.
- Enable History Storage by Default
- Whether or not store and forward should be enabled by default on all tags. The custom tag property 'CL Store Forward Enabled' can be used to override this default. (default: true)
- In-Order History
- Flush history in-order (synchronously) before live data resumes. (default: false)
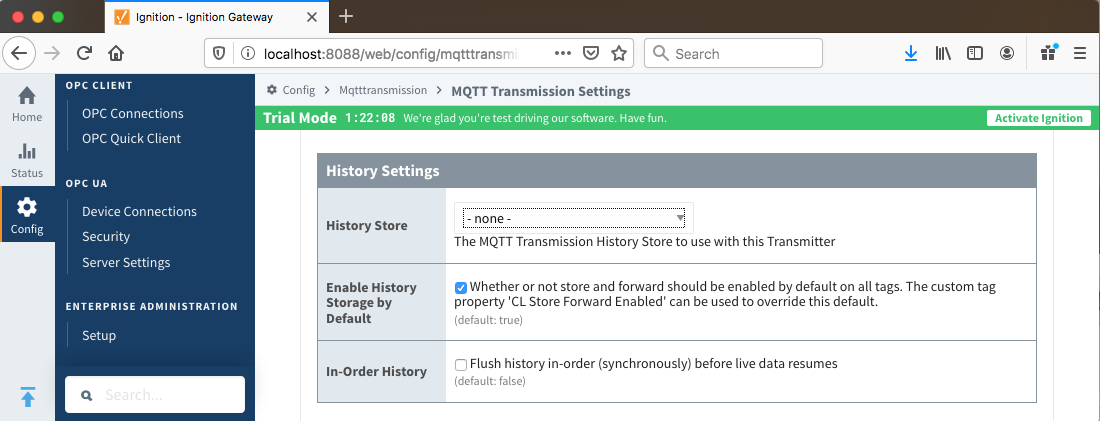 Image Added
Image Added
Custom Transmitters
Custom Transmitters behave in much the same way as the Default Transmitter. However, unlike the Default Transmitter, Custom Transmitters are not bound to a specific "Edge Nodes" folder and do not have any required folder path structure. The Group ID, Edge Node ID and Device ID are explicitly defined in a Custom Transmitter configuration instead of inferred from the tag path, as in the Default Transmitter. This allows Custom Transmitters to point at any folder in any provider and monitor the contained tags and/or tag folders.
...
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()